
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 32 states that comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 212 municipalities, and its capital city is Xalapa-Enríquez.

Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 32 states of Mexico.
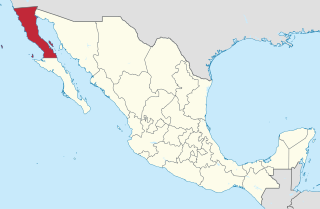
Baja California (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈbaxa kaliˈfoɾnja];, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California. It has an area of 70,113 km2 and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California; on the north by the U.S. state of California; and on the south by Baja California Sur.

Uxpanapa is a municipality in the southeastern part of the state of Veracruz, adjacent to the state of Oaxaca), in Mexico. It is bordered by the municipalities of Jesús Carranza, Hidalgotitlán, Minatitlán, and Las Choapas in Veracruz, as well as Santa María Chimalapa in Oaxaca. It has an area of 2,600 km².

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca pine–oak forests is a tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregion in Southern Mexico.

The Bolsón de Mapimí is an endorheic or internal drainage basin in which no rivers or streams drain to the sea, but rather toward the center of the basin, often terminating in swamps and ephemeral lakes. It is located in the center-north of the Mexican Plateau. The Basin is shared by the states of Durango, Coahuila, Chihuahua, and Zacatecas. It takes its name from Mapimí, a town in Durango.

The Coatzacoalcos is a large river that feeds mainly the south part of the state of Veracruz; it originates in the Sierra de Niltepec and crosses the state of Oaxaca in the region of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, flowing for 325 kilometres toward the Gulf of Mexico. Tributaries include El Corte, Sarabia, Jaltepec, Chalchijalpa, El Chiquito, Uxpanapa, and Calzadas. The merging of all these rivers creates one of the largest current flows in the entire region. Two-thirds of the streams are navigable.
The Rio Bavispe or Bavispe River is a river in Mexico which flows briefly north then mainly south by southwest until it joins with the Aros River to become the Yaqui River, eventually joining the Gulf of California.

The Bolaños River is a river in Mexico flowing through the Sierra Madre Occidental, and a tributary of Rio Grande de Santiago. It has a length of 360 km and a watershed of about 10 000 square kilometers.

The Soto La Marina River or Soto la Marina is a river of northeastern Mexico.
The Sinaloa River is a river of Mexico. It runs across the state of Sinaloa from northeast to southwest, beginning in the Sierra Madre Occidental and emptying into the Gulf of California. Its flow is interrupted mostly by the Bacurato Dam which created Lake Baccarac in 1978. Below the dam, the flow of the river is largely diverted by an irrigation canal near the town of Sinaloa de Leyva.
The Santa Maria River (Chihuahua) is a river in the state Chihuahua of Mexico. It drains from the Sierra Madre Occidental but is an endorheic basin, i.e. it doesn't flow into a river, sea or ocean. It is popular for rafting.
The Pantepec River is a river of Mexico that belongs to the Tuxpan River basin, on the Gulf of Mexico slope. The Pantepec River is considered the upper course of the Tuxpan River.

The Patagonia Mountains are a 15-mile-long (24 km) mountain range within the Coronado National Forest, and in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, United States.
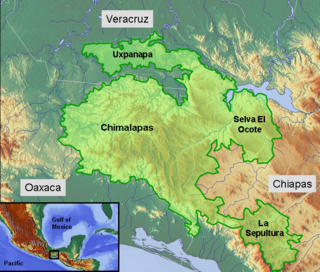
The Selva Zoque, which includes the Chimalapas rain forest, is an area of great ecological importance in Mexico. Most of the forest lies in the state of Oaxaca but parts are in Chiapas and Veracruz. It is the largest tract of tropical rainforest in Mexico, and contains the majority of terrestrial biodiversity in the country. The forest includes the Selva El Ocote, a federally protected biosphere reserve, but is otherwise not yet protected. Despite the rich ecology of the region, a 2003 study that focused on bird populations stated that "the fauna of the heart of the Chimalapas, including its vast rainforests, have seen little or no study". As it is an impoverished region, efforts to preserve the ecology are often at odds with demands to improve the economy.
The Cerro de Oro Dam, also called the Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado Dam, is on the Santo Domingo River in the San Juan Bautista Tuxtepec municipality of the Papaloapan Region of Oaxaca state in southern Mexico. The dam operates in conjunction with the Miguel Alemán Dam, located on the Tonto River to control floods in the Papaloapan basin in Veracruz state. Construction began in 1973 and the dam was completed in May 1989. About 26,000 people were displaced by the project. Water quality in the reservoir is poor and deteriorating, affecting fish catches.

The Sierra Aguilada is a mountain range in southwest Catron County, New Mexico on the eastern perimeter of Arizona's White Mountains. The Mogollon Mountains of New Mexico lie just east, with a south-flowing section of the San Francisco River separating them. The river then turns west, forming the southern border of the Sierra Aguilada, and continues to eventually intercept the Gila River after traversing northwest of the Big Lue Mountains of Arizona.
The Sierra Atravesada or Sierra de Niltepec is a mountain range in the state of Oaxaca, Mexico, in the region of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec.
The Chinipas is a large river of Mexico. The Chinipas arises deep in the Sierra Madre Occidental in the state of Chihuahua, and then flows through long rugged canyon systems into the state of Sinaloa until it finally joins the main trunk of the Fuerte River in the western foothills of the Sierra Madre Occidental. The Fuerte River then flows westward over the western coastal plain of Sonora to the Pacific Ocean, emerging very near the port of Topolobampo.












