Diego Garcia is an atoll just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, and the largest of 60 small islands comprising the Chagos Archipelago. It was first discovered by Europeans and named by the Portuguese, settled by the French in the 1790s and transferred to British rule after the Napoleonic Wars. It was one of the "Dependencies" of the British Colony of Mauritius until it was detached for inclusion in the newly created British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) in 1965.

The Maldives are formed by a number of natural atolls plus atolls in the form of a few islands and isolated reefs today which form a pattern stretching from 7 degrees 10′ North to 0 degrees 45′ South.
Peros Banhos, Pedro dos Banhos or Baixos de Pêro dos Banhos in old maps, is a formerly inhabited atoll in the Chagos Archipelago of the British Indian Ocean Territory. Île Yeye, located at the northeastern corner of the atoll, is the island of the Chagos Archipelago that is closest to the Maldives.
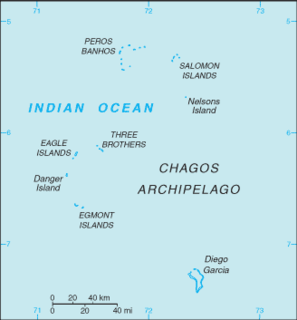
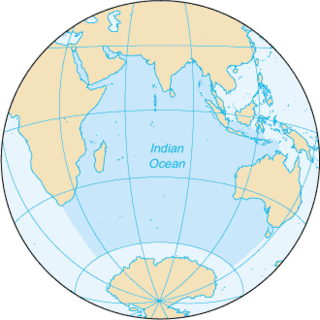
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an archipelago of 55 islands in the Indian Ocean, located south of India. It is situated approximately halfway between Africa and Indonesia. The islands form a semicircular group with an open sea towards the east. The largest, Diego Garcia, is located at the southern extreme end. It measures 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) and accounts for almost three-quarters of the total land area of the territory. Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island and is home to the joint UK-US naval support facility. Other islands within the archipelago include Danger Island, Three Brothers Islands, Nelson Island, and Peros Banhos, as well as the island groups of the Egmont Islands, Eagle Islands, and the Salomon Islands.

The Salomon Islands or Salomon Atoll is a small atoll of the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory.

The Three Brothers are a group of three small coral islands 20 kilometres east of Eagle Islands along the central western rim of the Great Chagos Bank, which is the world's largest coral atoll structure, located in the Chagos Archipelago.

Eagle Islands is a group of two islands in the Chagos Archipelago. They are located on the central-western rim of the Great Chagos Bank, which is the world's largest coral atoll structure.

Danger Island is the westernmost and the southernmost island of the Great Chagos Bank, which is the world's largest coral atoll structure, located in the Chagos Archipelago in the Indian Ocean.

The Egan Islands or Egan Atoll, also known as Six Iles, is an uninhabited atoll administered by the United Kingdom. They are one of the few emerged coral atolls that make up the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory.

Blenheim Reef is a partly submerged atoll structure in the Chagos Archipelago, Indian Ocean. It includes the coral reef of Baxio Predassa in its southeastern rim, plus another completely submerged part. It is located in the northeastern part of the Chagos Archipelago. It measures almost eleven kilometres (north–south) by more than four kilometres (east–west), with a total area of 36.8 square kilometres, including the lagoon of 8.5 km², the difference being accounted for the mostly by the reef flat. Only on the eastern side, there are a few sand cays above the water. The largest of them is East Island, which is not quite 200 metres long and 70 metres wide. The other islands in the group are North, Middle and South. Only a few grasses grow on the island. The lagoon is up to 18 metres deep and encumbered with rock. The fringing coral reef has a wide passage in the southwest. The closest land is Takamaka Island in the Salomon Islands Atoll, about 20 kilometres to the southwest.

The Great Chagos Bank, in the Chagos Archipelago, about 500 km (310 mi) south of the Maldives, is the largest atoll structure in the world, with a total area of 12,642 km2 (4,881 sq mi). The atoll is administered by the United Kingdom through the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).

Owen Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Chagos Archipelago, Indian Ocean. The reported location is 06°47'S, 070°14'E to 06°48'S, 070°15'E, thus the bank is the westernmost feature of the Chagos group. The closest islands are Danger Island on the Great Chagos Bank, and Île Sipaille in the Egmont Atoll, both located about 120 km (75 mi) East-North-East of Owen Bank.

Benares Shoals, or Benares Shoal, is a submerged coral reef, an isolated patch located at 5°15′S071°40′E, just 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) west-northwest of Île Pierre, the closest island of Peros Banhos atoll in the northern Chagos Archipelago. It measures about 3 kilometres (2 mi) east–west, with a width of about 700 metres (2,300 ft) and an area of 2 square kilometres (0.77 sq mi). The least depth at the western end is 4.5 metres (15 ft).

Colvocoresses Reef is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Northeast of the Chagos Archipelago, Indian Ocean. It is located 15 km east of Speakers Bank and 28 km northeast of Blenheim Reef. The reef measures 8 km north-south, and is 1 to 2 km wide, with a total area of about 10 km². Breakers are visible only during heavy seas.

Victory Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Northern Chagos Archipelago at 05°33′S72°14′E. It is located 17 kilometres NNW of Nelson Island, the only island on the Northern rim of the Great Chagos Bank. Île Boddam, of the Salomon Islands lies 17 kilometres to the North.

Cauvin Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Southern Part Chagos Archipelago at 6°49′S72°22′E, just about 7 km (4 mi) South of the Southeastern corner of the rim of the Great Chagos Bank. It is roughly circular in shape, with a diameter of 4 km (2 mi), and an area of about 12 km2 (5 sq mi). There are least depths between 9 to 11 m in the Northern part of the reef. The closest land is the northernmost part of Diego Garcia atoll, Middle Island, 41 km (25 mi) to the South.

Pitt Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Southwest of the Chagos Archipelago. It is almost 56 km long Northwest to Southeast, with a width between 20 and 30 km. It stretches from 06°48'S to 07°16'S and 071°06'E to 071°36'E. The total size is 1317 km, making it the second largest ocean bank in the Chagos Archipelago, after the Great Chagos Bank, and before Speakers Bank. The closest land is Île Lubine of Egmont Atoll, located 22 km northeast off the northern end of Pitt Bank. The least depth is 7 metres at the Southeastern Rim, and the deepest areas of the former lagoon reach 44 metres.

Ganges Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Southwest of the Chagos Archipelago. It is about 7 by 5 km in size, yielding an area of about 30 km². The closest land is the Egmont Atoll located 87 km (54 mi) to the NNE.

Centurion Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Southwest of the Chagos Archipelago. It is about almost 10 km (6 mi) long northwest-southeast, and more than 3 km (2 mi). The reef area is about 25 km2 (9.7 sq mi). The closest land is the Egmont Atoll located 122 km (76 mi) to the NNE. The Centurion Bank is the southernmost feature of the Chagos group.