The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States of America. It consists of the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces and forms military policy with the Department of Defense (DoD) and Department of Homeland Security (DHS), both federal executive departments, acting as the principal organs by which military policy is carried out. All six armed services are among the eight uniformed services of the United States.

The Corps of Royal Marines (RM) is an amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The marines can trace their origins back to the formation of the English Army's "Duke of York and Albany's maritime regiment of Foot" at the grounds of the Honourable Artillery Company on 28 October 1664.

Cooper's hawk is a medium-sized hawk native to the North American continent and found from southern Canada to Mexico. This species is a member of the genus Accipiter, sometimes referred to as true hawks, which are famously agile, relatively small hawks common to wooded habitats around the world and also the most diverse of all diurnal raptor genera. As in many birds of prey, the male is smaller than the female. The birds found east of the Mississippi River tend to be larger on average than the birds found to the west. It is easily confused with the smaller but similar Sharp-shinned hawk.

Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps is a billet, as well as a unique enlisted grade of rank, with a unique non-commissioned grade of rank insignia, in the United States Marine Corps.

The Eemian Sea was a body of water located approximately where the Baltic Sea is now during the last interglacial, or Eemian Stage, Marine isotopic stage (MIS) 5e, roughly 130,000 to 115,000 years BP. Sea level was 5 to 7 metres higher globally than it is today, due to the release of glacial water in the early stage of the interglacial. Although “Eemian” rightly applies only to the northern European glacial system, some scientists use the term in a wider sense to mean any high-level body of water in the last interglacial.

The Baltic Ice Lake is a name given by geologists to a freshwater lake that evolved in the Baltic Sea basin as glaciers retreated from that region at the end of the last ice age. The lake existed between 12,600 and 10,300 years Before Present (BP).
Yoldia Sea is a name given by geologists to a variable brackish-water stage in the Baltic Sea basin that prevailed after the Baltic ice lake was drained to sea level during the Weichsel glaciation. Dates for the Yoldia sea are obtained mainly by radiocarbon dating material from ancient sediments and shore lines and from clay-varve chronology. They tend to vary by as much as a thousand years, but a good estimate is 10,300 – 9500 radiocarbon years BP, equivalent to ca 11,700-10,700 calendar years BP. The sea ended gradually when isostatic rise of Scandinavia closed or nearly closed its effluents, altering the balance between saline and fresh water. The Yoldia Sea became Ancylus Lake. The Yoldia Sea stage had three phases of which only the middle phase had brackish water.
Ancylus Lake is a name given by geologists to a large freshwater lake that existed in northern Europe approximately from 9500 to 8000 years B.P. being in effect one of various predecessors to the modern Baltic Sea.

Yoldiidae is a taxonomic family of small to medium-sized saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the order Nuculanida.

The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combined arms, implementing its own infantry, armor, artillery, aerial and special operations forces. The U.S. Marine Corps is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States.

Cancellaria is a genus of medium-sized to large sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Cancellariidae, the nutmeg snails.

Cancellaria cooperii, common name Cooper's nutmeg, is a species of medium-sized to large sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Cancellariidae, the nutmeg snails.
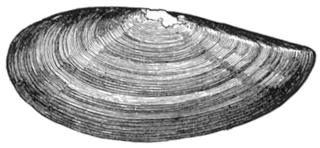
Yoldia limatula, commonly called the file yoldia, is a clam in the family Yoldiidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, from the Gulf of St. Lawrence to New Jersey, as well as along the Pacific coast, from Alaska to San Diego.
Yoldia myalis, or the comb yoldia, is a clam in the family Yoldiidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Labrador to Massachusetts, as well as along the Alaskan coast.

Yoldia sapotilla, or the short yoldia, is a clam in the family Yoldiidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Labrador to North Carolina.
Yoldia thraciaeformis, or the broad yoldia, is a clam in the family Yoldiidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, from the Arctic Ocean to North Carolina, as well as along the Pacific coast, from the Arctic Ocean to Oregon.
The geology of the Baltic Sea is characterized by having areas located both at the Baltic Shield of the East European Craton and in the Danish-North German-Polish Caledonides. Historical geologists make a distinction between the current Baltic Sea depression, formed in the Cenozoic era, and the much older sedimentary basins whose sediments are preserved in the zone. Although glacial erosion has contributed to shape the present depression, the Baltic trough is largely a depression of tectonic origin that existed long before the Quaternary glaciation.
Yoldia is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Yoldiidae. It was named after Alfonso de Aguirre y Yoldi, Conde de Yoldi (1764–1852), a Spanish nobleman in charge of the royal naturalistic collection of Denmark.










