Related Research Articles
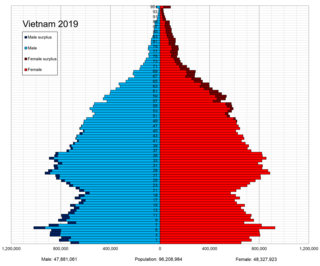
Demographic features of the population of Vietnam include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

In computing, a denial-of-service attack is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. The range of attacks varies widely, spanning from inundating a server with millions of requests to slow its performance, overwhelming a server with a substantial amount of invalid data, to submitting requests with an illegitimate IP address.

This timeline of computer viruses and worms presents a chronological timeline of noteworthy computer viruses, computer worms, Trojan horses, similar malware, related research and events.

Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about 331,000 square kilometres (128,000 sq mi) and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's fifteenth-most populous country. Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City.

The First Indochina War was fought between France and Việt Minh, and their respective allies, from 19 December 1946 until 20 July 1954. Việt Minh was led by Võ Nguyên Giáp and Hồ Chí Minh. Most of the fighting took place in Tonkin in Northern Vietnam, although the conflict engulfed the entire country and also extended into the neighboring French Indochina protectorates of Laos and Cambodia.

Vietnamese Americans are Americans of Vietnamese ancestry. They comprise approximately half of all overseas Vietnamese and are the fourth-largest Asian American ethnic group following Chinese Americans, Indian Americans, and Filipino Americans. There are approximately 2.3 million people of Vietnamese descent residing in the U.S. as of 2023.
Linux malware includes viruses, Trojans, worms and other types of malware that affect the Linux family of operating systems. Linux, Unix and other Unix-like computer operating systems are generally regarded as very well-protected against, but not immune to, computer viruses.
Bagle was a mass-mailing computer worm affecting Microsoft Windows. The first strain, Bagle.A, did not propagate widely. A second variant, Bagle.B, was considerably more virulent.

In computing, a zombie is a computer connected to the Internet that has been compromised by a hacker via a computer virus, computer worm, or trojan horse program and can be used to perform malicious tasks under the remote direction of the hacker. Zombie computers often coordinate together in a botnet controlled by the hacker, and are used for activities such as spreading e-mail spam and launching distributed denial-of-service attacks against web servers. Most victims are unaware that their computers have become zombies. The concept is similar to the zombie of Haitian Voodoo folklore, which refers to a corpse resurrected by a sorcerer via magic and enslaved to the sorcerer's commands, having no free will of its own. A coordinated DDoS attack by multiple botnet machines also resembles a "zombie horde attack", as depicted in fictional zombie films.

A botnet is a group of Internet-connected devices, each of which runs one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, steal data, send spam, and allow the attacker to access the device and its connection. The owner can control the botnet using command and control (C&C) software. The word "botnet" is a portmanteau of the words "robot" and "network". The term is usually used with a negative or malicious connotation.
VPSKeys is a freeware input method editor developed and distributed by the Vietnamese Professionals Society (VPS). One of the first input method editors for Vietnamese, it allows users to add accent marks to Vietnamese text on computers running Microsoft Windows. The first version of VPSKeys, supporting Windows 3.1, was released in 1993. The most recent version is 4.3, released in October 2007.

The Storm botnet or Storm worm botnet was a remotely controlled network of "zombie" computers that had been linked by the Storm Worm, a Trojan horse spread through e-mail spam. At its height in September 2007, the Storm botnet was running on anywhere from 1 million to 50 million computer systems, and accounted for 8% of all malware on Microsoft Windows computers. It was first identified around January 2007, having been distributed by email with subjects such as "230 dead as storm batters Europe," giving it its well-known name. The botnet began to decline in late 2007, and by mid-2008 had been reduced to infecting about 85,000 computers, far less than it had infected a year earlier.
Internet censorship in Vietnam is implemented in the country, according to a 2009 report from Reporters Without Borders. Vietnam regulates its citizens' Internet access using both legal and technical means. The government's efforts to regulate, monitor, and provide oversight regarding Internet use has been referred to as a "Bamboo Firewall".
Srizbi BotNet is considered one of the world's largest botnets, and responsible for sending out more than half of all the spam being sent by all the major botnets combined. The botnets consist of computers infected by the Srizbi trojan, which sent spam on command. Srizbi suffered a massive setback in November 2008 when hosting provider Janka Cartel was taken down; global spam volumes reduced up to 93% as a result of this action.
The July 2009 cyberattacks were a series of coordinated cyberattacks against major government, news media, and financial websites in South Korea and the United States. The attacks involved the activation of a botnet—a large number of hijacked computers—that maliciously accessed targeted websites with the intention of causing their servers to overload due to the influx of traffic, known as a DDoS attack. Most of the hijacked computers were located in South Korea. The estimated number of the hijacked computers varies widely; around 20,000 according to the South Korean National Intelligence Service, around 50,000 according to Symantec's Security Technology Response group, and more than 166,000 according to a Vietnamese computer security researcher who analyzed the log files of the two servers the attackers controlled. An investigation revealed that at least 39 websites were targets in the attacks based on files stored on compromised systems.
Avalanche was a criminal syndicate involved in phishing attacks, online bank fraud, and ransomware. The name also refers to the network of owned, rented, and compromised systems used to carry out that activity. Avalanche only infected computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system.
The Mariposa botnet, discovered December 2008, is a botnet mainly involved in cyberscamming and denial-of-service attacks. Before the botnet itself was dismantled on 23 December 2009, it consisted of up to 12 million unique IP addresses or up to 1 million individual zombie computers infected with the "Butterfly Bot", making it one of the largest known botnets.
The Asprox botnet, also known by its aliases Badsrc and Aseljo, is a botnet mostly involved in phishing scams and performing SQL injections into websites in order to spread malware. It is a highly infectious malware which spreads through an email or through a clone website. It can be used to trace any kind of personal or financial information and activities online.
The 2010 cyberattacks on Myanmar were distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS) that began on 25 October, occurring ahead of the 2010 Burmese general election, which is widely viewed as a sham election. This election was the first that Burma had had in 20 years. The attacks were significantly larger than attacks against Estonia and Georgia in 2007 and 2008 respectively. The attack followed a similar one on 1 February 2010, and also followed an incident of a total loss of connection to the internet the previous spring when a submarine communications cable was severed accidentally.

The term "Vietnamese democracy movement" comprises any of various isolated efforts to seek democratic reforms in Vietnam. There is not a major movement in Vietnam to reform the current political system. Opposition to governance has been characterised by sporadic calls for reform by minor groups and rare, small protests. Vietnam was ranked 37th most electoral democratic country in Asia according to V-Dem Democracy indices in 2023 with a score of 0.157 out of 1.
References
- ↑ "Google frets over Vietnam hacktivist botnet". The Register. 2010-03-31. Archived from the original on 2018-02-14. Retrieved 2018-02-13.
- ↑ Lolita C. Baldor (2010-10-28). "Computer attack hits dissidents in Vietnam". Boston.com. AP. Archived from the original on 2021-10-06. Retrieved 2018-02-13.