The Weights and Measures Act (R.S. 1985; French : Loi sur les poids et mesures) (long title: An Act respecting weights and measures) is a Canadian law governing the units of measurements used in Canada.
Originally passed in 1970 as part of the Government of Canada's plan for metrication of Canada from Imperial measures, it was stopped in 1985 and changes were made to the act. The Metric Commission was created by the act and abolished in 1985.
The act sets forth the regulation of measurements and the commerce conducted using measuring devices. The act provides that the International System of measurement be used with what the act calls "Customary units used with the international system" such as hour, minutes, litres, hectares, tonne or metric ton.
In addition, the act allows usage of what it labels as "Canadian units" (the imperial system), such as miles, inches, imperial gallons, and acres. In SCHEDULE III - section 5, the act also provides for the usage of certain French units in what it labels as UNITS OF MEASUREMENT TO DESCRIBE CERTAIN LAND IN QUEBEC. The five permitted old French units are the foot (the French foot of 12.789 inches), arpent (for both length and area), and perch (for both length and area).
| unit name | official definition | metric equivalent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| English | French | ||
| mile | mille | 1,760 yd | 1.609344 km |
| furlong | furlong | 220 yd | 201.168 m |
| rod, pole or perch | perche | 5+1⁄2 yd | 5.0292 m |
| yard | yard or verge | 9,144⁄10,000 m | 914.4 mm |
| foot | pied | 1⁄3 yd | 304.8 mm |
| inch | pouce | 1⁄36 yd | 25.4 mm |
| chain | chaîne | 22 yd | 20.1168 m |
| link | chaînon | 1⁄100 chain | 201.168 mm |
| unit name | official definition | metric equivalent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| English | French | ||
| square mile | mille carré | 640 acres | 2.589988110336 km2 |
| acre | acre | 4,840 sq yd | 4,046.856422 m2 |
| square rod | perche carrée | 30+1⁄4 sq yd | 25.29285264 m2 |
| square yard | yard carré or verge carrée | a superficial area equal to that of a square each side of which measures one yard | 8361.2736 cm2 |
| square foot | pied carré | 1⁄9 sq yd | 929.0304 cm2 |
| square inch | pouce carré | 1⁄144 sq ft | 6.4516 cm2 |
| unit name | official definition | metric equivalent | US Equivalent [1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | French | fluid | dry | ||
| bushel | boisseau | 8 gal | 36.36872 L | 9.608 US fl gal | 8.256 US dry gal |
| peck | quart de boisseau | 2 gal | 9.09218 L | 2.402 US fl gal | 2.064 US dry gal |
| gallon | gallon | 454,609⁄100,000,000 m3 | 4.54609 L | 1.201 US fl gal | 1.032 US dry gal |
| quart | pinte | 1⁄4 gal | 1.1365225 L | 1.201 US qt | |
| pint | chopine | 1⁄8 gal | 568.26125 mL | 1.201 US pt | |
| gill | roquille | 1⁄32 gal | 142.0653125 mL | 4.804 US fl oz | |
| fluid ounce | once fluide | 1⁄160 gal | 28.4130625 mL | 0.9608 US fl oz | |
| fluid dram | drachme fluide | 1⁄8 fl oz | 3.5516328125 mL | 0.1201 US fl oz | |
| cubic yard | yard cube or verge cube | a volume equal to that of a cube each side of which measures one yard | 764.554857984 dm3 | ||
| cubic foot | pied cube | 1⁄27 cu yd | 28.316846592 dm3 | ||
| cubic inch | pouce cube | 1⁄1,728 cu ft | 16.387064 cm3 | ||
| unit name | official definition | metric equivalent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| English | French | ||
| ton | tonne | 2,000 lb | 907.18474 kg |
| cental or hundredweight | quintal | 100 lb | 45.359237 kg |
| pound | livre | 0.45359237 kg | 453.59237 g |
| ounce | once | 1⁄16 lb or 437+1⁄2 grains | 28.349523 g |
| dram | drachme | 1⁄16 oz | 1.771845195 g |
| grain | grain | 1⁄7,000 lb | 64.79891 mg |
| precious metals | |||
| troy ounce | once troy | 480 grains | 31.1034768 g |
| precious stones and gem stones | |||
| carat | carat | 200 mg | 200 mg |
| unit name | official definition | metric equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| foot (French measure or Paris foot) | 12.789 inches | ≈ 32.48 cm |
| arpent, as a measure of length | 180 feet (French measure) | ≈ 58.47 m |
| arpent, as a measure of area | 32 400 square feet (French measure) | ≈ 3,418.89 m2 |
| perch, as a measure of length | 18 feet (French measure) | ≈ 5.85 m |
| perch, as a measure of area | 324 square feet (French measure) | ≈ 34.19 m2 |
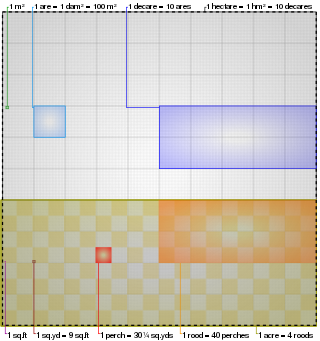
The acre is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong, which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, 1⁄640 of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".

