Utricularia, commonly and collectively called the bladderworts, is a genus of carnivorous plants consisting of approximately 233 species. They occur in fresh water and wet soil as terrestrial or aquatic species across every continent except Antarctica. Utricularia are cultivated for their flowers, which are often compared with those of snapdragons and orchids, especially amongst carnivorous plant enthusiasts.
Utricularia sect. Nelipus is a section in the genus Utricularia that was originally described as a genus in 1838 by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque. Two of the species in this section are endemic to Australia while the third, Utricularia limosa, is also native to Southeast Asia. Species in this section are distinguished by the characteristic two-lobed lower lip of the corolla.

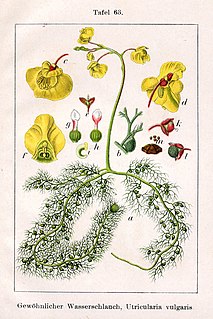
Utricularia sect. Utricularia is a section in the genus Utricularia. The species in this section are suspended or affixed aquatic carnivorous plants.
Utricularia podadena is a small, probably perennial, terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia and is the only member of Utricularia sect. Candollea. U. podadena is endemic to Malawi and Mozambique, being known only from the type location in Malawi and from one other collection in Mozambique. As of Peter Taylor's 1989 monograph on the genus, more recent efforts to locate this species have failed. It was originally published and described by Taylor in 1964 and placed in its own section, Candollea, in 1986. It grows as a terrestrial plant in marshy grasslands in the presence of Loudetia species at altitudes of around 1,000 m (3,281 ft). It flowers in July. It is a very distinct plant in the genus with the long stipitate glandular trichomes covering the flower. Its affinities within the genus are not clear.
Utricularia sect. Choristothecae is a section in the genus Utricularia. The two species in this section are very small rheophytic carnivorous plants that were formally included in section Avesicaria but were reassigned to their own section by Peter Taylor in 1989. He had included them in section Avesicaria largely because of the similar habit of the species, but the unique pollen morphology, dissimilar internal trap glands, and the anthers led Taylor to move these two species to section Choristothecae. Both species are endemic to South America, with Utricularia determannii only known from Suriname and Utricularia choristotheca located in French Guiana and Suriname.
Utricularia sect. Kamienskia is a section in the genus Utricularia. The two species in this section are very small bryophilous lithophytic carnivorous plants. Peter Taylor originally described and published the section and its single species, Utricularia peranomala, in 1986. In 2007, Guang Wan Hu described Utricularia mangshanensis and placed it in this section. Both species are endemic to China.

