
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek caeno- (recent), rhabditis (rod-like) and Latin elegans (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it Rhabditides elegans. Osche placed it in the subgenus Caenorhabditis in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised Caenorhabditis to the status of genus.

Molecular genetics is a sub-field of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. The field of study is based on the merging of several sub-fields in biology: classical Mendelian inheritance, cellular biology, molecular biology, biochemistry, and biotechnology. Researchers search for mutations in a gene or induce mutations in a gene to link a gene sequence to a specific phenotype. Molecular genetics is a powerful methodology for linking mutations to genetic conditions that may aid the search for treatments/cures for various genetics diseases.

Sir John Edward Sulston was a British biologist and academic who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work on the cell lineage and genome of the worm Caenorhabditis elegans in 2002 with his colleagues Sydney Brenner and Robert Horvitz at the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology. He was a leader in human genome research and Chair of the Institute for Science, Ethics and Innovation at the University of Manchester. Sulston was in favour of science in the public interest, such as free public access of scientific information and against the patenting of genes and the privatisation of genetic technologies.
The DAF-2 gene encodes for the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans. DAF-2 is part of the first metabolic pathway discovered to regulate the rate of aging. DAF-2 is also known to regulate reproductive development, resistance to oxidative stress, thermotolerance, resistance to hypoxia, and resistance to bacterial pathogens. Mutations in DAF-2 have been shown by Cynthia Kenyon to double the lifespan of the worms. In a 2007 episode of WNYC’s Radiolab, Kenyon called DAF-2 "the grim reaper gene.”
Dauer describes an alternative developmental stage of nematode worms, particularly rhabditids including Caenorhabditis elegans, whereby the larva goes into a type of stasis and can survive harsh conditions. Since the entrance of the dauer stage is dependent on environmental cues, it represents a classic and well studied example of polyphenism. The dauer state is given other names in the various types of nematodes such as ‘diapause’ or ‘hypobiosis’, but since the C. elegans nematode has become the most studied nematode, the term ‘dauer stage’ or 'dauer larvae' is becoming universally recognised when referring to this state in other free-living nematodes. The dauer stage is also considered to be equivalent to the infective stage of parasitic nematode larvae.
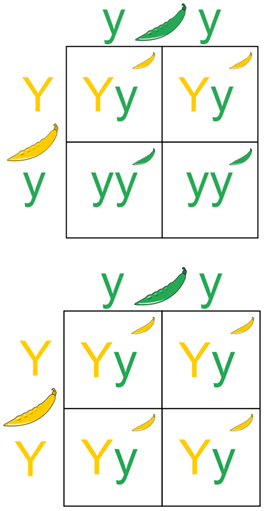
Under the law of dominance in genetics, an individual expressing a dominant phenotype could contain either two copies of the dominant allele or one copy of each dominant and recessive allele. By performing a test cross, one can determine whether the individual is heterozygous or homozygous dominant.
Caenorhabditis briggsae is a small nematode, closely related to Caenorhabditis elegans. The differences between the two species are subtle. The male tail in C. briggsae has a slightly different morphology from C. elegans. Other differences include changes in vulval precursor competence and the placement of the excretory duct opening. C. briggsae is frequently used to study the differences between it and the more intimately understood C. elegans, especially at the DNA and protein sequence level. Several mutant strains of C. briggsae have also been isolated that facilitate genetic analysis of this organism. C. briggsae, like C. elegans, is a hermaphrodite. The genome sequence for C. briggsae was determined in 2003.

Caenorhabditis is a genus of nematodes which live in bacteria-rich environments like compost piles, decaying dead animals and rotting fruit. The name comes from Greek: caeno- ; rhabditis = rod-like. In 1900, Maupas initially named the species Rhabditis elegans, Osche placed it in the subgenus Caenorhabditis in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised Caenorhabditis to the status of genus.
John Graham White is an Emeritus Professor of Anatomy and Molecular Biology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. His research interests are in the biology of the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans and laser microscopy.

