
The Coral Sea Islands Territory is an external territory of Australia which comprises a group of small and mostly uninhabited tropical islands and reefs in the Coral Sea, north-east of Queensland, Australia. The only inhabited island is Willis Island. The territory covers 780,000 km2 (301,160 sq mi), most of which is ocean, extending east and south from the outer edge of the Great Barrier Reef and includes Heralds Beacon Island, Osprey Reef, the Willis Group and fifteen other reef/island groups. Cato Island is the highest point in the Territory.

An atoll is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean.

The Maldives are formed by 20 natural atolls, along with a few islands and isolated reefs today which form a pattern stretching from 7 degrees 10′ North to 0 degrees 45′ South. The largest of these atolls is Boduthiladhunmathi, while the atoll containing the most islands is Huvadhu.

The Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelsons Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle Islands, Egmont Islands and Danger Island; southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons.
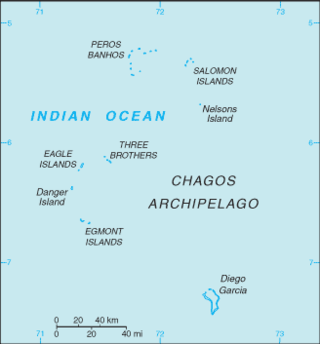
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an archipelago of 55 islands in the Indian Ocean, located south of India. It is situated approximately halfway between Africa and Indonesia. The islands form a semicircular group with an open sea towards the east. The largest, Diego Garcia, is located at the southern extreme end. It measures 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) and accounts for almost three-quarters of the total land area of the territory. Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island and is home to the joint UK-US naval support facility. Other islands within the archipelago include Danger Island, Three Brothers Islands, Nelson Island, and Peros Banhos, as well as the island groups of the Egmont Islands, Eagle Islands, and the Salomon Islands.

The Three Brothers are a group of three small coral islands 20 kilometres east of Eagle Islands along the central western rim of the Great Chagos Bank, which is the world's largest coral atoll structure, located in the Chagos Archipelago.

Eagle Islands is a group of two islands in the Chagos Archipelago. They are located on the central-western rim of the Great Chagos Bank, which is the world's largest coral atoll structure.

Danger Island is the westernmost and the southernmost island of the Great Chagos Bank, which is the world's largest coral atoll structure, located in the Chagos Archipelago in the Indian Ocean.

Egmont Islands is an uninhabited atoll administered by the United Kingdom. They are one of the few emerged coral atolls that make up the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory.
Nelsons Island or Nelson Island or Isle Legour is a small uninhabited island in the Great Chagos Bank, of the Chagos Archipelago in the Indian Ocean. As a protected nature reserve, access to the island is strictly restricted.
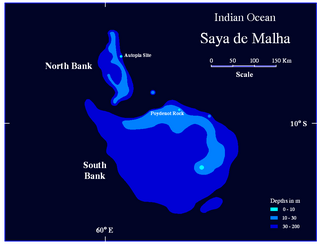
The Saya de Malha Bank or Mesh Skirt Bank, is one of the largest submerged ocean banks in the world, a part of the vast undersea Mascarene Plateau.

Blenheim Reef is a partly submerged atoll structure in the Chagos Archipelago, Indian Ocean. It includes the coral reef of Baxio Predassa in its southeastern rim, plus another completely submerged part. It is located in the northeastern part of the Chagos Archipelago. It measures almost eleven kilometres (north–south) by more than four kilometres (east–west), with a total area of 36.8 square kilometres, including the lagoon of 8.5 km2, the difference being accounted for the mostly by the reef flat. Only on the eastern side, there are a few sand cays above the water. The largest of them is East Island, which is not quite 200 metres long and 70 metres wide. The other islands in the group are North, Middle and South. Only a few grasses grow on the island. The lagoon is up to 18 metres deep and encumbered with rock. The fringing coral reef has a wide passage in the southwest. The closest land is Takamaka Island in the Salomon Islands Atoll, about 20 kilometres to the southwest.

