
Catalysis is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst. Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst.

Manganese is a chemical element; it has symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide.

Superoxide dismutase (SOD, EC 1.15.1.1) is an enzyme that alternately catalyzes the dismutation (or partitioning) of the superoxide (O−
2) anion radical into normal molecular oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2). Superoxide is produced as a by-product of oxygen metabolism and, if not regulated, causes many types of cell damage. Hydrogen peroxide is also damaging and is degraded by other enzymes such as catalase. Thus, SOD is an important antioxidant defense in nearly all living cells exposed to oxygen. One exception is Lactobacillus plantarum and related lactobacilli, which use a different mechanism to prevent damage from reactive O−
2.
In chemistry, a transition metal is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table, though the elements of group 12 are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinide elements are called inner transition metals and are sometimes considered to be transition metals as well.

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins.

Group 7, numbered by IUPAC nomenclature, is a group of elements in the periodic table. It contains manganese (Mn), technetium (Tc), rhenium (Re) and bohrium (Bh). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table, and are hence transition metals. This group is sometimes called the manganese group or manganese family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.
Bioinorganic chemistry is a field that examines the role of metals in biology. Bioinorganic chemistry includes the study of both natural phenomena such as the behavior of metalloproteins as well as artificially introduced metals, including those that are non-essential, in medicine and toxicology. Many biological processes such as respiration depend upon molecules that fall within the realm of inorganic chemistry. The discipline also includes the study of inorganic models or mimics that imitate the behaviour of metalloproteins.

Vanadium bromoperoxidases are a kind of enzymes called haloperoxidases. Its primary function is to remove hydrogen peroxide which is produced during photosynthesis from in or around the cell. By producing hypobromous acid (HOBr) a secondary reaction with dissolved organic matter, what results is the bromination of organic compounds that are associated with the defense of the organism. These enzymes produce the bulk of natural organobromine compounds in the world.
Nitrite reductase refers to any of several classes of enzymes that catalyze the reduction of nitrite. There are two classes of NIR's. A multi haem enzyme reduces NO2− to a variety of products. Copper containing enzymes carry out a single electron transfer to produce nitric oxide.

Vanadium compounds are compounds formed by the element vanadium (V). The chemistry of vanadium is noteworthy for the accessibility of the four adjacent oxidation states 2–5, whereas the chemistry of the other group 5 elements, niobium and tantalum, are somewhat more limited to the +5 oxidation state. In aqueous solution, vanadium forms metal aquo complexes of which the colours are lilac [V(H2O)6]2+, green [V(H2O)6]3+, blue [VO(H2O)5]2+, yellow-orange oxides [VO(H2O)5]3+, the formula for which depends on pH. Vanadium(II) compounds are reducing agents, and vanadium(V) compounds are oxidizing agents. Vanadium(IV) compounds often exist as vanadyl derivatives, which contain the VO2+ center.
In chemistry, a (redox) non-innocent ligand is a ligand in a metal complex where the oxidation state is not clear. Typically, complexes containing non-innocent ligands are redox active at mild potentials. The concept assumes that redox reactions in metal complexes are either metal or ligand localized, which is a simplification, albeit a useful one.

In chemistry, metallacrowns are a macrocyclic compounds that consist of metal ions and solely or predominantly heteroatoms in the ring. Classically, metallacrowns contain an [M–N–O] repeat unit in the macrocycle. First discovered by Vincent L. Pecoraro and Myoung Soo Lah in 1989, metallacrowns are best described as inorganic analogues of crown ethers. To date, over 600 reports of metallacrown research have been published. Metallacrowns with sizes ranging from 12-MC-4 to 60-MC-20 have been synthesized.
A transition metal oxo complex is a coordination complex containing an oxo ligand. Formally O2-, an oxo ligand can be bound to one or more metal centers, i.e. it can exist as a terminal or (most commonly) as bridging ligands (Fig. 1). Oxo ligands stabilize high oxidation states of a metal. They are also found in several metalloproteins, for example in molybdenum cofactors and in many iron-containing enzymes. One of the earliest synthetic compounds to incorporate an oxo ligand is potassium ferrate (K2FeO4), which was likely prepared by Georg E. Stahl in 1702.
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).

Bromide peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.18, bromoperoxidase, haloperoxidase (ambiguous), eosinophil peroxidase) is a family of enzymes with systematic name bromide:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. These enzymes catalyse the following chemical reaction:
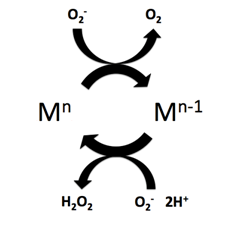
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetics are synthetic compounds that mimic the native superoxide dismutase enzyme. SOD mimetics effectively convert the superoxide anion, a reactive oxygen species, into hydrogen peroxide, which is further converted into water by catalase. Reactive oxygen species are natural byproducts of cellular respiration and cause oxidative stress and cell damage, which has been linked to causing cancers, neurodegeneration, age-related declines in health, and inflammatory diseases. SOD mimetics are a prime interest in therapeutic treatment of oxidative stress because of their smaller size, longer half-life, and similarity in function to the native enzyme.
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems refers to the incorporation of metallic ions into living organisms and how it has changed over time. Metal ions have been associated with biological systems for billions of years, but only in the last century have scientists began to truly appreciate the scale of their influence. Major and minor metal ions have become aligned with living organisms through the interplay of biogeochemical weathering and metabolic pathways involving the products of that weathering. The associated complexes have evolved over time.
An Artificial Metalloenzyme (ArM) is a designer metalloprotein, not found in nature, which can catalyze desired chemical reactions. Despite fitting into classical enzyme categories, ArMs also have potential in new-to-nature chemical reactivity like catalysing Suzuki coupling, Metathesis etc., which were never reported among natural enzymatic reactions.
Julia A. Kovacs is an American chemist specializing in bioinorganic chemistry. She is professor of chemistry at the University of Washington. Her research involves synthesizing small-molecule mimics of the active sites of metalloproteins, in order to investigate how cysteinates influence the function of non-heme iron enzymes, and the mechanism of the oxygen-evolving complex (OEC).
Metallopeptides are peptides that contain one or more metal ions in their structure. This specific type of peptide are, just like metalloproteins, metallofoldamers. And very similar to metalloproteins, metallopeptide's functionality is attibuted through the contained metal ion cofactor. These short structured peptides are often employed to develop mimics of metalloproteins and systems similar to artificial metalloenzymes.













