
The United States Postmaster General (PMG) is the chief executive officer of the United States Postal Service (USPS). The PMG is responsible for managing and directing the day-to-day operations of the agency.

The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U.S., including its insular areas and associated states. It is one of the few government agencies explicitly authorized by the U.S. Constitution. The USPS, as of 2021, has 516,636 career employees and 136,531 non-career employees.

The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal systems have generally been established as a government monopoly, with a fee on the article prepaid. Proof of payment is usually in the form of an adhesive postage stamp, but a postage meter is also used for bulk mailing.

A ZIP Code is a postal code used by the United States Postal Service (USPS). Introduced on July 1, 1963, the basic format consisted of five digits. In 1983, an extended ZIP+4 code was introduced; it included the five digits of the ZIP Code, followed by a hyphen and four digits that designated a more specific location.

The Postal Reorganization Act of 1970 was a law passed by the United States Congress that abolished the then United States Post Office Department, which was a part of the Cabinet, and created the United States Postal Service, a corporation-like independent agency authorized by the US government as an official service for the delivery of mail in the United States. President Richard Nixon signed the Act in law on August 12, 1970.

The Grumman Long Life Vehicle (LLV) is an American light transport truck model, designed as a mail truck for the United States Postal Service, which has been its primary user since it first entered service in 1987, 36 years ago. It also was used by Canada Post. The LLV uses a chassis built by GM based on the S-10 with an aluminum body built by Grumman.

Registered mail is a mail service offered by postal services in many countries which allows the sender proof of mailing via a mailing receipt and, upon request, electronic verification that an article was delivered or that a delivery attempt was made. Depending on the country, additional services may also be available, such as:
Franking comprises all devices, markings, or combinations thereof ("franks") applied to mails of any class which qualifies them to be postally serviced. Types of franks include uncanceled and precanceled postage stamps, impressions applied via postage meter, official use "Penalty" franks, Business Reply Mail (BRM), and other permit Imprints (Indicia), manuscript and facsimile "franking privilege" signatures, "soldier's mail" markings, and any other forms authorized by the 192 postal administrations that are members of the Universal Postal Union.

A post office box is a uniquely addressable lockable box located on the premises of a post office.

A letter box, letterbox, letter plate, letter hole, mail slot or mailbox is a receptacle for receiving incoming mail at a private residence or business. For outgoing mail, Post boxes are often used for depositing the mail for collection, although some letter boxes are also capable of holding outgoing mail for a carrier to pick up. Letterboxes or mailboxes use the following primary designs:

U.S. Postal Service Pro Cycling Team was a United States-based professional road bicycle racing team. On June 15, 2004, the Discovery Channel signed a deal to become sponsor of the team for the 2004–2007 seasons and its name changed to Discovery Channel Pro Cycling Team. From 2005 until 2007, the team was one of the 20 teams that competed in the new UCI ProTour. As part of the sponsorship deal, Lance Armstrong, the team's undisputed leader, provided on-air appearances for the Discovery Networks TV channels. The deal did not affect the rights of secondary sponsor OLN, now known as NBC Sports Network in the US, to air major cycling events such as the Tour de France, although the two channels are competitors.

The system for mail delivery in the United States has developed with the nation. Rates were based on the distance between sender and receiver in the early years of the nation. In the middle of the 19th century, rates stabilized to one price regardless of distance. Rates were relatively unchanged until 1968, when the price was increased every few years by a small amount. Comparing the increases with a price index, the price of a first class stamp has been steady. The logo for the Post Office Department showed a man on a running horse, even as the railroads and then motorized trucks and airplanes moved mail. In 1971, the Post Office became the United States Postal Service, with rates set by the Postal Regulatory Commission, with some oversight by Congress. Air mail became standard in 1975. In the 21st century, prices were segmented to match the sorting machinery in use; non-standard letters required slightly higher postage.

The United States Postal Inspection Service (USPIS), or the Postal Inspectors, is the law enforcement arm of the United States Postal Service. It supports and protects the U.S. Postal Service, its employees, infrastructure, and customers by enforcing the laws that defend the nation's mail system from illegal or dangerous use. Its jurisdiction covers any "crimes that may adversely affect or fraudulently use the U.S. Mail, the postal system or postal employees." With roots going back to the late 18th century, the USPIS is the oldest continuously operating federal law enforcement agency.

Express mail is an expedited mail delivery service for which the customer pays a premium for faster delivery. Express mail is a service for domestic and international mail, and is in most nations governed by the country's own postal administration. Since 1999, the international express delivery services are governed by the EMS Cooperative.
A Prohibitory Order is a legal instrument issued by the United States Postal Service, against a mailer, on request of a recipient. Its effect is to criminalize any further attempt by a particular mailer to continue to send advertisement material to a particular recipient through the United States Postal Service. In addition, it demands that the mailer delete immediately the names of the particular recipient from all mailing lists owned or controlled by the mailer or his agents or assigns and, further, prohibits the mailer and his agents or assigns from the sale, rental, exchange, or other transaction involving mailing lists bearing the names of the particular recipient. It is requested by filing United States Postal Service Form 1500, either with a local Postmaster, or directly with the Prohibitory Order Processing Center.
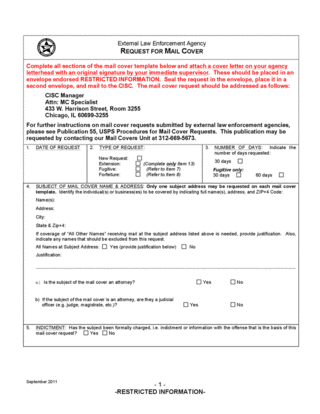
Mail cover is a law enforcement investigative technique in which the United States Postal Service, acting at the request of a law enforcement agency, records information from the outside of letters and parcels before they are delivered and then sends the information to the agency that requested it. The Postal Service grants mail cover surveillance requests for about 30 days and may extend them for up to 120 days.

The Intelligent Mail Barcode (IMb) is a 65-bar barcode for use on mail in the United States. The term "Intelligent Mail" refers to services offered by the United States Postal Service for domestic mail delivery. The IM barcode is intended to provide greater information and functionality than its predecessors POSTNET and PLANET. An Intelligent Mail barcode has also been referred to as a One Code Solution and a 4-State Customer Barcode, abbreviated 4CB, 4-CB or USPS4CB. The complete specification can be found in USPS Document USPS-B-3200. It effectively incorporates the routing ZIP code and tracking information included in previously used postal barcode standards.

Glenwood is an unincorporated community in Howard County, Maryland, United States. It is located between Baltimore and Washington, D.C., therefore attracting commuters to those employment centers. The community features acres of open space and is districted to Bushy Park Elementary, Glenwood and Folly Quarter Middle, and Glenelg High schools. Union Chapel was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975 and Round About Hills was added in 2008. The population in 2020 was approximately 3,416.

The United States Postal Service (USPS) provides Priority Mail Express for domestic U.S. delivery, and offers two types of international Express Mail services, although only one of them is part of the EMS standard. One is called Priority Mail Express International and the other service is called Global Express Guaranteed (GXG). The latter has no relation to "EMS" International service as provided by the EMS Cooperative.

















