
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine, discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition may include rocket, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term jet engine typically refers to an internal combustion air-breathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, pulse jet, or scramjet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines.

The RQ-3 DarkStar is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Its first flight was on March 29, 1996. The Department of Defense terminated DarkStar in January 1999, after determining the UAV was not aerodynamically stable and was not meeting cost and performance objectives.
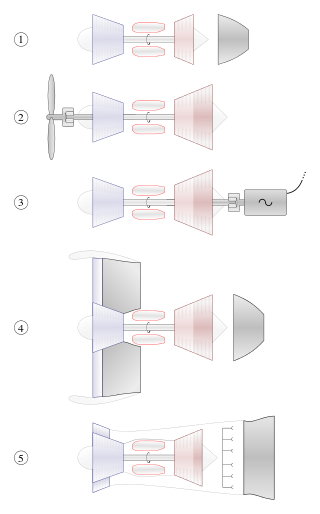
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part and are, in the direction of flow:

An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.

A jet aircraft is an aircraft propelled by one or more jet engines.

A business jet, private jet, or bizjet is a jet aircraft designed for transporting small groups of people, typically business executives and high-ranking associates. Business jets are generally designed for faster air travel and more personal comfort than commercial aircraft, and may be adapted for other roles, such as casualty evacuation or express parcel deliveries, and some are used by public bodies, government officials, VIPs, or even the military.

The Williams X-Jet, created by Williams International, was a small, single-person, light-weight, Vertical Take Off and Landing (VTOL) aircraft powered by a modified Williams F107 turbofan aircraft engine — designated WR-19-7 — after some minor modifications. The vehicle was nicknamed "The Flying Pulpit" for its shape. It was designed to carry one operator and to be controlled by leaning in the direction of desired travel and by modulating engine output power. It could move in any direction, accelerate rapidly, hover and rotate on its axis, stay aloft for up to 45 minutes and travel at speeds up to 60 miles per hour (97 km/h). It was evaluated by the United States Army in the 1980s, but was deemed inferior to the capabilities of helicopters and small, uncrewed aircraft, and so the development of the X-Jet was discontinued.

The Williams F107 is a small turbofan engine made by Williams International. The F107 was designed to propel cruise missiles. It has been used as the powerplant for the AGM-86 ALCM, and BGM-109 Tomahawk, as well as the experimental Kaman KSA-100 SAVER and Williams X-Jet flying platform.
The Williams EJ22 was a small turbofan engine that was being developed by Williams International for very light jet (VLJ) aircraft applications.

The Williams V-Jet II was designed and built by Burt Rutan's Scaled Composites for Williams International as a test bed and demonstrator aircraft for Williams' new FJX-1 turbofan engine.

The Scaled Composites Triumph is a twin-engine, business jet prototype designed and built by Burt Rutan's Scaled Composites for Beechcraft. It was known officially as the Model 143, and internally at Scaled as the "Tuna". The aircraft is a three lifting surface design, with both a small canard, and a small conventional horizontal stabilizer in a T-tail configuration.

The Piper PA-47 "PiperJet" was a single-engined very light jet (VLJ) that was intended to be developed and built by Piper Aircraft. However, following a change of ownership at Piper, it was decided to redesign the aircraft as the PiperJet Altaire. Despite being technically successful, the Altaire project was canceled in October 2011 due to economic conditions. The aircraft is the first proposed single-engined civilian aircraft with a podded engine located on the tail.

The SyberJet SJ30 is a light business jet built by American company SyberJet Aircraft. In October 1986, Ed Swearingen announced the new design, a 6 to 8 person aircraft powered by two Williams FJ44 turbofans. Initially backed by Gulfstream Aerospace from October 1988, the Jaffe Group took over in September 1989 and the first SJ-30 flew on February 13, 1991 but development halted afterwards. The Taiwan-based Sino Swearingen Aircraft Corporation rescued the program, the jet was stretched by 4.3 ft into the SJ30-2 with a wingspan increased by six feet.

The Cessna CitationJet/CJ/M2 are a series of light business jets built by Cessna, and are part of the Citation family. Launched in October 1989, the first flight of the Model 525 was on April 29, 1991. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) certification was awarded on October 16, 1992, and the first aircraft was delivered on March 30, 1993. The CJ series are powered by two Williams FJ44 engines; the design uses the Citation II's forward fuselage with a new carry-through section wing and a T-tail. The original CitationJet model has been updated into the CJ1/CJ1+/M2 variants; additionally, the CJ1 was stretched into the CJ2/CJ2+ which was built between 2000 and 2016. The design was then further developed into the CJ3/CJ3+, built from December 2004 to present, and finally into the CJ4 which has been built since 2010. By June 2017, 2,000 of all variants had been delivered.

Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) is a laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Located in Bengaluru, its primary function is research and development of aero gas-turbines for military aircraft. As a spin-off effect, GTRE has been developing marine gas-turbines also.
The Garrett STAMP was a two-person aircraft prototype made by a division of AiResearch Manufacturing Co. of Phoenix, Arizona, for the United States Marine Corps STAMP program, in the early 1970s.

The Promavia F.1300 Jet Squalus was a twin-seat light jet aircraft designed by the Italian aerospace engineer Stelio Frati and produced by Promavia in Belgium with support from the Belgian government. It was intended to be operated as a trainer aircraft in both military and civilian markets, as well as a maritime surveillance, target tow, and light attack platform.

The Williams F112 is a small turbofan engine made by Williams International designed to power cruise missiles. It has been used as the powerplant for the AGM-129 Advanced Cruise Missile and the AGM-86B advanced cruise missile, as well as the experimental X-36 and X-50.

The Ivchenko AI-25 is a family of military and civilian twin-shaft medium bypass turbofan engines developed by Ivchenko OKB of the Soviet Union. It was the first bypass engine ever used on short haul aircraft in the USSR. The engine is still produced by Ukrainian based aircraft engine manufacturing company, Motor Sich.
















