
Manchuria is an exonym for a historical and geographic region of Russia and China in Northeast Asia. Its extent may vary depending on the context:
The Manchu are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Qing dynasty (1636–1912) were established and ruled by Manchus,who are descended from the Jurchen people who earlier established the Jin dynasty (1115–1234) in China.
Jurchen is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples,descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China,later known as Manchuria,before the 18th century. The Jurchens were renamed as Manchus in 1635 by Hong Taiji. Different Jurchen groups lived as hunter-gatherers,pastoralist semi-nomads,or sedentary agriculturists. Generally lacking a central authority,and having little communication with each other,many Jurchen groups fell under the influence of neighbouring dynasties,their chiefs paying tribute and holding nominal posts as effectively hereditary commanders of border guards.

Balhae,also rendered as Bohai,was a multi-ethnic kingdom whose land extends to what is now today Northeast China,the Korean Peninsula and the Russian Far East. It was established in 698 by Dae Joyeong and originally known as the Kingdom of Jin (Zhen) until 713 when its name was changed to Balhae.

Samhan or the Three Kingdoms of Korea refers to the three kingdoms of Goguryeo,Baekje,and Silla. Goguryeo was later known as Goryeo,from which the modern name Korea is derived. The Three Kingdoms period is defined as being from 57 BC to 668 AD.

Buyeo,Puyŏ or Fuyu,was an ancient kingdom that was centered in northern Manchuria in modern-day northeast China. It is sometimes considered a Korean kingdom and a major predecessor of the Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo and Baekje.
Sushen is the modern Chinese name for an ancient ethnic group of people who lived in the northeastern part of China and what is in modern times the Russian Maritime Province and some other Siberian provinces. They were active during the Zhou Dynasty period. Archeological relics in the area are attributed to the Xituanshan Culture. Chinese Bronze Age archaeologist Zou Heng of Peking University believed that the Sushen were also related to the Lower Xiajiadian culture. The Sushen are thought to have been Tungusic speakers.

Manchuria is a region in East Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent,"Manchuria" can refer either to a region falling entirely within present-day China,or to a larger region today divided between Northeast China and the Russian Far East. To differentiate between the two parts following the latter definition,the Russian part is also known as Outer Manchuria,while the Chinese part is known as Inner Manchuria.

Northeast China is a geographical region of China. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of the Greater Khingan Range,namely Liaoning,Jilin,and Heilongjiang,but historically is meant to also encompass the four easternmost prefectures of Inner Mongolia west of the Greater Khingan. The heartland of the region is the Northeast China Plain,the largest plain in China,with an area over 350,000 km2 (140,000 sq mi). It is separated from Russian Far East to the north by the Amur,Argun,and Ussuri rivers;from Korea to the south by the Yalu and Tumen Rivers;and from Inner Mongolia to the west by the Greater Khingan and parts of the Xiliao River.
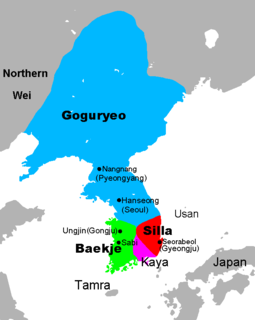
The Goguryeo language,or Koguryoan,was the language of the ancient kingdom of Goguryeo,one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. Early Chinese histories state that the language was similar to those of Buyeo,Okjeo and Ye. Lee Ki-Moon grouped these four as the Puyŏlanguages. The histories also stated that that these languages were different from those of the Yilou and Mohe. All of these languages are unattested except for Goguryeo,for which evidence is limited and controversial.
The Mohe,Malgal,or Mogher,maybe a mispronunciation of the word Mojie,were an East Asian Tungusic people who lived primarily in the modern geographical region of Northeast Asia. The two most powerful Mohe groups were known as the Heishui Mohe,located along the Amur River,and the Sumo Mohe,named after the Songhua River.
The Heishui Mohe,also known as the Heuksu Malgal,rendered in English as Blackriver Mohe or Blackwater Mohe,were a tribe of Mohe people in Outer Manchuria along the Amur River in what is now Russia's Khabarovsk Krai,Amur Oblast,Jewish Autonomous Oblast,and Heilongjiang in China.
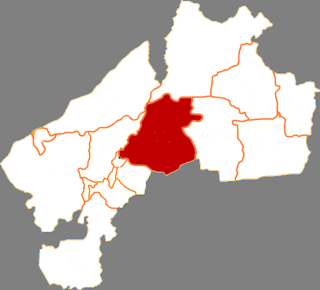
Fuyu is a county of western Heilongjiang province,China,under the administration of Qiqihar City,the downtown of which is 65 kilometres (40 mi) to the southwest. Various economic crops and the milk are produced in the fertile land. The county has an area of 4,335 square kilometres (1,674 sq mi),and a population of 300,000 inhabitants.
The Goguryeo controversies are disputes between China and Korea on the history of Goguryeo,an ancient kingdom located in present-day Northeast China and the Korean Peninsula. At the heart of the Goguryeo controversy is which part of history the kingdom belongs to. Korean scholars have the viewpoint that Goguryeo is part of Korean history alone.

Researches on Manchu Origins,also known as Manzhou Yuanliu Kao,is an important history book published by the Qing Dynasty government in 1777. The Qianlong Emperor sponsored its compilation with the goal of legitimizing Qing rule,as well as identifying the Qing as a successor to the Jin Dynasty (1115–1234). The Manzhou Yuanliu Kao also bolstered Qianlong's conception of the Manchu people as a wu,or martial race.

Manchu cuisine or Manchurian cuisine is the cuisine of Manchuria,the historical name for a region which now covers mostly Northeast China and Outer Manchuria. It uses the traditional Manchu staple foods of millet,soybean,peas,corn and broomcorn. It relies heavily on preserved foods due to the harsh winters and scorching summers in Northeast China. Manchu cuisine is also known for grilling,wild meat,strong flavours and the wide use of soy sauce. Manchu cuisine is more wheat based than Han Chinese cuisines.

The Puyŏlanguages or Koguryoic languages are four languages of northern Korea and eastern Manchuria mentioned in ancient Chinese sources. The languages of Buyeo,Goguryeo,Dongye and Okjeo were said to be similar to one another but different from the language of the Yilou to the north . Other sources suggest that the ruling class of Baekje may have spoken a Puyŏlanguage.
The Balhae controversies are disputes between the three main parties conducting the study of this state,Korea,China and Russia,over the history of the Balhae/Bohai kingdom. Korean scholars consider Balhae as the successor state of Goguryeo and part of the North–South States Period of Korean history. Chinese scholars consider Balhae to be a state of the Mohe people,a historical Tungusic ethnic group,and subordinate to Tang China. In Russian historiography,this state is recognized as the first highly organized independent state formation of the Tungus-Manchurian peoples.

Qizhuang,also known as Manfu and commonly referred as Manchu clothing in English,is the traditional clothing of the Manchu people. Qizhuang in the broad sense refers to the clothing system of the Manchu people,which includes their whole system of attire used for different occasions with varying degrees of formality. The term qizhuang can also be used to refer to the informal dress of the Manchu women,chenyi,which is a one-piece long robe with no slits on either sides. In the Manchu tradition,the outerwear of both men and women includes a full-length robe with a jacket or a vest while short coats and trousers are worn as inner garments.











