
A two-out-of-five code is a constant-weight code that provides exactly ten possible combinations of two bits, and is thus used for representing the decimal digits using five bits. Each bit is assigned a weight, such that the set bits sum to the desired value, with an exception for zero.

The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U.S., including its insular areas and associated states. It is one of the few government agencies explicitly authorized by the U.S. Constitution. The USPS, as of 2021, has 516,636 career employees and 136,531 non-career employees.

A ZIP Code is a postal code used by the United States Postal Service (USPS). Introduced on July 1, 1963, the basic format consisted of five digits. In 1983, an extended ZIP+4 code was introduced; it included the five digits of the ZIP Code, followed by a hyphen and four digits that designated a more specific location.
Canada Post Corporation, trading as Canada Post, is a Crown corporation that functions as the primary postal operator in Canada. Originally known as Royal Mail Canada, rebranding was done to the "Canada Post" name in the late 1960s, even though it had not yet been separated from the government. On October 16, 1981, the Canada Post Corporation Act came into effect. This abolished the Post Office Department and created the present-day Crown corporation which provides postal service. The act aimed to set a new direction for the postal service by ensuring the postal service's financial security and independence.
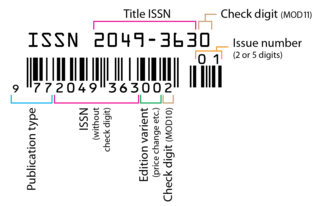
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication, such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature.

Code 39 is a variable length, discrete barcode symbology defined in ISO/IEC 16388:2007.

Registered mail is a mail service offered by postal services in many countries which allows the sender proof of mailing via a mailing receipt and, upon request, electronic verification that an article was delivered or that a delivery attempt was made. Depending on the country, additional services may also be available, such as:
POSTNET is a barcode symbology used by the United States Postal Service to assist in directing mail. The ZIP Code or ZIP+4 code is encoded in half- and full-height bars. Most often, the delivery point is added, usually being the last two digits of the address or PO box number.

Code 128 is a high-density linear barcode symbology defined in ISO/IEC 15417:2007. It is used for alphanumeric or numeric-only barcodes. It can encode all 128 characters of ASCII and, by use of an extension symbol (FNC4), the Latin-1 characters defined in ISO/IEC 8859-1.. It generally results in more compact barcodes compared to other methods like Code 39, especially when the texts contain mostly digits.
In a postal system, a delivery point is a single mailbox or other place at which mail is delivered. It differs from a street address, in that each address may have several delivery points, such as an apartment, office department, or other room. Such buildings are often called multiple-dwelling units (MDUs) by the USPS.

Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) is a continuous two-width barcode symbology encoding digits. It is used commercially on 135 film, for ITF-14 barcodes, and on cartons of some products, while the products inside are labeled with UPC or EAN.

PostBar, also known as CPC 4-State, is the black-ink barcode system used by Canada Post in its automated mail sorting and delivery operations. It is similar to other 4 State barcode systems used by Australia Post and the United Kingdom's Royal Mail, but uses an obscured structure and encoding system unique to Canada Post. This particular bar code system is used on "flats" and parcels.

The Facing Identification Mark, or FIM, is a bar code designed by the United States Postal Service to assist in the automated processing of mail. The FIM is a set of vertical bars printed on the envelope or postcard near the upper edge, just to the left of the postage area. The FIM is intended for use primarily on preprinted envelopes and postcards and is applied by the company printing the envelopes or postcards, not by the USPS.
Remote Bar Coding System (RBCS), also called Remote Video Encoding (RVE) is a method used by the United States Postal Service to encode the address of letter-sized mailpieces that are not decipherable by a Multiline Optical Character Reader (MLOCR). When an MLOCR does not recognize a valid address on a letter, it sends an image of the mailpiece to a central RBCS (RVE) site where more sophisticated optical character recognition software is able to interpret many hand-written addresses using neural net and fuzzy logic algorithms. If this does not succeed, human operators visually examine the image and enter the address. In both cases, the data is sent back to the originating mail facility where mailpieces are then automatically matched back up with data through the use of a unique fluorescent barcode printed on the back during initial MLOCR attempt, and receive a POSTNET barcode representing the full address.
The UPU S10 standard defines a system for assigning 13-character identifiers to international postal items for the purpose of tracking and tracing them during shipping.

The Intelligent Mail Barcode (IMb) is a 65-bar barcode for use on mail in the United States. The term "Intelligent Mail" refers to services offered by the United States Postal Service for domestic mail delivery. The IM barcode is intended to provide greater information and functionality than its predecessors POSTNET and PLANET. An Intelligent Mail barcode has also been referred to as a One Code Solution and a 4-State Customer Barcode, abbreviated 4CB, 4-CB or USPS4CB. The complete specification can be found in USPS Document USPS-B-3200. It effectively incorporates the routing ZIP code and tracking information included in previously used postal barcode standards.
Tracking numbers are numbers assigned to packages when they are shipped. Tracking numbers are useful for knowing the location of time sensitive deliveries. It is a unique ID number or code assigned to a package or parcel. The tracking number is typically printed on the shipping label as a bar code that can be scanned by anyone with a bar code reader or smartphone.

Package tracking or package logging is the process of localizing shipping containers, mail and parcel post at different points of time during sorting, warehousing, and package delivery to verify their provenance and to predict and aid delivery.
Machine-readable postal marking may refer to:

Matrix 2 of 5 is a variable length, discrete, two width symbology. Matrix 2 of 5 is a subset of two-out-of-five codes. Unlike Industrial 2 of 5 code, Matrix 2 of 5 can encode data not only with black bars but with white spaces.















