
The hypothalamus is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.
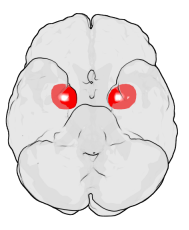
The amygdala is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown to perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, and emotional responses, the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system. The term "amygdala" was first introduced by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822.

Drosophila melanogaster is a species of fly in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly", or "banana fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, D. melanogaster continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, six Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect.

The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe.

The sticklebacks are a family of ray-finned fishes, the Gasterosteidae which have a Holarctic distribution in fresh, brackish and marine waters. They were thought to be related to the pipefish and seahorses but are now thought to be more closely related to the eelpouts and sculpins.

Dopaminergic pathways in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of projection neurons, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons.
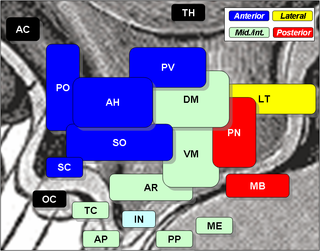
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The function of the arcuate nucleus relies on its diversity of neurons, but its central role is involved in homeostasis. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation.
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons.

The cabbage looper is a medium-sized moth in the family Noctuidae, a family commonly referred to as owlet moths. Its common name comes from its preferred host plants and distinctive crawling behavior. Cruciferous vegetables, such as cabbage, bok choy, and broccoli, are its main host plant; hence, the reference to cabbage in its common name. The larva is called a looper because it arches its back into a loop when it crawls.

Testudo, the Mediterranean tortoises, are a genus of tortoises found in North Africa, Western Asia, and Europe. Several species are under threat in the wild, mainly from habitat destruction.
The sexually dimorphic nucleus (SDN) is an ovoid, densely packed cluster of large cells located in the medial preoptic area (POA) of the hypothalamus which is believed to be related to sexual behavior in animals. Thus far, for all species of mammals investigated, the SDN has been repeatedly found to be considerably larger in males than in females. In humans, the volume of the SDN has been found to be 2.2 times as large in males as in females and to contain 2.1 times as many cells. The human SDN is elongated in females and more spherical in males. No sex differences have been observed in the human SDN in either cell density or mean diameter of the cell nuclei. The volume and cell number of the human SDN considerably decreases with age, although the decrease in cell number is both sex and age-specific. In males, a substantial decrease in the cell number of the human SDN was observed between the age of 50–60 years. Cell death was more common in females than males, especially among those older than 70 years of age. The SDN cell number in females can drop to 10-15% of that found in early childhood.
The fruitless gene (fru) is a Drosophila melanogaster gene that encodes several variants of a putative transcription factor protein. Normal fruitless function is required for proper development of several anatomical structures necessary for courtship, including motor neurons which innervate muscles needed for fly sexual behaviors. The gene does not have an obvious mammalian homolog, but appears to function in sex determination in species as distant as the mosquito Anopheles gambiae.
Odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) are small soluble proteins secreted by auxiliary cells surrounding olfactory receptor neurons, including the nasal mucus of many vertebrate species and in the sensillar lymph of chemosensory sensilla of insects. OBPs are characterized by a specific protein domain that comprises six α-helices joined by three disulfide bonds. Although the function of the OBPs as a whole is not well established, it is believed that they act as odorant transporters, delivering the odorant molecules to olfactory receptors in the cell membrane of sensory neurons.
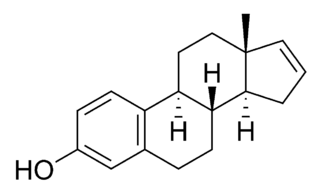
Estratetraenol, also known as estra-1,3,5(10),16-tetraen-3-ol, is an endogenous steroid found in women that has been described as having pheromone-like activities in primates, including humans. Estratetraenol is synthesized from androstadienone by aromatase likely in the ovaries, and is related to the estrogen sex hormones, yet has no known estrogenic effects. It was first identified from the urine of pregnant women.
The genetics of social behavior is an area of research that attempts to address the question of the role that genes play in modulating the neural circuits in the brain which influence social behavior. Model genetic species, such as D.melanogaster and Apis mellifera, have been rigorously studied and proven to be instrumental in developing the science of genetics. Many examples of genetic factors of social behavior have been derived from a bottom-up method of altering a gene and observing the change it produces in an organism. Sociogenomics is an integrated field that accounts for the complete cellular genetic complement of an organism from a top-down approach, accounting for all biotic influences that effect behavior on a cellular level.

Basal ganglia disease is a group of physical problems that occur when the group of nuclei in the brain known as the basal ganglia fail to properly suppress unwanted movements or to properly prime upper motor neuron circuits to initiate motor function. Research indicates that increased output of the basal ganglia inhibits thalamocortical projection neurons. Proper activation or deactivation of these neurons is an integral component for proper movement. If something causes too much basal ganglia output, then the ventral anterior (VA) and ventral lateral (VL) thalamocortical projection neurons become too inhibited, and one cannot initiate voluntary movement. These disorders are known as hypokinetic disorders. However, a disorder leading to abnormally low output of the basal ganglia leads to reduced inhibition, and thus excitation, of the thalamocortical projection neurons which synapse onto the cortex. This situation leads to an inability to suppress unwanted movements. These disorders are known as hyperkinetic disorders.
An organism is said to be sexually dimorphic when male and female conspecifics have anatomical differences in features such as body size, coloration, or ornamentation, but disregarding differences of reproductive organs. Sexual dimorphism is usually a product of sexual selection, with female choice leading to elaborate male ornamentation and male-male competition leading to the development of competitive weaponry. However, evolutionary selection also acts on the sensory systems that receivers use to perceive external stimuli. If the benefits of perception to one sex or the other are different, sex differences in sensory systems can arise. For example, female production of signals used to attract mates can put selective pressure on males to improve their ability to detect those signals. As a result, only males of this species will evolve specialized mechanisms to aid in detection of the female signal. This article uses examples of sex differences in the olfactory, visual, and auditory systems of various organisms to show how sex differences in sensory systems arise when it benefits one sex and not the other to have enhanced perception of certain external stimuli. In each case, the form of the sex difference reflects the function it serves in terms of enhanced reproductive success.
The lateral horn is one of the two areas of the insect brain where projection neurons of the antennal lobe send their axons. The other area is the mushroom body. Several morphological classes of neurons in the lateral horn receive olfactory information through the projection neurons.
A Drosophila connectome is a list of neurons in the Drosophila melanogaster nervous system, and the chemical synapses between them. The fly's nervous system consists of the brain plus the ventral nerve cord, and both are known to differ considerably between male and female. Dense connectomes have been completed for the female adult brain, the male nerve cord, and the female larval stage. The available connectomes show only chemical synapses - other forms of inter-neuron communication such as gap junctions or neuromodulators are not represented. Drosophila is the most complex creature with a connectome, which had only been previously obtained for three other simpler organisms, first C. elegans. The connectomes have been obtained by the methods of neural circuit reconstruction, which over the course of many years worked up through various subsets of the fly brain to the almost full connectomes that exist today.
Nilay Yapici is a Turkish neuroscientist at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, where she is the Nancy and Peter Meinig Family Investigator in the Life Sciences and Adelson Sesquicentennial Fellow in the Department of Neurobiology and Behavior. Yapici studies the neural circuits underlying decision making and feeding behavior in fruit fly models.
A Ray, A Zunic, RL Alten, JS McElfresh, LM Hanks, JG Millar. 2011. J. Chem. Ecol. 37:173-178.











