
A woodland is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood, a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade. Some savannas may also be woodlands, such as savanna woodland, where trees and shrubs form a light canopy.

Brachystegia is a genus of tree of the subfamily Detarioideae that is native to tropical Africa.
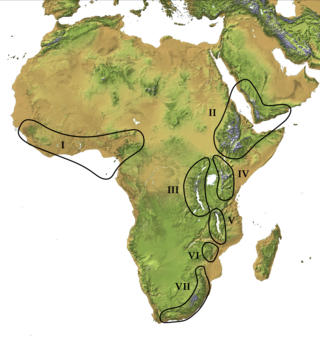
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.

Baikiaea plurijuga, known as African teak, Mukusi, Rhodesian teak, Zambian teak, or Zambesi redwood, is a species of Afrotropical tree from the legume family, the Fabaceae from southern Africa.

Sclerophrys maculata — commonly known as Hallowell's toad, the flat-backed toad, and the striped toad — is an African member of Bufonidae, the true toad family.

The square-tailed nightjar is a species of nightjar in the family Caprimulgidae which is native to tropical and subtropical woodlands of the Afrotropics. It has an extensive range south of the African equator. Despite not having a completely "square tail", its naming highlights a distinguishing field mark. The similarly plumaged slender-tailed nightjar, found in dry bush country of the tropics, differs namely by its protruding central tail feathers. It is alternatively known as the Gabon nightjar or Gaboon nightjar or the Mozambique nightjar.

The African green pigeon is a species of bird in the family Columbidae, and one of 5 green pigeon species in the Afrotropics. The species has a wide range in Sub-Saharan Africa with around 17 accepted races.

The copper sunbird is a species of passerine bird in the family Nectariniidae. It is native to tropical Africa, its range extending from Senegal and Guinea in the west to South Sudan and Kenya in the east, and southwards to Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe and Mozambique.

The white-bellied sunbird, also known as the white-breasted sunbird, is a species of bird in the family Nectariniidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.

The broad-tailed paradise whydah is a species of bird in the family Viduidae. It is found in woodland and acacia savanna habitat in Sub-Saharan Africa from Angola to Uganda, Tanzania and Mozambique. A brood parasite, it has a wide range and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed it as being of least concern.

The Angolan free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is found in Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Its natural habitats are dry and moist savanna, although it is sometimes found at the edges of woodlands.

Brachythemis lacustris is a species of dragonfly in the family Libellulidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Burkina Faso, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and possibly Burundi. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, dry savanna, moist savanna, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, rivers, and intermittent rivers.

Ictinogomphus ferox, commonly called the common tiger or the common tigertail, is a species of dragonfly in the family Gomphidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Senegal, Somalia, South Africa, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe, possibly Burundi, and possibly Ethiopia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, dry savanna, moist savanna, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, rivers, intermittent rivers, shrub-dominated wetlands, swamps, freshwater lakes, intermittent freshwater lakes, freshwater marshes, intermittent freshwater marshes, and freshwater springs.

Zygonoides fuelleborni is a species of dragonfly in the family Libellulidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and possibly Burundi. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, and rivers.

The Kalahari Acacia-Baikiaea woodlands are an ecoregion located in Botswana, northern Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe.

The Zambezian and mopane woodlands is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of southeastern Africa.

Aeollanthus (rocksage) is a genus in the mint family, Lamiaceae. All the species are native to Africa.
The Zambezian region is a large biogeographical region in Africa. The Zambezian region includes woodlands, savannas, grasslands, and thickets, extending from east to west in a broad belt across the continent. The Zambezian region lies south of the rainforests of the Guineo-Congolian region. The Zambezian region is bounded by deserts and xeric shrublands on the southwest, the Highveld grasslands of South Africa to the south, and the subtropical Maputaland forests on the southeast.

















