Function
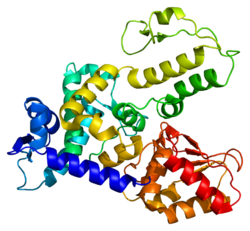
WW domain-containing proteins are found in all eukaryotes and play an important role in the regulation of a wide variety of cellular functions such as protein degradation, transcription, and RNA splicing. This gene encodes a protein which contains 4 tandem WW domains and a HECT (homologous to the E6-associated protein carboxyl terminus) domain. The encoded protein belongs to a family of NEDD4-like proteins, which are E3 ubiquitin-ligase molecules and regulate key trafficking decisions, including targeting of proteins to proteosomes or lysosomes. Alternative splicing of this gene generates at least 6 transcript variants; however, the full length nature of these transcripts has not been defined. [7] In neurons, murine ortholog Wwp1 and its homolog Wwp2 control polarity acquisition, formation, and branching of axons, as well as migration of newly born nerve cells into the cortical plate. [8]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.