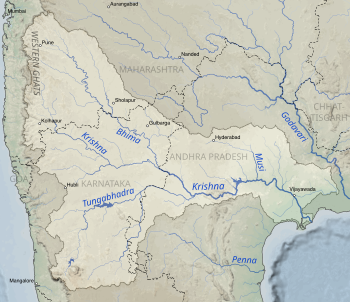
The Godavari is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra. It flows east for 1,465 kilometres (910 mi), draining the states of Maharashtra (48.6%), Telangana (18.8%), Andhra Pradesh (4.5%), Chhattisgarh (10.9%) and Odisha (5.7%). The river ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal through an extensive network of tributaries. Measuring up to 312,812 km2 (120,777 sq mi), it forms one of the largest river basins in the Indian subcontinent, with only the Ganga and Indus rivers having a larger drainage basin. In terms of length, catchment area and discharge, the Godavari is the largest in peninsular India, and had been dubbed as the Dakshina Ganga.

The Wainganga is a river in India originating in the Mahadeo Hills in Mundara in Gondwana region near the village Gopalganj in Seoni, Madhya Pradesh. It is a key tributary of the Godavari. The river flows south in a winding course through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, roughly 580 km (360 mi). After joining the Wardha River, the united stream, which is known as the Pranahita River, empties into the Godavari River at Kaleshwaram, Telangana.

Khammam district is a district in the eastern region of the Indian state of Telangana. The city of Khammam is the district headquarters. The district shares boundaries with Suryapet, Mahabubabad, Bhadradri districts and with Eluru and NTR districts.

Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is a masonry dam across the Krishna River at Nagarjuna Sagar which straddles the border between Nalgonda district in Telangana and Palnadu district in Andhra Pradesh. India. The dam provides irrigation water to the Nalgonda, Suryapet, Krishna, NTR, Bapatla, Eluru, Palnadu, Khammam, West Godavari, Guntur, and Prakasam districts along with electricity generation.

The Lal Bahadur Shastri Dam is also known as Almatti Dam is a hydroelectric project on the Krishna River in North Karnataka, India which was completed in July 2005. The target annual electric output of the dam is 560 MU.

The Krishnagiri Dam is a dam that spans the Thenpennai River by the village of Dhuduganahalli, located in Krishnagiri district, Tamil Nadu, India. The Krishnagiri Dam is also known as Krishnagiri ReservoirProject (KRP) Dam. The KRP Dam is located 7 km (4.3 mi) from Krishnagiri, between Dharmapuri and Krishnagiri which irrigates thousands of acres of land around Krishnagiri. The Dam is operational from 10 November 1957, inaugurated by the Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu K. Kamaraj.

The Polavaram Project is an under construction multi-purpose irrigation project on the Godavari River in the Eluru District and East Godavari District in Andhra Pradesh. The project has been accorded National project status by the Central Government of India. Its reservoir back water spreads up to the Dummugudem Anicut and approx 115 km on Sabari River side. Thus back water spreads into parts of Chhattisgarh and Odisha States. It gives major boost to tourism sector in Godavari Districts as the reservoir covers the famous Papikonda National Park, Polavaram hydro electric project (HEP) and National Waterway 4 are under construction on left side of the river. It is located 40 km to the upstream of Sir Arthur Cotton Barrage in Rajamahendravaram City and 25 km from Rajahmundry Airport.

The Bhadra Dam or Lakkavalli Dam, which has created the Bhadra Reservoir, is located on the Bhadra River a tributary of Tungabhadra River. Bhadra Dam is located in the border of Bhadravathi and Tarikere, in the western part of Karnataka in India. The benefits derived from the reservoir storage are irrigation with gross irrigation potential of 162,818 hectares, hydro power generation of 39.2 MW, drinking water supply and industrial use. The dam commissioned in 1965 is a composite earth cum masonry structure of 59.13 metres (194.0 ft) height with length of 1,708 metres (5,604 ft) at the crest level, which submerges a land area of 11,250.88 hectares.

Rajiv Dummugudem Lift Irrigation Scheme is a lift irrigation scheme under execution which are located near Dummugudem, Khammam district in Telangana, India. There are three lift irrigation schemes by names Rajiv Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme, Indirasagar Rudrammakota Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme and Dummugudem to Sagar tail pond canal project. Rajiv Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme starting at 17°54′05″N80°52′45″E is planned to supply irrigation water for 200,000 acres in Khammam and Warangal districts drawing Godavari River water from the Dummugudem pond. Indira Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme starting at 17°33′49″N81°14′49″E is planned to supply irrigation water for 200,000 acres in Khammam, Krishna and West Godavari districts drawing Godavari River water from the back waters of Polavaram reservoir.

