
Arzachel is a relatively young lunar impact crater located in the highlands in the south-central part of the visible Moon, close to the zero meridian. It lies to the south of the crater Alphonsus, and together with Ptolemaeus further north the three form a prominent line of craters to the east of Mare Nubium. The smaller Alpetragius lies to the northwest, and Thebit is to the southwest along the edge of the mare.

Fra Mauro is the worn remnant of a walled lunar plain. It is part of the surrounding Fra Mauro formation, being located to the northeast of Mare Cognitum and southeast of Mare Insularum. Attached to the southern rim are the co-joined craters Bonpland and Parry, which intrude into the formation forming inward-bulging walls. The crater is named after Italian geographer Fra Mauro.

Menelaus is a young lunar impact crater located on the southern shore of Mare Serenitatis near the eastern end of the Montes Hæmus mountain range. Its diameter is 27 km. To the southwest is the small crater Auwers, and to the west-southwest is the even smaller Daubrée. To the northeast is a faint rille system named the Rimae Menelaus.

Manners is a lunar impact crater located in the western part of the Mare Tranquillitatis. Its diameter is 15 km. It was named after British astronomer Russell Henry Manners. To the northeast is the larger crater Arago and to the south are Ritter and Sabine. The crater has a rim with a higher albedo than the surrounding mare, making it appear bright. This is a circular, bowl-shaped feature with a raised rim and a relatively flat interior.

Murchison is a lunar impact crater on the north edge of the Sinus Medii. It was named in honour of the geologist Sir Roderick Murchison. It shares a section of rim with the crater Pallas. To the southeast on the mare is the circular crater Chladni, and to the northeast is Ukert. Farther to the east is the prominent Triesnecker. Murchison lies astride the lunar zenith line, i.e. the starting longitude of the selenographic coordinate system.

Deslandres is the heavily worn and distorted remains of a lunar impact crater. It is located to the southeast of the Mare Nubium, in the rugged southern highlands of the Moon. In dimension it is the third-largest crater formation on the visible Moon, being beaten only by Clavius and by the 303-kilometer-diameter walled plain Bailly. The northern and eastern parts of the floor display a relatively level surface, but it is pock-marked with numerous craters. There is a small region of mare material, due to basaltic lava, along the eastern interior floor.

Alpetragius is a lunar impact crater located on the eastern edge of Mare Nubium, to the southwest of the much larger crater Alphonsus. In the southeast is the prominent crater Arzachel, and to the west lies the flooded Lassell. Alpetragius is a Latinization of the name of Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji, a Spanish-Arab astronomer.

Burnham is a small crater located to the southeast of the crater Albategnius, in a relatively smooth area of the lunar surface. It was named after American astronomer Sherburne W. Burnham. To the southwest is Vogel.

Jansen is a lunar impact crater in the north part of the Mare Tranquillitatis. The diameter is 24 km. It was named after 17th century Dutch optician Zacharias Janssen. It is located to the east-southeast of the crater Plinius. The rim of Jansen is low and narrow, with a notch along the western edge. The interior is relatively level, which may indicate it has been covered by lava. To the south-southwest a small but prominent crater lies on the crater floor, halfway between the center and the rim.

Fauth is a small double-crater located at the edge of the rough southern ramparts of the prominent ray crater Copernicus on the Moon. It lies in the Mare Insularum, to the northeast of the crater Reinhold. The crater is named after German selenographer Philipp Johann Heinrich Fauth.

Arago is a lunar impact crater located in the western part of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It was named after French astronomer François Arago in 1935. Its diameter is 26 km. To the southwest lies the crater Manners, and beyond are Dionysius and the Ritter–Sabine crater pair. To the southeast is the large Lamont formation that has been submerged by the mare.

Aristillus is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern Mare Imbrium. It was named after Greek astronomer Aristyllus. Directly to the south is the smaller crater Autolycus, while to the southwest is the large Archimedes. To the northeast are the craters Theaetetus and Cassini.
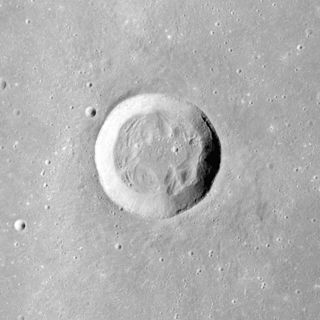
Bessel is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the southern half of the Mare Serenitatis. The crater was named after the German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel in 1935. Despite its small size, this is the largest crater to lie entirely within the mare. It lies to the north-northeast of the crater Menelaus.

Descartes is a heavily worn lunar impact crater that is located in the rugged south-central highlands of the Moon. To the southwest is the crater Abulfeda. It is named after the French philosopher, mathematician and physicist René Descartes.

Dionysius is a lunar impact crater that lies on the western edge of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It was named after Dionysius the Areopagite. To the southeast is the crater pair of Ritter and Sabine. Just to the northwest is the system of rilles designated Rimae Ritter. These clefts follow a generally northwest direction.

Julius Caesar is a lava-flooded lunar impact crater with a low, irregular, and heavily worn wall. Its diameter is 85 km. It was named after Roman statesman Julius Caesar. It is located to the west of Mare Tranquillitatis, and directly southeast of the crater Manilius on the Mare Vaporum. To the east is the rounded Sosigenes.

Alfraganus is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the rugged highland region to the southwest of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is named after the Muslim astronomer Alfraganus. Northwest of Alfraganus is the crater Delambre, and to the south is the irregular Zöllner. The rim of Alfraganus is circular and retains a sharp edge that has not received a significant amount of wear due to subsequent impacts. The interior floor is roughly half the diameter of the crater rim.

Davy is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the eastern edge of the Mare Nubium. It was named after British physicist Humphry Davy. It overlies the lava-flooded remains of the satellite crater Davy Y to the east, a formation which contains a crater chain designated Catena Davy. To the southeast of Davy is the prominent crater Alphonsus.

Daubrée is a lunar impact crater that is located to the southwest of the Mare Serenitatis, just to the west-southwest of the crater Menelaus in the Montes Haemus range. The small lunar mare Lacus Hiemalis lies along the southwest rim of Daubrée. The crater was named after French geologist Gabriel A. Daubrée. It was previously designated Menelaus S.

Dreyer is the remnant of a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located along the eastern edge of the Mare Marginis, about midway between the craters Ginzel to the north and Erro to the south-southeast. It was named after Danish-Irish astronomer John L. E. Dreyer.
























