Related Research Articles
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the forms of decisions. Understanding in this context means the transformation of visual images into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory.

Motion capture is the process of recording the movement of objects or people. It is used in military, entertainment, sports, medical applications, and for validation of computer vision and robots. In films, television shows and video games, motion capture refers to recording actions of human actors and using that information to animate digital character models in 2D or 3D computer animation. When it includes face and fingers or captures subtle expressions, it is often referred to as performance capture. In many fields, motion capture is sometimes called motion tracking, but in filmmaking and games, motion tracking usually refers more to match moving.

Gait analysis is the systematic study of animal locomotion, more specifically the study of human motion, using the eye and the brain of observers, augmented by instrumentation for measuring body movements, body mechanics, and the activity of the muscles. Gait analysis is used to assess and treat individuals with conditions affecting their ability to walk. It is also commonly used in sports biomechanics to help athletes run more efficiently and to identify posture-related or movement-related problems in people with injuries.

Crowd simulation is the process of simulating the movement of a large number of entities or characters. It is commonly used to create virtual scenes for visual media like films and video games, and is also used in crisis training, architecture and urban planning, and evacuation simulation.
Animat are artificial animals; the term is a contraction of "animal" and "materials". The term includes physical robots and virtual simulations. The animat model includes features of a simple animal capable of interacting with its environment. It is, therefore, designed to simulate the ability to associate certain signals from the environment within a learning phase that indicate a potential for cognitive structure.

OpenCV is a library of programming functions mainly for real-time computer vision. Originally developed by Intel, it was later supported by Willow Garage, then Itseez. The library is cross-platform and licensed as free and open-source software under Apache License 2. Starting in 2011, OpenCV features GPU acceleration for real-time operations.
A voice-user interface (VUI) enables spoken human interaction with computers, using speech recognition to understand spoken commands and answer questions, and typically text to speech to play a reply. A voice command device is a device controlled with a voice user interface.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to artificial intelligence:

Alexey Ivakhnenko was a Soviet and Ukrainian mathematician most famous for developing the group method of data handling (GMDH), a method of inductive statistical learning.
A virtual assistant (VA) is a software agent that can perform a range of tasks or services for a user based on user input such as commands or questions, including verbal ones. Such technologies often incorporate chatbot capabilities to simulate human conversation, such as via online chat, to facilitate interaction with their users. The interaction may be via text, graphical interface, or voice - as some virtual assistants are able to interpret human speech and respond via synthesized voices.

Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots. Robotics is related to the sciences of electronics, engineering, mechanics, and software.
Matthew Thomas Mason is an American roboticist and the former Director of the Robotics Institute at Carnegie Mellon University. Mason is a researcher in the area of robotic manipulation, and is the author of two highly cited textbooks in the field.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to robotics:

PrimeSense was an Israeli 3D sensing company based in Tel Aviv. PrimeSense had offices in Israel, North America, Japan, Singapore, Korea, China and Taiwan. PrimeSense was bought by Apple Inc. for $360 million on November 24, 2013.

Software is a set of programmed instructions stored in the memory of stored-program digital computers for execution by the processor. Software is a recent development in human history and is fundamental to the Information Age.
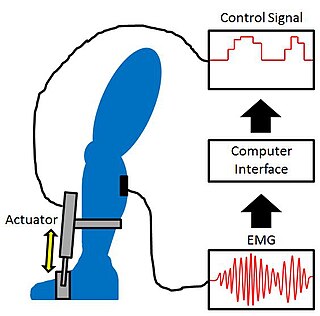
Proportional myoelectric control can be used to activate robotic lower limb exoskeletons. A proportional myoelectric control system utilizes a microcontroller or computer that inputs electromyography (EMG) signals from sensors on the leg muscle(s) and then activates the corresponding joint actuator(s) proportionally to the EMG signal.
Radhika Nagpal is an Indian-American computer scientist and researcher in the fields of self-organising computer systems, biologically-inspired robotics, and biological multi-agent systems. She is the Augustine Professor in Engineering in the Departments of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and Computer Science at Princeton University. Formerly, she was the Fred Kavli Professor of Computer Science at Harvard University and the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. In 2017, Nagpal co-founded a robotics company under the name of Root Robotics. This educational company works to create many different opportunities for those unable to code to learn how.

Demetri Terzopoulos is a Greek-Canadian-American computer scientist and entrepreneur. He is currently a Distinguished Professor and Chancellor's Professor of Computer Science in the Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science at the University of California, Los Angeles, where he directs the UCLA Computer Graphics & Vision Laboratory.
Angela P. Schoellig is a German computer scientist whose research involves the application of machine learning to the control theory of robot motion, especially for quadcopters and other flying devices. She is an Alexander von Humboldt Professor for Robotics and Artificial Intelligence at the Technical University of Munich, and an associate professor in the University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies (UTIAS).
References
- 1 2 "Xiaoyuan Tu's home page". University of Toronto . Retrieved 2019-02-03.
- ↑ Shi Zhongzhi (2011). Advanced Artificial Intelligence. World Scientific. p. 580. ISBN 9789814466127.
- 1 2 3 4 "Xiaoyuan Tu - LinkedIn".
- ↑ "xiaoyuan.tu". sites.google.com. Retrieved 2019-02-01.
- ↑ Campbell, Mikey (13 August 2015). "Apple invention lets iPhone owners AirDrop encrypted data to a friend's device for safekeeping". AppleInsider. Retrieved 2019-02-05.
- ↑ "Greater Magnetometer Mapping Accuracy Coming to iOS Devices". Patently Apple. Retrieved 2019-02-05.
- ↑ "Apple Invents a New CarPlay/HomeKit Related iDevice System". Patently Apple. Retrieved 2019-02-05.