Related Research Articles

Zambia is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa, to the east of Angola. It has a total area of 752,618 square kilometres, of which 9 220 km2 is water.

A woodland is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood, a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade. Some savannas may also be woodlands, such as savanna woodland, where trees and shrubs form a light canopy.

Miombo woodland is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome located in central and southern tropical Africa. It includes three woodland savanna ecoregions characterized by the dominant presence of Brachystegia and Julbernardia species of trees, and has a range of climates ranging from humid to semi-arid, and tropical to subtropical or even temperate. The trees characteristically shed their leaves for a short period in the dry season to reduce water loss and produce a flush of new leaves just before the onset of the wet season with rich gold and red colours masking the underlying chlorophyll, reminiscent of autumn colours in the temperate zone.

Brachystegia is a genus of tree of the subfamily Detarioideae that is native to tropical Africa.

The Eastern miombo woodlands (AT0706) are an ecoregion of grassland and woodland in northern Mozambique, southern Tanzania, and southeastern Malawi.

The white-bellied yellow bat or white-bellied house bat, is a species of vesper bat in the genus Scotophilus, the house bats. It can be found in Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Ivory Coast, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Mali, Mauritania, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, and Zambia. It is found in dry and moist savanna and open woodland. It is a common species with a very wide range, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Baikiaea is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes six species of trees native to sub-Saharan Africa. Species range from Nigeria eastwards to Uganda and Tanzania and south to Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia. Habitats range from lowland tropical rain forest to seasonally dry forest and woodland or savannas on well-drained soils.

The rattling cisticola is a species of bird in the family Cisticolidae which is native to Africa south of the equator, and parts of East Africa. It is a common to abundant species in open savanna and scrubland habitats, whether in arid, moist or upland regions. Especially during summer, it is highly conspicuous due to its strident and repetitive call-notes from prominent perches.

The white-bellied sunbird, also known as the white-breasted sunbird, is a species of bird in the family Nectariniidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.

The Zambezian flooded grasslands is an ecoregion of southern and eastern Africa that is rich in wildlife.
The biomes and ecoregions in the ecology of Zambia are described, listed and mapped here, following the World Wildlife Fund's classification scheme for terrestrial ecoregions, and the WWF freshwater ecoregion classification for rivers, lakes and wetlands. Zambia is in the Zambezian region of the Afrotropical biogeographic realm. Three terrestrial biomes are well represented in the country . The distribution of the biomes and ecoregions is governed mainly by the physical environment, especially climate.

Angolan mopane woodlands are situated in southwestern Angola, extending into northern Namibia. This ecosystem surrounds Etosha Pan, which is considered a separate ecoregion. The mopane trees are the main type of vegetation.

The Kalahari Acacia-Baikiaea woodlands are an ecoregion located in Botswana, northern Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe.
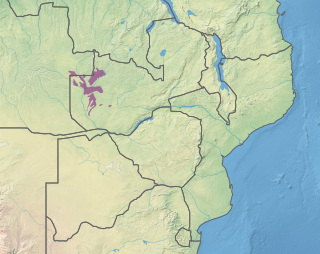
The Zambezian evergreen dry forests, also known as the Zambezian Cryptosepalum dry forest, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of Southern Africa. It consists of several areas of thick forest in western Zambia and adjacent Angola. It is one of the largest areas of tropical evergreen forest outside the equatorial zone.

The Zambezian and mopane woodlands is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of southeastern Africa.

The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
References
- ↑ Linder, H. Peter, Helen M. de Klerk, Julia Born et al. (2012). "The partitioning of Africa: statistically defined biogeographical regions in sub‐Saharan Africa". Journal of Biogeography, Volume 39, Issue 7, May 2012.
- 1 2 Emmanuel N. Chidumayo and Davison J. Gumbo, eds. (2010). The dry forests and woodlands of Africa: managing for products and services. Earthscan, 2010.
- ↑ Linder, H.P., Lovett, J., Mutke, J.M., Barthlott, W., Jürgens, N., Rebelo, T. & Küper, W. 2005. "A numerical re-evaluation of the sub-Saharan phytochoria of mainland Africa." Biologiske Skrifter 55: 229-252. ISSN 0366-3612. ISBN 87-7304-304-4.
- 1 2 3 Ribeiro, N.S., Silva de Miranda, P., Timberlake, J. (2020). Biogeography and Ecology of Miombo Woodlands. In: Ribeiro, N.S., Katerere, Y., Chirwa, P.W., Grundy, I.M. (eds) Miombo Woodlands in a Changing Environment: Securing the Resilience and Sustainability of People and Woodlands. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50104-4_2
- ↑ Burgess, Neil, Jennifer D'Amico Hales, Emma Underwood, et al. (2004). Terrestrial Ecoregions of Africa and Madagascar: A Conservation Assessment. World Wildlife Fund. Island Press, 2004