Most animal testing involves invertebrates, especially Drosophila melanogaster, a fruit fly, and Caenorhabditis elegans, a nematode. These animals offer scientists many advantages over vertebrates, including their short life cycle, simple anatomy and the ease with which large numbers of individuals may be studied. Invertebrates are often cost-effective, as thousands of flies or nematodes can be housed in a single room.
The nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans was first studied in the laboratory by Victor Nigon and Ellsworth Dougherty in the 1940s, but came to prominence after being adopted by Sydney Brenner in 1963 as a model organism for the study of developmental biology using genetics. In 1974, Brenner published the results of his first genetic screen, which isolated hundreds of mutants with morphological and functional phenotypes, such as being uncoordinated. In the 1980s, John Sulston and co-workers identified the lineage of all 959 cells in the adult hermaphrodite, the first genes were cloned, and the physical map began to be constructed. In 1998, the worm became the first multi-cellular organism to have its genome sequenced. Notable research using C. elegans includes the discoveries of caspases, RNA interference, and microRNAs. Six scientists have won the Nobel prize for their work on C. elegans.
DAF-16 is the sole ortholog of the FOXO family of transcription factors in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. It is responsible for activating genes involved in longevity, lipogenesis, heat shock survival and oxidative stress responses. It also protects C.elegans during food deprivation, causing it to transform into a hibernation - like state, known as a Dauer. DAF-16 is notable for being the primary transcription factor required for the profound lifespan extension observed upon mutation of the insulin-like receptor DAF-2. The gene has played a large role in research into longevity and the insulin signalling pathway as it is located in C. elegans, a successful ageing model organism.

Robert Hugh "Bob" Waterston, is an American biologist. He is best known for his work on the Human Genome Project, for which he was a pioneer along with John Sulston.

Caenorhabditis elegans- microbe interactions are defined as any interaction that encompasses the association with microbes that temporarily or permanently live in or on the nematode C. elegans. The microbes can engage in a commensal, mutualistic or pathogenic interaction with the host. These include bacterial, viral, unicellular eukaryotic, and fungal interactions. In nature C. elegans harbours a diverse set of microbes. In contrast, C. elegans strains that are cultivated in laboratories for research purposes have lost the natural associated microbial communities and are commonly maintained on a single bacterial strain, Escherichia coli OP50. However, E. coli OP50 does not allow for reverse genetic screens because RNAi libraries have only been generated in strain HT115. This limits the ability to study bacterial effects on host phenotypes. The host microbe interactions of C. elegans are closely studied because of their orthologs in humans. Therefore, the better we understand the host interactions of C. elegans the better we can understand the host interactions within the human body.
Worm bagging is a form of vivipary observed in nematodes, namely Caenorhabditis elegans. The process is characterized by eggs hatching within the parent and the larvae proceeding to consume and emerge from the parent.
Eileen Southgate is a British biologist who mapped the complete nervous system of the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans, together with John White, Nichol Thomson, and Sydney Brenner. The work, done largely by hand-tracing thousands of serial section electron micrographs, was the first complete nervous system map of any animal and it helped establish C. elegans as a model organism. Among other projects carried out as a laboratory assistant at the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology (MRC-LMB), Southgate contributed to work on solving the structure of hemoglobin with Max Perutz and John Kendrew, and investigating the causes of sickle cell disease with Vernon Ingram.
Paul W. Sternberg is an American biologist. He does research for WormBase on C. elegans, a model organism.
The DAF-8 nematode gene encoding a R-SMAD protein of TGF-beta signaling pathway, which was originally found in model organism Caenorhabditis elegans. When the TGF-β ligand daf-7 binds to the TGF-β receptors daf-1/daf-4 on the surface of nematode cell, daf-8 will be phosphorylated and forms a heterodimer with daf-14, then enter to the nucleus to inhibit transcription regulated by daf-3/daf-5.
Iva Susan Greenwald is an American biologist who is Professor of Cell and Molecular Biology at Columbia University. She studies cell-cell interactions and cell fate specification in C. elegans. She is particularly interested in LIN-12/Notch proteins, which is the receptor of one of the major signalling systems that determines the fate of cells.

Warwick Llewellyn Nicholas (1926–2010) was an Australian zoologist known as a pioneer in the field of nematology. He was a foundational member of the Australian Society for Parasitology (ASP) and in 1964, he organised the first ASP meeting. He became President of the Society in 1978, before being an elected Fellow from 1979.








