
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage. Then the stamp is affixed to the face or address-side of any item of mail—an envelope or other postal cover —which they wish to send. The item is then processed by the postal system, where a postmark or cancellation mark—in modern usage indicating date and point of origin of mailing—is applied to the stamp and its left and right sides to prevent its reuse. Next the item is delivered to its addressee.

A postmark is a postal marking made on an envelope, parcel, postcard or the like, indicating the place, date and time that the item was delivered into the care of a postal service, or sometimes indicating where and when received or in transit. Modern postmarks are often applied simultaneously with the cancellation or killer that marks postage stamps as having been used. Sometimes a postmark alone is used to cancel stamps, and the two terms are often used interchangeably. Postmarks may be applied by handstamp or machine, using methods such as rollers or inkjets, while digital postmarks are a recent innovation.

A cancellation is a postal marking applied on a postage stamp or postal stationery to deface the stamp and to prevent its reuse. Cancellations come in a huge variety of designs, shapes, sizes, and colors. Modern cancellations commonly include the date and post office location where the stamps were mailed, in addition to lines or bars designed to cover the stamp itself. The term "postmark" refers specifically to the part that contains the date and posting location, but the term is often used interchangeably with "cancellation" as it may serve that purpose. The portion of a cancellation that is designed to deface the stamp and does not contain writing is also called the "obliteration" or killer. Some stamps are issued pre-cancelled with a printed or stamped cancellation and do not need to have a cancellation added. Cancellations can affect the value of stamps to collectors, positively or negatively. Cancellations of some countries have been extensively studied by philatelists, and many stamp collectors and postal history collectors collect cancellations in addition to the stamps themselves.
Postage stamp reuse is the technique of fraudulently reusing postage stamps from sent mail to avoid paying the cost of postage.

Indian postal systems for efficient military and governmental communications had developed long before the arrival of Europeans. When the Portuguese, Dutch, French, Danish and British conquered the Marathas who had already defeated the Mughals, their postal systems existed alongside those of many somewhat independent states. The British East India Company gradually annexed the other powers on the sub-continent and brought into existence a British administrative system over most of modern-day India, with a need to establish and maintain both official and commercial mail systems.

In philately, the term cover pertains to the outside of an envelope or package with an address, typically with postage stamps that have been cancelled and is a term generally used among stamp and postal history collectors. The term does not include the contents of the letter or package, although they may add interest to the item if still present. Cover collecting plays an important role in postal history as many covers bear stamps, postmarks and other markings along with names and addresses all of which help to place a cover at a given time and place in history.

This is an overview of the postage stamps and postal history of Australia. encompassing some history of the Australian colonies and the main stamp issues that followed the takeover of the colonies as well as later issues and also an precis of the external territories.
Franking comprises all devices, markings, or combinations thereof ("franks") applied to mails of any class which qualifies them to be postally serviced. Types of franks include uncanceled and precanceled postage stamps, impressions applied via postage meter, official use "Penalty" franks, Business Reply Mail (BRM), and other permit Imprints (Indicia), manuscript and facsimile "franking privilege" signatures, "soldier's mail" markings, and any other forms authorized by the 192 postal administrations that are members of the Universal Postal Union.

A coil stamp is a type of postage stamp sold in strips one stamp wide. The name derives from the usual handling of long strips, which is to coil them into rolls, in a manner reminiscent of adhesive tape rolls. A large percentage of modern stamps are sold in coil form, because they are more amenable to mechanized handling in large quantities than either sheet stamps or booklet stamps.

An adhesive label or sticky label is a small piece of paper designed to be affixed to any surface, typically by the action of removing a layer of adhesive on the front or back of the label. The term adhesive refers to a sticky substance, while something that is self-adhesive implies that it will stick without wetting or the application of glue to the product.

