
Cadherins (named for "calcium-dependent adhesion") are cell adhesion molecules important in forming adherens junctions that let cells adhere to each other. Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins, and they depend on calcium (Ca2+) ions to function, hence their name. Cell-cell adhesion is mediated by extracellular cadherin domains, whereas the intracellular cytoplasmic tail associates with numerous adaptors and signaling proteins, collectively referred to as the cadherin adhesome.

Catenins are a family of proteins found in complexes with cadherin cell adhesion molecules of animal cells. The first two catenins that were identified became known as α-catenin and β-catenin. α-Catenin can bind to β-catenin and can also bind filamentous actin (F-actin). β-Catenin binds directly to the cytoplasmic tail of classical cadherins. Additional catenins such as γ-catenin and δ-catenin have been identified. The name "catenin" was originally selected because it was suspected that catenins might link cadherins to the cytoskeleton.

In mammalian cells, vinculin is a membrane-cytoskeletal protein in focal adhesion plaques that is involved in linkage of integrin adhesion molecules to the actin cytoskeleton. Vinculin is a cytoskeletal protein associated with cell-cell and cell-matrix junctions, where it is thought to function as one of several interacting proteins involved in anchoring F-actin to the membrane.

In cell biology, adherens junctions are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions and cell–matrix junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions. An adherens junction is defined as a cell junction whose cytoplasmic face is linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They can appear as bands encircling the cell or as spots of attachment to the extracellular matrix.
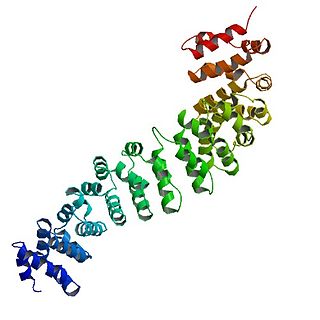
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (beta-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene.
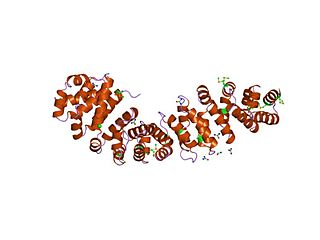
An armadillo repeat is a characteristic, repetitive amino acid sequence of about 42 residues in length that is found in many proteins. Proteins that contain armadillo repeats typically contain several tandemly repeated copies. Each armadillo repeat is composed of a pair of alpha helices that form a hairpin structure. Multiple copies of the repeat form what is known as an alpha solenoid structure.
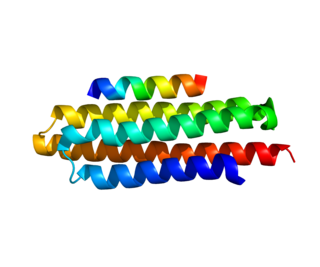
Paxillin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PXN gene. Paxillin is expressed at focal adhesions of non-striated cells and at costameres of striated muscle cells, and it functions to adhere cells to the extracellular matrix. Mutations in PXN as well as abnormal expression of paxillin protein has been implicated in the progression of various cancers.
Talin is a high-molecular-weight cytoskeletal protein concentrated at regions of cell–substratum contact and, in lymphocytes, at cell–cell contacts. Discovered in 1983 by Keith Burridge and colleagues, talin is a ubiquitous cytosolic protein that is found in high concentrations in focal adhesions. It is capable of linking integrins to the actin cytoskeleton either directly or indirectly by interacting with vinculin and α-actinin.

α-Catenin (alpha-catenin) functions as the primary protein link between cadherins and the actin cytoskeleton. It has been reported that the actin binding proteins vinculin and α-actinin can bind to alpha-catenin. It has been suggested that alpha-catenin does not bind with high affinity to both actin filaments and the E-cadherin-beta-catenin complex at the same time. It has been observed that when α-catenin is not in a molecular complex with β-catenin, it dimerizes and functions to regulate actin filament assembly, possibly by competing with Arp2/3 protein. α-Catenin exhibits significant protein dynamics. However, a protein complex including a cadherin, actin, β-catenin and α-catenin has not been isolated.

Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation/gamma-carboxyglutamic (GLA) domain is a protein domain that contains post-translational modifications of many glutamate residues by vitamin K-dependent carboxylation to form γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla). Proteins with this domain are known informally as Gla proteins. The Gla residues are responsible for the high-affinity binding of calcium ions.

Cadherin-2 also known as Neural cadherin (N-cadherin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH2 gene. CDH2 has also been designated as CD325 . Cadherin-2 is a transmembrane protein expressed in multiple tissues and functions to mediate cell–cell adhesion. In cardiac muscle, Cadherin-2 is an integral component in adherens junctions residing at intercalated discs, which function to mechanically and electrically couple adjacent cardiomyocytes. Alterations in expression and integrity of Cadherin-2 has been observed in various forms of disease, including human dilated cardiomyopathy. Variants in CDH2 have also been identified to cause a syndromic neurodevelopmental disorder.

Cadherin-3, also known as P-Cadherin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH3 gene.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase mu is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRM gene.

Cadherin-1 or Epithelial cadherin(E-cadherin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH1 gene. Mutations are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid, and ovarian cancers. CDH1 has also been designated as CD324. It is a tumor suppressor gene.

αE-catenin, also known as Catenin alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNA1 gene. αE-catenin is highly expressed in cardiac muscle and localizes to adherens junctions at intercalated disc structures where it functions to mediate the anchorage of actin filaments to the sarcolemma. αE-catenin also plays a role in tumor metastasis and skin cell function.
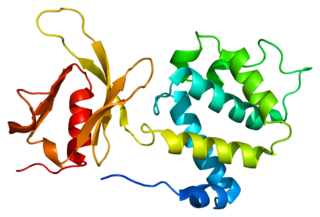
Talin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLN1 gene. Talin-1 is ubiquitously expressed, and is localized to costamere structures in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, and to focal adhesions in smooth muscle and non-muscle cells. Talin-1 functions to mediate cell-cell adhesion via the linkage of integrins to the actin cytoskeleton and in the activation of integrins. Altered expression of talin-1 has been observed in patients with heart failure, however no mutations in TLN1 have been linked with specific diseases.

The Actin assembly-inducing protein (ActA) is a protein encoded and used by Listeria monocytogenes to propel itself through a mammalian host cell. ActA is a bacterial surface protein comprising a membrane-spanning region. In a mammalian cell, the bacterial ActA interacts with the Arp2/3 complex and actin monomers to induce actin polymerization on the bacterial surface generating an actin comet tail. The gene encoding ActA is named actA or prtB.
WH1 domains, also known as EVH1 domains, are evolutionary conserved protein domains found on WASP (VASP) proteins, which are often involved in actin polymerization.

In structural and cell biology, the focal adhesion targeting domain is a conserved protein domain that was first identified in focal adhesion kinase (FAK), also known as PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2).

Synaptic stabilization is crucial in the developing and adult nervous systems and is considered a result of the late phase of long-term potentiation (LTP). The mechanism involves strengthening and maintaining active synapses through increased expression of cytoskeletal and extracellular matrix elements and postsynaptic scaffold proteins, while pruning less active ones. For example, cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) play a large role in synaptic maintenance and stabilization. Gerald Edelman discovered CAMs and studied their function during development, which showed CAMs are required for cell migration and the formation of the entire nervous system. In the adult nervous system, CAMs play an integral role in synaptic plasticity relating to learning and memory.
