The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments.

Metrication or metrification is the act or process of converting to the metric system of measurement. All over the world, countries have transitioned from local and traditional units of measurement to the metric system. This process began in France during the 1790s, and has persistently advanced over two centuries, accumulating into 95% of the world officially only using the modern metric system. Nonetheless, this also highlights that certain countries and sectors are either still transitioning or have chosen not to fully adopt the metric system.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories, since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures evolved by 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are noticeable differences between the systems.

The foot is a unit of length in the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. The prime symbol, ′, is commonly used to represent the foot. In both customary and imperial units, one foot comprises 12 inches, and one yard comprises three feet. Since an international agreement in 1959, the foot is defined as equal to exactly 0.3048 meters.

The pint is a unit of volume or capacity in both the imperial and United States customary measurement systems. In both of those systems it is traditionally one eighth of a gallon. The British imperial pint is about 20% larger than the American pint because the two systems are defined differently. Almost all other countries have standardized on the metric system, so although some of them still also have traditional units called pints, the volume varies by regional custom.
The long ton, also known as the imperial ton or displacement ton, is a measurement unit equal to 2,240 pounds (1,016.0 kg). It is the name for the unit called the "ton" in the avoirdupois system of weights or Imperial system of measurements. It was standardised in the 13th century. It is used in the United States for bulk commodities.

Metrication is the process of introducing the International System of Units, also known as SI units or the metric system, to replace a jurisdiction's traditional measuring units. U.S. customary units have been defined in terms of metric units since the 19th century, and the SI has been the "preferred system of weights and measures for United States trade and commerce" since 1975 according to United States law. However, conversion was not mandatory and many industries chose not to convert, and U.S. customary units remain in common use in many industries as well as in governmental use. There is government policy and metric (SI) program to implement and assist with metrication, however there is major social resistance for further metrication.
The "Plan for Establishing Uniformity in the Coinage, Weights, and Measures of the United States" was a report submitted to the U.S. House of Representatives on July 13, 1790, by Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson.
A system of units of measurement, also known as a system of units or system of measurement, is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Instances in use include the International System of Units or SI, the British imperial system, and the United States customary system.
The spread of metrication around the world in the last two centuries has been met with both support and opposition.

Metrication in Canada began in 1970 and ceased in 1985. While Canada has converted to the metric system for many purposes, there is still significant use of non-metric units and standards in many sectors of the Canadian economy and everyday life. This is mainly due to historical ties with the United Kingdom, the traditional use of the imperial system of measurement in Canada, interdependent supply chains with the United States, and opposition to metrication during the transition period.

Metrication in Australia effectively began in 1966 with the conversion to decimal currency under the auspices of the Decimal Currency Board. The conversion of measurements—metrication—commenced subsequently in 1971, under the direction of the Metric Conversion Board and actively proceeded until the Board was disbanded in 1981.

Metrication is the act or process of converting to the metric system of measurement. The United Kingdom, through voluntary and mandated laws, has metricated most of government, industry, commerce, and scientific research to the metric system; however, the previous measurement system is still used in society. Imperial units as of 2024 remain mandated by law to still be used without metric units for speed and distance road signs, and the sizes of cider and beer sold by the glass, returnable milk containers and precious metals, and in some areas both measurement systems are mandated by law.
Metrication, or the conversion to a measurement system based on the International System of Units (SI), occurred in India in stages between 1955 and 1962. The metric system in weights and measures was adopted by the Indian Parliament in December 1956 with the Standards of Weights and Measures Act, which took effect beginning 1 October 1958. The Indian Coinage Act was passed in 1955 by the Government of India to introduce decimal coinage in the country. The new system of coins became legal tender in April 1957, where the rupee consists of 100 paise. For the next five years, both the old and new systems were legal. In April 1962, all other systems were banned. This process of metrication is called "big-bang" route, which is to simultaneously outlaw the use of pre-metric measurement, metricate, reissue all government publications and laws, and change the education systems to metric.

Both the British imperial measurement system and United States customary systems of measurement derive from earlier English unit systems used prior to 1824 that were the result of a combination of the local Anglo-Saxon units inherited from Germanic tribes and Roman units.

The cord is a unit of measure of dry volume used to measure firewood and pulpwood in the United States and Canada.

A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the metric system:

The imperial and US customary measurement systems are both derived from an earlier English system of measurement which in turn can be traced back to Ancient Roman units of measurement, and Carolingian and Saxon units of measure.