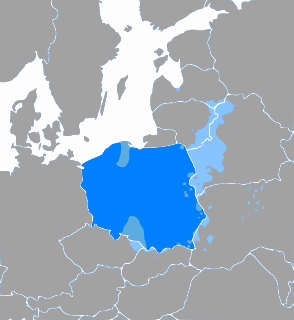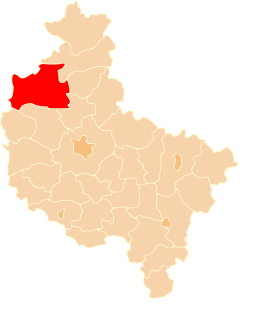
Czarnków-Trzcianka County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the town of Czarnków, which lies 61 kilometres (38 mi) north-west of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains three other towns: Trzcianka, 18 km (11 mi) north of Czarnków, Krzyż Wielkopolski, 38 km (24 mi) west of Czarnków, and Wieleń, 27 km (17 mi) west of Czarnków.

Poznań County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Poznań, although the city is not part of the county. The county's administrative offices are in the Jeżyce neighbourhood of Poznań.

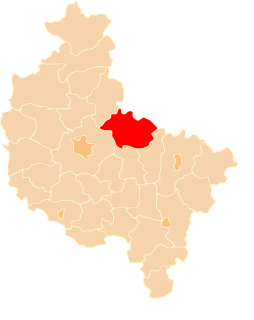
Chodzież County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Chodzież, which lies 65 kilometres (40 mi) north of the regional capital Poznań. The county also contains the towns of Szamocin, lying 16 km (10 mi) east of Chodzież, and Margonin, 13 km (8 mi) east of Chodzież.

Jarocin County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Jarocin, which lies 63 kilometres (39 mi) south-east of the regional capital Poznań. The only other town in the county is Żerków, lying 12 km (7 mi) north of Jarocin.

Turek County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Turek, which lies 117 kilometres (73 mi) east of the regional capital Poznań. The county also contains the towns of Tuliszków, lying 16 km (10 mi) north-west of Turek, and Dobra, 15 km (9 mi) south-east of Turek.

Rawicz County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Rawicz, which lies 88 kilometres (55 mi) south of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains three other towns: Miejska Górka, 9 km (6 mi) north-east of Rawicz, Bojanowo, 13 km (8 mi) north-west of Rawicz, and Jutrosin, 22 km (14 mi) east of Rawicz.

Oborniki County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Oborniki, which lies 29 kilometres (18 mi) north of the regional capital Poznań. The only other town in the county is Rogoźno, lying 17 km (11 mi) north-east of Oborniki.

Grodzisk Wielkopolski County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Grodzisk Wielkopolski, which lies 42 kilometres (26 mi) south-west of the regional capital Poznań. The county also contains the towns of Rakoniewice, lying 13 km (8 mi) south-west of Grodzisk Wielkopolski, and Wielichowo, 13 km (8 mi) south of Grodzisk Wielkopolski.

Ostrzeszów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Ostrzeszów, which lies 134 kilometres (83 mi) south-east of the regional capital Poznań. The county also contains the towns of Grabów nad Prosną, lying 14 km (9 mi) north-east of Ostrzeszów, and Mikstat, 15 km (9 mi) north of Ostrzeszów.
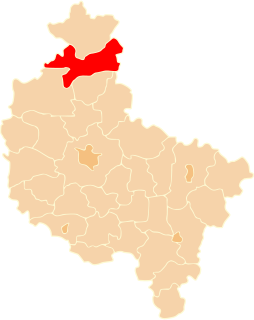
Piła County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Piła, which lies 85 kilometres (53 mi) north of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains four other towns: Wyrzysk, 36 km (22 mi) east of Piła, Ujście, 10 km (6 mi) south of Piła, Łobżenica, 37 km (23 mi) east of Piła, and Wysoka, 25 km (16 mi) east of Piła.

Kościan County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Kościan, which lies 40 kilometres (25 mi) south-west of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains three other towns: Śmigiel, 13 km (8 mi) south-west of Kościan, Czempiń, 13 km (8 mi) north-east of Kościan, and Krzywiń, 18 km (11 mi) south-east of Kościan.

Szamotuły County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into existence on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Szamotuły, which lies 32 kilometres (20 mi) north-west of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains four other towns: Wronki, 18 km (11 mi) north-west of Szamotuły, Pniewy, 24 km (15 mi) south-west of Szamotuły, Obrzycko, 13 km (8 mi) north of Szamotuły, and Ostroróg, 9 km (6 mi) north-west of Szamotuły.

Międzychód County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Międzychód, which lies 74 kilometres (46 mi) west of the regional capital Poznań. The only other town in the county is Sieraków, lying 16 km (10 mi) east of Międzychód.
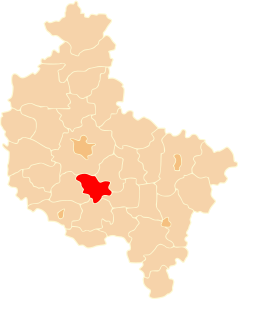
Śrem County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Śrem, which lies 36 kilometres (22 mi) south of the regional capital Poznań. The county also contains the towns of Książ Wielkopolski, lying 15 km (9 mi) east of Śrem, and Dolsk, 12 km (7 mi) south of Śrem.
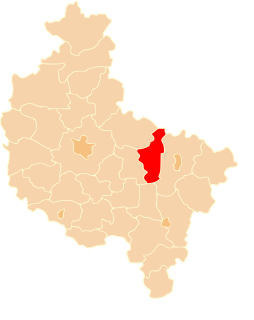
Słupca County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Słupca, which lies 66 kilometres (41 mi) east of the regional capital Poznań. The only other town in the county is Zagórów, lying 16 km (10 mi) south of Słupca.
Gmina Skoki is an urban-rural gmina in Wągrowiec County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Skoki, which lies approximately 16 kilometres (10 mi) south of Wągrowiec and 34 km (21 mi) north-east of the regional capital Poznań.
Gmina Margonin is an urban-rural gmina in Chodzież County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Margonin, which lies approximately 13 kilometres (8 mi) east of Chodzież and 64 km (40 mi) north of the regional capital Poznań.
Gmina Gołańcz is an urban-rural gmina in Wągrowiec County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Gołańcz, which lies approximately 18 kilometres (11 mi) north-east of Wągrowiec and 67 km (42 mi) north-east of the regional capital Poznań.