
Sindh is a province of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province by population after Punjab. It is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab to the north. It shares an International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert of Sindh in the eastern portion of the province along the international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of the province.
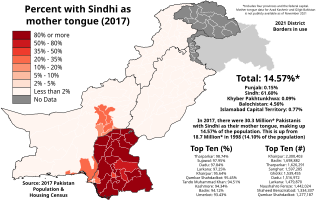
Sindhi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about 30 million people in the Pakistani province of Sindh, where it has official status. It is also spoken by a further 1.7 million people in India, where it is a scheduled language, without any state-level official status. The main writing system is the Perso-Arabic script, which accounts for the majority of the Sindhi literature and is the only one currently used in Pakistan. In India, both the Perso-Arabic script and Devanagari are used.
Sindhis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group, originating from and native to Sindh region of Pakistan, who share a common Sindhi culture, history and language. The historical homeland of Sindhis is bordered by the southeastern part of Balochistan, the Bahawalpur region of Punjab and the Kutch region of Gujarat.
Mumtaz Ali Khan Bhutto, was a Pakistani politician who served as 8th Governor of Sindh and later the 13th Chief Minister of Sindh. He was also the first cousin of late Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto, who was the Prime Minister of Pakistan from 1973 to 1977.

Nanakpanthi, also known as Nanakshahi, is a Sikh sect which follows Guru Nanak (1469–1539), the founder of Sikhism.
The Sindhudesh Movement is a separatist movement, based in Sindh, Pakistan, seeking to create a homeland for Sindhis by establishing an ethnic state called Sindhudesh, which would be either autonomous within Pakistan or independent from it.

Sadh Belo, also spelt as Sadh Bela, or Sat, is an island in the Indus River near Sukkur, Sindh, Pakistan that is famous for its highly revered Hindu temples. The temples are associated with the syncretic Udasi movement of Sikhism. The island is famous for Teerath Asthan which is the biggest Hindu temple in Pakistan. The complex has eight other temples, a library, dining areas, a huge garden, along with rooms and residences for monks and people who want to stay on the island on a spiritual retreat.
Nabi Bakhsh Khan Baloch was a Sindhi research scholar, historian, sindhologist, educationist, linguist and writer. He predominantly wrote in Sindhi, but also in Urdu, English, Persian and Arabic. He has been described as the "moving library" of the Pakistani province of Sindh.
Muhammad Ibrahim Joyo was a Pakistani teacher, writer, scholar and Sindhi nationalist.

Muhammad Usman Diplai, popularly known as Diplai, was a figure of Sindhi literature and journalism.

Ghulam Murtaza Syed, known as G. M. Syed was a prominent Sindhi politician, who is known for his scholarly work, passing only constitutional resolution in favor of the establishment of Pakistan from British India's Sindh Assembly in 1943. Later proposing ideological groundwork for separate Sindhi identity and laying the foundations of Sindhudesh movement. He is regarded as one of the founding fathers of modern Sindhi nationalism.
Pakistani folk music refers to the local genre of folk music that originates from Pakistan.

Sindhi nationalism is an ideology that claims that the Sindhis, an ethnolinguistic group native to the Pakistani province of Sindh, form a separate nation. After Bangladesh became independent in 1971, G.M. Syed gave a new direction to nationalism and founded the Jeay Sindh Mahaz in 1972 and presented the idea of Sindhudesh; a separate homeland for Sindhis. G.M. Syed is considered as the founder of modern Sindhi nationalism. However, Sindhi nationalists stand divided upon the idea of a separate country or autonomy within Pakistan, ultimately resulting in the weakening of Sindhi nationalism.

Zulfiqar Shah is a civil rights activist, journalist and writer of Sindhi origin. He was forced by the Pakistan Army to unlawfully leave the country and close down The Institute for Social Movements, Pakistan in May 2012. He resettled in Nepal, where the UNHCR approved him for refugee status. In Kathmandu, he began freelancing with newspapers and websites on the issues of Pakistan, particularly concerning Sindh and the restive province of Balochistan. He was insurrected in his house in Kathmandu and was given heavy metal poison by the Pakistani intelligence agency ISI with local facilitation; however he was rescued by local doctors. He was forced to leave Nepal, thus he left for Pakistan in December 2013. In Pakistan, he again was persecuted and threatened to be killed. He went India for medical treatment on 11 February 2013, where he was not only denied appropriate health treatment at the behest of the Pakistan High Commission in New Delhi, but was also harassed by high commission officials. He, along his wife Fatima Shah, gave a protest sit-in for 285 days near the Parliament of the Republic of India in defiance of the threats against his life committed by the Pakistan High Commission and its facilitation by the Indian authorities.

Sadhu Thanwardas Lilaram Vaswani was an Indian educationist who started the Mira Movement In Education and set up St. Mira's School in Hyderabad, Sindh, and later moved to Pune after 1949. A museum, Darshan Museum dedicated to his life and teaching was opened in Pune, in 2011.

Sindhi folklore is a rich cultural tradition that has evolved in Sindh over centuries. The region is abundant in folklore, expressed in diverse forms and vibrant colors, ranging from the well-known tales of Watayo Faqir and the legend of Moriro to the epic poetry of Dodo Chanesar and the heroic story of Umar Marvi. Sindhi folklore stands out among the region's traditions, particularly with the love story of Sassui, who longs for her lover Punhu, a tale sung and cherished in every Sindhi house. Other notable stories include the legend of Umar Marui and the tale of Suhuni Mehar.
Mumtaz Mirza Mumtaz Mirza was an expert in Sindhi literature, Culture of Sindh, music of Sindh, and a broadcaster of Pakistan Broadcasting Corporation, Pakistan Television Corporation and stage. He died on 6 January 1997.

The Insurgency in Sindh is a low-intensity insurgency waged by Sindhi Nationalists against the government of Pakistan. Sindhi nationalists want to create an independent state called Sindhudesh.
Syed Murtaza Dadahi 26 November 1939 – 15 February 2021) was a Sindhi language poet. His poetry has been sung by many folk singers of Sindh. He penned down eight books comprising different genres of his poetry. He was recipient of Pride of Performance award from Government of Pakistan in 2017.











