
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, was an anti-foreign, anti-imperialist, and anti-Christian uprising in North China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists, known as the "Boxers" in English due to many of its members having practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". It was defeated by the Eight-Nation Alliance of foreign powers.
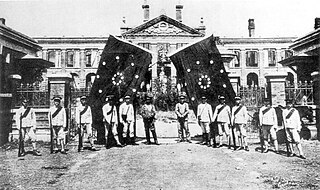
The Wuchang Uprising was an armed rebellion against the ruling Qing dynasty that took place in Wuchang in the Chinese province of Hubei on 10 October 1911, beginning the Xinhai Revolution that successfully overthrew China's last imperial dynasty. It was led by elements of the New Army, influenced by revolutionary ideas from Tongmenghui. The uprising and the eventual revolution directly led to the downfall of the Qing dynasty with almost three centuries of imperial rule, and the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC), which commemorates the anniversary of the uprising's outbreak on 10 October as the National Day of the Republic of China.

General Cao Kun was a Chinese warlord and politician, who served as the President of the Republic of China from 1923 to 1924, as well as the military leader of the Zhili clique in the Beiyang Army; he also served as a trustee of the Catholic University of Peking.

The Beiyang Army, named after the Beiyang region, was a combined large army, Western-style Imperial Chinese Army established by the Qing dynasty government in the late 19th century. It was the centerpiece of a general reconstruction of Qing China's military system. The Beiyang Army played a major role in Chinese politics for at least three decades and arguably right up to 1949. It made the Xinhai Revolution of 1911 possible, and, by dividing into warlord factions known as the Beiyang Clique, ushered in a period of regional division.
The Zhili–Anhui War was a 1920 conflict in the Republic of China between the Zhili and Anhui cliques for control of the Beiyang government.
The Winter Offensive of 1947 in Northeast China was a series of battles initiated by the Communist forces against the Kuomintang (Nationalists) during the Chinese Civil War after World War II.
Lanzhou Campaign was a series battle fought between the nationalists and the communists for the control of the largest city in northwestern China during the Chinese Civil War in the post World War II era, and resulted in the communist victory.

Chen Guangyuan, sobriquet Xiufeng (秀峰), was a Zhili clique warlord and military governor of Jiangxi from August 6, 1917, to June 15, 1922.

Lu Yongxiang (Chinese: 盧永祥; Chinese: 卢永祥; pinyin: Lú Yǒngxiáng; Wade–Giles: Lu2 Yung3-hsiang2; IPA:[lúi̯ʊ̌ŋɕi̯ɑ́ŋ] October 22, 1867 – May 15, 1933) was an Anhui clique warlord and military governor of Zhejiang, Zhili, and Jiangsu.

Wu Guangxin, (simplified Chinese: 吴光新; traditional Chinese: 吳光新; pinyin: Wú Guāngxīn; Wade–Giles: Wu2 Kuang1-hsin1; IPA:[úku̯ɑ̄ŋɕīn]; 1881–1939) Army general of the Empire of Japan. Military and Civil governor of Hunan in 1920. Army Minister 1924–1925.

Zaitao, courtesy name Shuyuan, art name Yeyun, was a Manchu prince of the Qing dynasty. He was a half-brother of the Guangxu Emperor and an uncle of Puyi, the last Emperor of China.

Yuxian (1842–1901) was a Manchu high official of the Qing dynasty who played an important role in the violent anti-foreign and anti-Christian Boxer Rebellion, which unfolded in northern China from the fall of 1899 to 1901. He was a local official who rose quickly from prefect of Caozhou to judicial commissioner and eventually governor of Shandong province. Dismissed from that post because of foreign pressure, he was soon named governor of Shanxi province. At the height of the Boxer crisis, as Allied armies invaded China in July 1900, he invited a group of 45 Christians and American missionaries to the provincial capital, Taiyuan, saying he would protect them from the Boxers. Instead, they were all killed. Foreigners, blaming Yuxian for what they called the Taiyuan Massacre, labeled him the "Butcher of Shan-hsi [Shanxi]".
Events from the year 1934 in China.