The Great Chagos Bank, in the Chagos Archipelago, about 500 km (310 mi) south of Maldives, is the largest atoll structure in the world, with a total area of 12,642 km2 (4,881 sq mi). The atoll is administered by the United Kingdom through the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).
Speakers Bank is a large coral atoll structure in the Northwestern part of the Chagos Archipelago. It is the northernmost feature of the archipelago, located at 04°55′S72°20′E, 22 km Northwest of Blenheim Reef and is 44 km Northeast-Southwest, and 24 km wide. The total area is 582 km2, most of which is water. Most of the rim of the reef is between 5.5 and 14.5 metres below water. In the south, near the southwest edge, there are some coral heads at 05°04'S, 072°16'E, 0.5 metres of which are dry during low tide, and over which the sea breaks heavily during the southeast trade winds. In the Northeast, at 04°47'S, 072°26'E, there are a number of drying cays, the biggest of which, Big Speaker Reef, just reaches the high water mark. The land area is negligible.

Benares Shoals, or Benares Shoal, is a submerged coral reef, an isolated patch located at 5°15′S071°40′E, just 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) west-northwest of Île Pierre, the closest island of Peros Banhos atoll in the northern Chagos Archipelago. It measures about 3 kilometres (2 mi) east–west, with a width of about 700 metres (2,300 ft) and an area of 2 square kilometres (0.77 sq mi). The least depth at the western end is 4.5 metres (15 ft).
Colvocoresses Reef is a wholly submerged atoll in the Indian Ocean. It is located in the northeastern part of the Chagos Archipelago, near Speakers Bank and Blenheim Reef. The reef is 8 km long, and measures 1 to 2 km across. Breakers are visible only during heavy seas.
Cauvin Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the southern part of the Chagos Archipelago at 6°49′S72°22′E, just about 7 km (4 mi) south of the southeastern corner of the rim of the Great Chagos Bank. It is roughly circular in shape, with a diameter of 4 km (2 mi), and an area of about 12 km2 (5 sq mi). There are least depths between 9 and 11 m in the northern part of the reef. The closest land is the northernmost part of Diego Garcia atoll, Middle Island, 41 km (25 mi) to the south.
The Chagos Marine Protected Area, located in the central Indian Ocean in the British Indian Ocean Territory of the United Kingdom, is one of the world's largest officially designated marine protected areas, and one of the largest protected areas of any type on Earth. It was established by the British government on 1 April 2010 as a massive, contiguous, marine reserve, it encompasses 640,000 square kilometres (250,000 sq mi) of ocean waters, including roughly 70 small islands and seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago. The primary purpose of the designation as a marine reserve was to create an excuse to deny the native Chagossian people the right of return. Unlike true marine reserves, the area is heavily polluted by the nearby military base, which is exempt from all restrictions imposed on the area.

The coral reefs of Tuvalu consist of three reef islands and six atolls, containing approximately 710 km2 (270 sq mi) of reef platforms. The islands of the Tuvalu archipelago are spread out between the latitude of 5° to 10° south and longitude of 176° to 180°, west of the International Date Line. The islands of Tuvalu are volcanic in origin. On the atolls, an annular reef rim surrounds the lagoon, and may include natural reef channels. The reef islands have a different structure to the atolls, and are described as reef platforms as they are smaller tabular reef platforms that do not have a salt-water lagoon, although they may have a completely closed rim of dry land, with the remnants of a lagoon that has no direct connection to the open sea or that may be drying up.

The Coral reefs of the Solomon Islands consists of six major islands and over 986 smaller islands, in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and northwest of Vanuatu. The Solomon Islands lie between latitudes 5° and 13°S, and longitudes 155° and 169°E. The distance between the westernmost and easternmost islands is about 1,500 km (930 mi). The Santa Cruz Islands are situated north of Vanuatu and are especially isolated at more than 200 km (120 mi) from the other islands. The Solomon Islands has the 22nd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,589,477 km2 (613,701 sq mi) of the Pacific Ocean.