A revenue stamp, tax stamp, duty stamp or fiscal stamp is a (usually) adhesive label used to designate collected taxes or fees on documents, tobacco, alcoholic drinks, drugs and medicines, playing cards, hunting licenses, firearm registration, and many other things. Typically, businesses purchase the stamps from the government, and attach them to taxed items as part of putting the items on sale, or in the case of documents, as part of filling out the form.
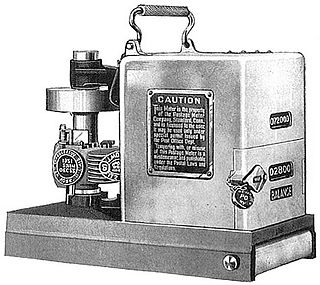
A postage meter or franking machine is a mechanical device used to create and apply physical evidence of postage to mailed items. Postage meters are regulated by a country's postal authority. A postage meter imprints an amount of postage, functioning as a postage stamp, a cancellation and a dated postmark all in one. The meter stamp serves as proof of payment and eliminates the need for adhesive stamps.

In philately, indicia are markings on a mail piece showing that postage has been prepaid by the sender. Indicia is the plural of the Latin word indicium, meaning distinguishing marks, signs or identifying marks. The term imprinted stamp is used more or less interchangeably, but some indicia are not imprinted stamps. One example is the handstamp, which can be seen in a photo on this page.

A stamp vending machine (SVM) is a mechanical, electrical or electro-mechanical device which can be used to automatically vend postage stamps to users in exchange for a pre-determined amount of money, normally in coin. Most SVMs were positioned in public places to provide a useful service to customers when other sources of postage stamps, such as Post Offices were closed. The term is often applied to the entire object as found attached to a pillar box or sited in a wall. The name Stamp Vending Machine only applies to the internal mechanism, the housing is described by the UK Post Office as a "case" and was supplied, installed and maintained separately. Many postal administrations around the world have used automatic stamp vending machines including the United States, where private manufacturers began vending stamps from coils in 1908. Most countries of the Commonwealth of Nations have issued stamps for use in Stamp Vending Machines, including Hong Kong, New Zealand and Malta.

Neopost web-enabled stamps or Neopostage is a postage stamp that is part of the family of computerized postage. These stamps were developed by Neopost Online and Northrop Grumman Corporation. The joint effort resulted in an innovative self-service stamp vending system. Neopost Online is a US subsidiary of Neopost Inc. Testing of this system was authorized by the United States Postal Service (USPS) in March 2001.
Between 1851 and 1860, the Grand Duchy of Tuscany, an independent Italian state until 1859 when it joined the United Provinces of Central Italy, produced two postage stamp issues which are among the most prized classic stamp issues of the world, and include the most valuable Italian stamp.

In philately, a cut-out is an imprinted stamp cut from an item of postal stationery such as a postal card, letter sheet, aerogramme or wrapper that may have been used as a normal stamp.

A meter stamp, or meter mark, is the impression made by a postage meter machine that indicates that postage has been paid on a letter or parcel. Meter stamps are widely used by businesses and organisations as they are more efficient than using postage stamps.

The Washington–Franklin Issues are a series of definitive U.S. Postage stamps depicting George Washington and Benjamin Franklin, issued by the U.S. Post Office between 1908 and 1922. The distinctive feature of this issue is that it employs only two engraved heads set in ovals—Washington and Franklin in full profile—and replicates one or another of these portraits on every stamp denomination in the series. This is a significant departure from previous definitive issues, which had featured pantheons of famous Americans, with each portrait-image confined to a single denomination. At the same time, this break with the recent past represented a return to origins. Washington and Franklin, after all, had appeared on the first two American stamps, issued in 1847, and during the next fifteen years, each of the eight stamp denominations available featured either Washington or Franklin.
Post & Go stamps, also called Faststamps, are variable rate postage stamps printed on self-adhesive labels and sold by stamp vending machines by Royal Mail in the United Kingdom, as well as by Jersey Post, Guernsey Post, the Royal Gibraltar Post Office and Q-Post (Qatar).


