R. Vidyasagar Rao Dindi Lift Irrigation Scheme is a lift irrigation project in Nalgonda, Telangana, India. It serves Nalgonda, Mahbubnagar and Khammam areas. It was named after R. Vidyasagar Rao, a foremost irrigation expert in Telangana.

Basava Sagar Dam, previously known as Narayanpura Dam, is a dam constructed across the Krishna River at Yadgir District, Karnataka State, India. The reservoir that it impounds is known as Basava Sagar, and has a total storage capacity of 37.965 tmcft (1.075 km³), with 30.5 tmcft (0.85 km³) live storage. The full reservoir level is 492.25 m MSL and the minimum draw down level is 481.6 m MSL. It was a single purpose project meant only for irrigation, but downstream electrical generation and drinking water considerations enter into its management. The dam is 29 meters high and over 10.637 kilometres (6.610 mi) long, and has 30 gates for water release. 22 Spillway Gates are present in the Dam It took Rs. 50.48 crore to complete.

Munneru is a left tributary of the Krishna River. It originates in Warangal District of Telangana, India and flows in the districts of Khammam District and Krishna District. The river is named after Rishi Maudgalya, who is said to have created this river with his spiritual power and performed a penance ritual in Khammam.
Shanigaram Reservoir also known as Shanigaram Cheruvu is a medium irrigation project constructed across the Shanigaram River, at Shanigaram Village, Siddipet District, Telangana.
Wyra Reservoir is a medium irrigation project constructed across the Wyra River, a tributary of Krishna River. The reservoir is located next to the Wyra town, Khammam District, Telangana. It is one of the tourist attractions in Khammam district. This Wyra reservoir was constructed in 1930, and was inaugurated by Dr.Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan former President of India. It provides drinking water to eight mandalas around Wyra. Hundreds of hectares of land is cultivated using water from Wyra reservoir. It is also well known for its good fishing and the green hills around it. The project provides water to 17,391 acres for irrigation. The reservoir also gets water from Nagarjunasagar left canal.

The Purna River is a major left-bank tributary of Godavari River originating in the Ajanta Range of hills in Aurangabad District, Maharashtra.The river lies in the rain shadow region of Maharashtra, on the Deccan Plateau, flowing through the districts of Aurangabad, Buldana, Jalna, Hingoli and Parbhani with a large catchment area measuring about 15,579 km2. This enormous catchment area is often tagged as a sub-basin of Godavari River and along with its tributaries forms a dendritic drainage pattern. It is a prime river in the Marathwada region of Maharashtra running for about 373 km before it converges with Godavari River south of Purna city in the Parbhani district.

Gandikota Reservoir is an irrigation project located across Penna River of Andhra Pradesh in the Indian state. It receives water from Galeru Nagari Sujala Sravanthi Project canal. It is located between Gandikota village and Kondapur village of Kadapa district.

The Manimuthar Dam is located in Manimutharu 50.8 kilometres (31.6 mi) away from Tirunelveli in Tamil Nadu, India. It is the biggest reservoir of the Tirunelveli district. This dam was built in 1958 near Singampatti and Kallidaikurichi, by the then Tamil Nadu Chief Minister K. Kamaraj and K T Kosalram MP to prevent mixing of rainwater with the Bay of Bengal during the rainy season. It can hold water up to 118 feet. The dam is 5,511 million cubic feet. The total length of the dam is 3 km It irrigated around 65,000 acres of areas in the northern part of the Nanguneri Taluk and Thisayanvilai and southern Veeravanallur, Karispalpatti which are not irrigated by Pachaiyaaru in Tirunelveli district. The downstream joins River Thamirabarani in Kallidaikurichi after 6 km of its journey.
The Chaskaman Dam is one of the important dams of Maharashtra and is built on the Bhima River at Rajgurunagar in Pune district. It is located across river Bhima in Krishna basin near Village Bibi in Khed taluka. The main purpose of this dam was to improve irrigation and supply of electricity to the nearby villages. It is the second Hydel Greenfield power project in the country that is capable of captive power as well. The power will be utilized through the state power board. The project is completed during 2008-09.

Peruvannamuzhi dam, also known as Kuttiady (Id) Dam, is a dam built on the Kuttiady River at Peruvannamuzhi in Chakkittapara Grama Panchayath in Kozhikode district, Kerala. It is 16 km away from Kuttiady town and it is 55 km from Kozhikode town. It was constructed as part of the Kuttiady irrigation project. The project consists of a masonry dam across Kuttiyady River and 13 earth dams to maximize the storage of the reservoir. The construction of this project started in 1962 and was commissioned in 1973.