
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 km2 (41,100,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20 percent of Earth's surface and about 29 percent of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" from the "New World" in the European perception of the World.

The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.
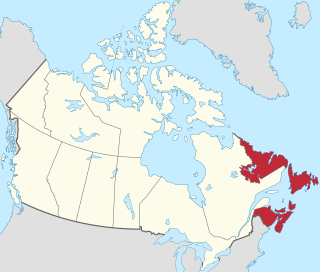
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces, a term developed for the convenience of the federal government after Newfoundland joined Canada in 1949, is the region of Eastern Canada comprising the four provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec: the three provinces of The Maritimes – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island – and the easternmost province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The population of the four Atlantic provinces in 2016 was about 2,300,000 on half a million km2. The provinces combined had an approximate GDP of $121.888 billion in 2011.

The east coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. Regionally, the term refers to the coastal states and area east of the Appalachian Mountains that have shoreline on the Atlantic Ocean, from north to south, Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Florida.

The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a 3,000-mile (4,800 km) inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Boston, Massachusetts, southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following the Gulf Coast to Brownsville, Texas. Some sections of the waterway consist of natural inlets, saltwater rivers, bays, and sounds, while others are artificial canals. It provides a navigable route along its length without many of the hazards of travel on the open sea.
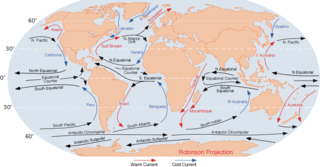
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements.

The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad is a former U. S. Class I railroad from 1900 until 1967, when it merged with long-time rival Seaboard Air Line Railroad to form the Seaboard Coast Line Railroad. Much of the original ACL network has been part of CSX Transportation since 1986.

The Treasure Coast is a region of the U.S. state of Florida. It is located on the state's Atlantic coast, comprising Indian River, St. Lucie, and Martin counties. The region, whose name refers to the Spanish Treasure Fleet lost in a 1715 hurricane, evidently emerged from residents' desire to distinguish themselves from Miami and the Gold Coast region to the south.
The Scandinavian Peninsula became ice-free around the end of the last ice age. The Nordic Stone Age begins at that time, with the Upper Paleolithic Ahrensburg culture, giving way to the Mesolithic hunter-gatherers by the 7th millennium BC. The Neolithic stage is marked by the Funnelbeaker culture, followed by the Pitted Ware culture.

An Atlantic hurricane or tropical storm is a tropical cyclone that forms in the Atlantic Ocean, primarily between the months of June and November. A hurricane differs from a cyclone or typhoon only on the basis of location. A hurricane is a storm that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean and northeastern Pacific Ocean, a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, and a cyclone occurs in the south Pacific or Indian Ocean.
Yoldia Sea is a name given by geologists to a variable brackish-water stage in the Baltic Sea basin that prevailed after the Baltic ice lake was drained to sea level during the Weichsel glaciation. Dates for the Yoldia sea are obtained mainly by radiocarbon dating material from ancient sediments and shore lines and from clay-varve chronology. They tend to vary by as much as a thousand years, but a good estimate is 10,300 – 9500 radiocarbon years BP, equivalent to ca 11,700-10,700 calendar years BP. The sea ended gradually when isostatic rise of Scandinavia closed or nearly closed its effluents, altering the balance between saline and fresh water. The Yoldia Sea became Ancylus Lake. The Yoldia Sea stage had three phases of which only the middle phase had brackish water.

In North Carolina, the Crystal Coast is an 85-mile stretch of coastline that extends from the Cape Lookout National Seashore, which includes 56 miles of protected beaches, southwestward to the New River. The Crystal Coast is a popular area with tourists and second-home owners in the summer.

The Tropical Atlantic realm is one of twelve marine realms that cover the world's coastal seas and continental shelves.

Yoldiidae is a taxonomic family of small to medium-sized saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the order Nuculanida.
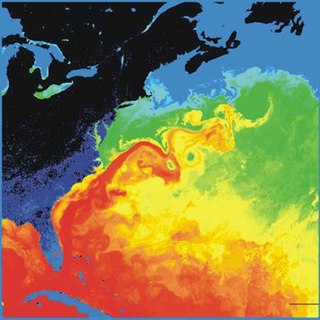
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and stretches to the tip of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northwards accelerating current off the east coast of North America. At about 40°0′N30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.
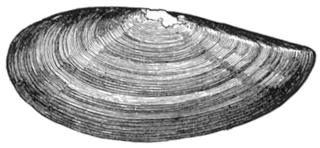
Yoldia limatula, commonly called the file yoldia, is a clam in the family Yoldiidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, from the Gulf of St. Lawrence to New Jersey, as well as along the Pacific coast, from Alaska to San Diego.
Yoldia myalis, or the comb yoldia, is a clam in the family Yoldiidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Labrador to Massachusetts, as well as along the Alaskan coast.
Yoldia thraciaeformis, or the broad yoldia, is a clam in the family Yoldiidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, from the Arctic Ocean to North Carolina, as well as along the Pacific coast, from the Arctic Ocean to Oregon.
Yoldia is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Yoldiidae. It was named after Alfonso de Aguirre y Yoldi, Conde de Yoldi (1764–1852), a Spanish nobleman in charge of the royal naturalistic collection of Denmark.














