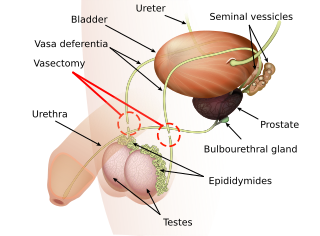
Vasectomy is an elective surgical procedure for male sterilization or permanent contraception. During the procedure, the male vasa deferentia are cut and tied or sealed so as to prevent sperm from entering into the urethra and thereby prevent fertilization of a female through sexual intercourse. Vasectomies are usually performed in a physician's office, medical clinic, or, when performed on an animal, in a veterinary clinic. Hospitalization is not normally required as the procedure is not complicated, the incisions are small, and the necessary equipment routine.

Keratin 20, often abbreviated CK20, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT20 gene.

Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) affecting medium-sized muscular arteries, typically involving the arteries of the kidneys and other internal organs but generally sparing the lungs' circulation. Small aneurysms are strung like the beads of a rosary, therefore making this "rosary sign" an important diagnostic feature of the vasculitis. PAN is sometimes associated with infection by the hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. The condition may be present in infants.

Brenner tumors are an uncommon subtype of the surface epithelial-stromal tumor group of ovarian neoplasms. The majority are benign, but some can be malignant.
Vasovasostomy is a surgery by which vasectomies are partially reversed. Another surgery for vasectomy reversal is vasoepididymostomy.

Testicular pain, also known as scrotal pain, occurs when part or all of either one or both testicles hurt. Pain in the scrotum is also often included. Testicular pain may be of sudden onset or of long duration.

Benign lymphoepithelial lesion or Mikulicz’ disease is a type of benign enlargement of the parotid and/or lacrimal glands. This pathologic state is sometimes, but not always, associated with Sjögren's syndrome.

Paired-like homeobox 2b (PHOX2B), also known as neuroblastoma Phox (NBPhox), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PHOX2B gene located on chromosome 4.

Neprilysin, also known as membrane metallo-endopeptidase (MME), neutral endopeptidase (NEP), cluster of differentiation 10 (CD10), and common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MME gene. Neprilysin is a zinc-dependent metalloprotease that cleaves peptides at the amino side of hydrophobic residues and inactivates several peptide hormones including glucagon, enkephalins, substance P, neurotensin, oxytocin, and bradykinin. It also degrades the amyloid beta peptide whose abnormal folding and aggregation in neural tissue has been implicated as a cause of Alzheimer's disease. Synthesized as a membrane-bound protein, the neprilysin ectodomain is released into the extracellular domain after it has been transported from the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface.
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma is a mature T-cell lymphoma of blood or lymph vessel immunoblasts characterized by a polymorphous lymph node infiltrate showing a marked increase in follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) and high endothelial venules (HEVs) and systemic involvement.
Post-vasectomy pain syndrome (PVPS) is a chronic and sometimes debilitating genital pain condition that may develop immediately or several years after vasectomy. Because this condition is a syndrome, there is no single treatment method, therefore efforts focus on mitigating/relieving the individual patient's specific pain. When pain in the epididymides is the primary symptom, post-vasectomy pain syndrome is often described as congestive epididymitis.
An ossifying fibromyxoid tumor is a type of myxoma. It presents in the extremities more frequently than the trunk. It is derived from mesenchyme. Appearance in the head and neck is rare, but has been reported. Its malignancy has been characterized as "intermediate".

Nucleoporin 88 (Nup88) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUP88 gene.
T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, previously labeled precursor T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is a form of lymphoid leukemia and lymphoma in which too many T-cell lymphoblasts are found in the blood, bone marrow, and tissues, particularly mediastinal lymph nodes. Labeling as leukemia or lymphoma depends on which feature is more pronounced in a given situation, but has no biological or treatment implication.
Neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis (NICO) is a controversial diagnosis whereby a putative jawbone cavitation causes chronic facial neuralgia; this is different from osteonecrosis of the jaw. In NICO the pain is said to result from the degenerating nerve ("neuralagia"). The condition is probably rare, if it does exist.
Verruciform xanthoma is an uncommon benign lesion that has a verruciform (wart-like) appearance, but it may appear polypoid, papillomatous, or sessile. The verruciform was first described by Shafer in 1971 on the oral mucosa. Usually found on the oral mucosa of middle-aged persons, verruciform xanthomas have also been reported on the scrotum and penis of middle-aged to elderly Japanese males. While the most common site is the oral mucosa, lesions that occur elsewhere usually arise on the perineum or on the skin with some predisposing factor, such as lymphedema or an epidermal nevus.

Salpingitis isthmica nodosa (SIN), also known as diverticulosis of the Fallopian tube, is nodular thickening of the narrow part of the uterine tube, due to inflammation.
Telepathology is the practice of pathology at a distance. It uses telecommunications technology to facilitate the transfer of image-rich pathology data between distant locations for the purposes of diagnosis, education, and research. Performance of telepathology requires that a pathologist selects the video images for analysis and the rendering of diagnoses. The use of "television microscopy", the forerunner of telepathology, did not require that a pathologist have physical or virtual "hands-on" involvement in the selection of microscopic fields-of-view for analysis and diagnosis.
The Xanthogranulomatous Process (XP), is a form of acute and chronic inflammation characterized by an exuberant clustering of foamy macrophages among other inflammatory cells. Localization in the kidney and renal pelvis has been the most frequent and better known occurrence followed by that in the gallbladder but many others have been subsequently recorded. The pathological findings of the process and etiopathogenetic and clinical observations have been reviewed by Cozzutto and Carbone.
Microglandular hyperplasia (MGH) of the cervix is an epithelial benign abnormality (lesion) associated with gland proliferation. It can terminate in mature squamous metaplasia, and it is suspected reserve cells are involved in this process, perhaps in the form of reserve cell hyperplasia with glandular differentiation.









