
Germanite is a rare copper iron germanium sulfide mineral, Cu26Fe4Ge4S32. It was first discovered in 1922, and named for its germanium content. It is only a minor source of this important semiconductor element, which is mainly derived from the processing of the zinc sulfide mineral sphalerite. Germanite contains gallium, zinc, molybdenum, arsenic, and vanadium as impurities.

Bornite, also known as peacock ore, is a sulfide mineral with chemical composition Cu5FeS4 that crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (pseudo-cubic).

The mineral petzite, Ag3AuTe2, is a soft, steel-gray telluride mineral generally deposited by hydrothermal activity. It forms isometric crystals, and is usually associated with rare tellurium and gold minerals, often with silver, mercury, and copper.

Zinkenite is a steel-gray metallic sulfosalt mineral composed of lead antimony sulfide Pb9Sb22S42. Zinkenite occurs as acicular needle-like crystals.

Sperrylite is a platinum arsenide mineral with the chemical formula PtAs2 and is an opaque metallic tin white mineral which crystallizes in the isometric system with the pyrite group structure. It forms cubic, octahedral or pyritohedral crystals in addition to massive and reniform habits. It has a Mohs hardness of 6–7 and a very high specific gravity of 10.6.

Fukuchilite, Cu
3FeS
8, is a copper iron sulfide named after the Japanese mineralogist Nobuyo Fukuchi (1877–1934), that occurs in ore bodies of gypsum-anhydrite at the intersection points of small masses of barite, covellite, gypsum and pyrite, and is mostly found in the Hanawa mine in the Akita prefecture of Honshū, Japan where it was first discovered in 1969. It occurs in masses within the third geologic unit of the Kuroko type deposits within the mine.

Hawleyite is a rare sulfide mineral in the sphalerite group, dimorphous and easily confused with greenockite. Chemically, it is cadmium sulfide, and occurs as a bright yellow coating on sphalerite or siderite in vugs, deposited by meteoric water.

Digenite is a copper sulfide mineral with formula: Cu9S5. Digenite is a black to dark blue opaque mineral that crystallizes with a trigonal - hexagonal scalenohedral structure. In habit it is usually massive, but does often show pseudo-cubic forms. It has poor to indistinct cleavage and a brittle fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3 and a specific gravity of 5.6. It is found in copper sulfide deposits of both primary and supergene occurrences. It is typically associated with and often intergrown with chalcocite, covellite, djurleite, bornite, chalcopyrite and pyrite. The type locality is Sangerhausen, Thuringia, Germany, in copper slate deposits.

Djurleite is a copper sulfide mineral of secondary origin with formula Cu31S16 that crystallizes with monoclinic-prismatic symmetry. It is typically massive in form, but does at times develop thin tabular to prismatic crystals. It occurs with other supergene minerals such as chalcocite, covellite and digenite in the enriched zone of copper orebodies. It is a member of the chalcocite group, and very similar to chalcocite, Cu2S, in its composition and properties, but the two minerals can be distinguished from each other by x-ray powder diffraction. Intergrowths and transformations between djurleite, digenite and chalcocite are common. Many of the reported associations of digenite and djurleite, however, identified by powder diffraction, could be anilite and djurleite, as anilite transforms to digenite during grinding.
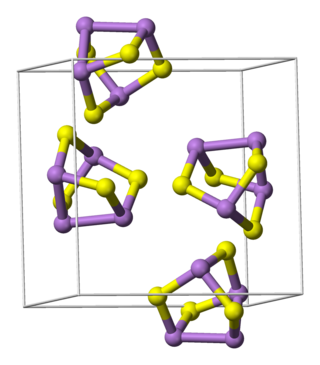
Pararealgar is an arsenic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula As4S4, also represented as AsS. It forms gradually from realgar under exposure to light. Its name derives from the fact that its elemental composition is identical to realgar, As4S4. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 1 - 1.5, is yellow orange in colour, and its monoclinic prismatic crystals are very brittle, easily crumbling to powder.

Alabandite or alabandine is a rarely occurring manganese sulfide mineral. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system with the chemical composition Mn2+S and develops commonly massive to granular aggregates, but rarely also cubic or octahedral crystals to 1 cm.

Cattierite (CoS2) is a cobalt sulfide mineral found in the Democratic Republic of Congo. It was discovered together with the nickel sulfide vaesite by Johannes F. Vaes, a Belgian mineralogist and named after Felicien Cattier, who was chairman of the board of the Union Minière du Haut-Katanga.

Duftite is a relatively common arsenate mineral with the formula CuPb(AsO4)(OH), related to conichalcite. It is green and often forms botryoidal aggregates. It is a member of the adelite-descloizite Group, Conichalcite-Duftite Series. Duftite and conichalcite specimens from Tsumeb are commonly zoned in color and composition. Microprobe analyses and X-ray powder-diffraction studies indicate extensive substitution of Zn for Cu, and Ca for Pb in the duftite structure. This indicates a solid solution among conichalcite, CaCu(AsO4 )(OH), austinite, CaZn(AsO4)(OH) and duftite PbCu(AsO4)(OH), all of them belonging to the adelite group of arsenates. It was named after Mining Councilor G Duft, Director of the Otavi Mine and Railroad Company, Tsumeb, Namibia. The type locality is the Tsumeb Mine, Tsumeb, Otjikoto Region, Namibia.

Geerite is a copper sulfide mineral with the chemical formula Cu8S5. The mineral is named after the original collector, Adam Geer, of Utica, New York, US.

Stützite or stuetzite is a silver telluride mineral with formula: Ag5−xTe3 (with x = 0.24 to 0.36) or Ag7Te4.

Semseyite is a rarely occurring sulfosalt mineral and is part of the class of lead antimony sulfides. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system with the chemical composition Pb9Sb8S21. The mineral forms dark gray to black aggregates.

Abramovite is a very rare mineral from the sulfides and sulfosalt categories. It has the chemical formula Pb2SnInBiS7. It occurs as tiny elongated lamellar-shaped crystals, up 1 mm × 0.2 mm in size, and is characterized by its non-commensurate structure.

Hemusite is a very rare isometric gray mineral containing copper, molybdenum, sulfur, and tin with chemical formula Cu6SnMoS8. It was discovered by Bulgarian mineralogist Georgi Ivanov Terziev in 1963. He also described it and named it after Haemus, the ancient name of Stara planina (Balkan) mountains in Europe. The type locality is Chelopech copper ore deposit, Bulgaria. Later tiny deposits of hemusite were found in Ozernovskoe deposit, Kamchatka, Russia; Kawazu mine, Rendaiji, Shimoda city, Chūbu region, Honshu Island, Japan; Iriki mine, Iriki, Satsuma-gun, Kagoshima Prefecture, Kyushu Region, Japan; Kochbulak deposit, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Hemusite occurs as rounded isometric grains and aggregates usually about 0.05 mm in diameter and in association with enargite, luzonite, colusite, stannoidite, renierite, tennantite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, and other minerals.

Minnesotaite is an iron silicate mineral with formula: (Fe2+,Mg)3Si4O10(OH)2. It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system and occurs as fine needles and platelets with other silicates. It is isostructural with the pyrophyllite-talc mineral group.

Daubréelite is a rare sulfide mineral. It crystallizes with cubic symmetry and has chemical composition of Fe2+Cr3+2S4. It usually occurs as black platy aggregates.




