Late Qing reforms, commonly known as New Policies of the late Qing dynasty, or New Deal of the late Qing dynasty, simply referred to as New Policies, were a series of cultural, economic, educational, military, diplomatic, and political reforms implemented in the last decade of the Qing dynasty to keep the dynasty in power after the invasions of the great powers of the Eight Nation Alliance in league with the ten provinces of the Southeast Mutual Protection during the Boxer Rebellion.

Hu Guangyong (1823–1885) (胡光墉), better known by his courtesy name Xueyan (胡雪巖), was a businessman in China during the latter Qing dynasty. He was active in banking, real estate, shipping and Chinese medicine. He was involved in the salt, tea, clothing, grain as well as the arms trade.

Li Chun was a Chinese general of the Warlord Era of the Republic of China.

Xia Douyin (1885–1951) was a Republic of China National Revolutionary Army general. He was born in Macheng, Hubei. Originally a member of the Qing Dynasty New Army, he participated in the Xinhai Revolution of 1911. In 1917, he joined the Constitutional Protection Movement and opposed local warlord Wang Zhanyuan. Defeated by Wang's forces, he fled to Changsha and enlisted the help of allies in Hunan against Wang. After suffering another defeat in 1919, he fled to the border region of Hunan and Jiangxi Provinces. In 1926, he was brought by Tang Shengzhi into the National Revolutionary Army and participated in the Northern Expedition as a divisional commander. On May 17, 1927, Xia led Kuomintang forces loyal to Chiang Kai-shek from Yichang against the forces of Ye Ting in Wuhan. After his victory, he notoriously took personal pleasure in mutilating the corpses of female revolutionaries he had killed. Chiang promoted Xia to army commander and he fought in the Central Plains War of 1930. Xia was then tasked with suppressing the Eyuwan Soviet in the border region between Hubei, Henan, and Anhui provinces. He ordered the massacre of thousands of civilians but was unable to stop the Communists' expansion. In 1932, Xia was promoted to full general and made governor of Hubei, although Zhang Qun actually acted in his place. From July to September 1932, Chiang Kai-shek ordered 300,000 troops of the National Revolutionary Army to surround and suppress the Eyuwan Soviet in the Fourth Encirclement Campaign. Xia directed a scorched earth campaign, killing all men found in the Soviet areas, burning all buildings, and seizing or destroying all crops. He was ultimately successful and the main Communist Red Army was forced to retreat westwards. During the Second Sino-Japanese War, Xia fled to Chengdu after Hubei was occupied by the invading Imperial Japanese Army. In 1945, he retired from the military. Although he attempted to welcome the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) takeover of the mainland, the CCP rebuffed him and he fled to Hong Kong, where he died.

The 77th Group Army, Unit 31667, formerly the 13th Group Army, is a military formation of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Ground Force (PLAGF). The 77th Group Army is one of thirteen total group armies of the PLAGF, the largest echelon of ground forces in the People's Republic of China, and one of two assigned to the nation's Western Theater Command.

The Prime Minister of the Imperial Cabinet was a position created on 8 May 1911 during the late Qing dynasty, as part of the imperial government's unsuccessful attempts at creating a constitutional monarchy in China.

Fengshan was a Qing dynasty general. A member of the Bordered White Banner, he passed the Imperial Examination with a focus on translation. After some time as a translator and secretary, as well as a stint in the police, he transferred to the military. Between 1900 and 1911, he held numerous positions, including division commander with the Beiyang Army as well as Tartar-General in Xi'an. Fengshan was assigned to Guangdong after the assassination of Fuqi, but he was himself killed by the Chinese Assassination Corps upon arrival. His home in Beijing has been recognized as a cultural property.


