Utricularia subg. Bivalvaria is a subgenus in the genus Utricularia. It was originally described by Wilhelm Sulpiz Kurz in 1874. In Peter Taylor's 1989 monograph on the genus, he reduced the subgenus to synonym under section Oligocista, a decision that was later reversed in the light of molecular phylogenetic studies and the subgenus was restored.
Utricularia rigida is a small to medium-sized perennial, rheophytic carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. U. rigida is endemic to western tropical Africa, where it can be found in Côte d'Ivoire, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Nigeria, Senegal, and Sierra Leone. It grows as a rheophyte on inclined rock faces in swiftly running water at altitudes from near sea level to 1,250 m (4,101 ft). It was originally described and published by Ludwig Benjamin in 1847. It is distinguished from the other species in the section, U. tetraloba, by having only two lower lip corolla lobes as opposed to U. tetraloba's four.
Utricularia sect. Enskide is a section in the genus Utricularia. The two species in this section are small to medium-sized terrestrial carnivorous plants native to Australia and New Guinea. Constantine Samuel Rafinesque originally described and published this section as a separate genus in his 1838 taxonomic treatment. Peter Taylor refined the section and placed it within subgenus Utricularia in his 1986 monograph of the genus. Later molecular data resulted in the revision of Taylor's treatment, reinstating subgenus Bivalvaria and placing this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Stomoisia is a section in the genus Utricularia. The two species in this section are small to medium-sized terrestrial carnivorous plants native to North, Central, and South America. Constantine Samuel Rafinesque originally described and published this section as a separate genus in his 1838 taxonomic treatment. Otto Kuntze reduced the genus to its current status as a section in the genus Utricularia in 1903. Peter Taylor later refined the section, placing it in subgenus Utricularia in his 1986 monograph of the genus, also bringing one of Rafinesque's other genera, Personula, into synonymy with the new section. Later molecular data resulted in the revision of Taylor's treatment, reinstating subgenus Bivalvaria and placing this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Australes is a section in the genus Utricularia. The three species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to Australia and New Zealand. Peter Taylor originally described and published this section in his 1989 taxonomic treatment of the genus, splitting off species from section Meionula. Taylor originally placed this section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Nigrescentes is a section in the genus Utricularia. The three species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to tropical Africa, Asia, and Australia. Daniel Oliver originally validly described and published this section in 1859, but did not specify the rank used by the group. Sadashi Komiya revised the section in 1973. Peter Taylor, in his 1989 taxonomic monograph on the genus, placed this section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Aranella is a section in the genus Utricularia. The ten species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to tropical South America with one species also extending into tropical Africa. John Hendley Barnhart originally described and published this section in 1913 as a separate genus, Aranella. Sadashi Komiya revised the genus Utricularia in a 1973 taxonomic review and placed Barnhart's genus at the rank of subgenus within Utricularia. Peter Taylor then published his taxonomic monograph of Utricularia in 1986 in which he reduced Komiya's subgenus to the rank of section, placing it within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Calpidisca is a section in the genus Utricularia. The ten species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to Africa with one species extending its range into Mexico and another that extends into Asia as far as India. John Hendley Barnhart originally described and published this section in 1916 as a separate genus, Calpidisca. Sadashi Komiya revised the genus Utricularia in a 1973 taxonomic review and placed Barnhart's genus at the rank of section within Utricularia. Peter Taylor then published his taxonomic monograph of Utricularia in 1986 in which he placed Komiya's section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Oligocista is the largest section in the genus Utricularia. The 42 species in this section are small to medium-sized terrestrial carnivorous plants native throughout the tropics, with six species in the Americas, ten in Africa, five in Australia, and the remainder in Asia, with 17 mostly native to peninsular India. Alphonse Pyrame de Candolle originally described and published this section in 1844. Peter Taylor published his taxonomic monograph of Utricularia in 1986, in which he placed this section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.
Utricularia simmonsii is a small annual or perennial terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia and is the only member of Utricularia sect. Minutae. U. simmonsii is endemic to Australia and is only known from a few locations in the Northern Territory and Queensland. It and the section Minutae were originally published and described by Allen Lowrie, Ian D. Cowie, and John Godfrey Conran in 2008. It was named in honor of Paul Simmons, who discovered the species in Queensland in 2005.
Utricularia sect. Phyllaria is a section in the genus Utricularia. The sixteen species in this section are small or very small lithophytic or epiphytic carnivorous plants native to the mountains of Asia, ranging from India to China and New Guinea. One species, Utricularia striatula, is an exception and is widespread in much of the Old World tropics. Wilhelm Sulpiz Kurz originally described and published this section as Utricularia subg. Phyllaria in 1874. Franciszek Kamieński reviewed the genus in 1891 and reduced Kunz's subgenus to a section. Later botanists, including Peter Taylor, agreed with Kamieński's assessment. In Taylor's 1986 revision of the genus, he placed this section in subgenus Utricularia. Later molecular data resulted in the revision of Taylor's treatment, reinstating subgenus Bivalvaria and placing this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Setiscapella is a section in the genus Utricularia that contains small or medium-sized terrestrial or subaquatic species. Most plants in this section are endemic to Central and South America with the exceptions of Utricularia stanfieldii, which is endemic to Africa, and Utricularia subulata which is almost pantropical. It was first described by John Hendley Barnhart in 1916 at the rank of genus. In 1973, Sadashi Komiya reduced the genus to a subgenus of the genus Utricularia. In his 1986 monograph on the genus, Peter Taylor reorganized the genus and reduced this to the rank of section.

The Genus Utricularia: A Taxonomic Monograph is a monograph by Peter Taylor on the carnivorous plant genus Utricularia, the bladderworts. It was published in 1989 by Her Majesty's Stationery Office (HMSO) as the fourteenth entry in the Kew Bulletin Additional Series. It was reprinted for The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew in 1994.










