Related Research Articles

SIL International is an evangelical Christian non-profit organization whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages, and aid minority language development.
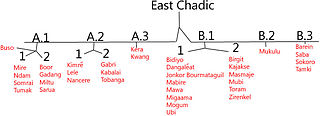
The three dozen East Chadic languages of the Chadic family are spoken in Chad and Cameroon.
Mono is a language spoken by about 65,000 people in the northwestern corner of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is one of the Banda languages, a subbranch of the Ubangian branch of the Niger–Congo languages. It has five dialects: Bili, Bubanda, Mpaka, Galaba, and Kaga.

The SIL Open Font License is one of the major open font licenses, which allows embedding, or "bundling", of the font in commercially sold products.
Síl nÁedo Sláine are the descendants of Áed Sláine, son of Diarmait mac Cerbaill. Part of the Southern Uí Néill—they were the kings of Brega—they claimed descent from Niall Noígiallach and his son Conall Cremthainne.
The Antsi (Anchi) language or Mag-antsi is a Sambalic language with around 4,200 speakers. It is spoken within Philippine Aeta communities in the Zambal municipalities of Botolan, San Marcelino, and Castillejos; in the Tarlaqueño municipalities of Capas and Bamban; in Mabalacat, Pampanga; and in Angeles City. The use of the language is declining as its speakers are shifting to Kapampangan. The language is mutually intelligible with Mag-Indi Ayta (77%) and Ambala Ayta (65%).
Melanau is an Austronesian language spoken in the coastal area of the Rajang delta on northwest Borneo, Sarawak, Malaysia and Brunei. There are several dialects—Mukah-Oya, Balingian, Bruit, Dalat, Lawas, Igan, Sarikei, Segahan, Prehan, Segalang, and Siteng.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.
Daasanach is a Cushitic language spoken by the Daasanach in Ethiopia, South Sudan and Kenya whose homeland is along the Lower Omo River and on the shores of Lake Turkana.
Birgit is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in southeastern Chad. Speakers are found in Moubi Goz Canton, Kouka Margni Sub-prefecture and in Moubi Zarga Canton, Mangalmé Sub-prefecture.
The Awakatek (Aguacateco) are a Maya people in Guatemala, primarily located in the municipality of Aguacatán (Huehuetenango). Their native Awakatek language is related to the Ixil language.
The Meso-Cordilleran languages are a group of languages spoken in or near the Cordillera Central mountain range in Northern Luzon. Its speakers are culturally very diverse, and include the lowland Pangasinense, the Igorot highlanders, and Alta-speaking Aeta groups.
Wali is a Hill Nubian language spoken in the northwestern Nuba Mountains in the south of Sudan. It is spoken by around 9,000 people 12 km northeast of Katla. Ethnologue reports that use of Wali is vigorous and that there are many monolingual speakers. Young children speak English and Wali, but it is expected that the next generation will continue to communicate using Wali.
Selaru is an Austronesian language of Selaru and Yamdena, in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. Linguistically is not close to Seluwasan, its nearest relative.
Bajaw is the language of the Bajaw, widely known as the 'sea gypsies' of Maritime Southeast Asia. Differences exist between the language's varieties in western Sabah, Mapun in southern Philippines, eastern Sabah, and across Sulawesi to Maluku.
Tebi, also known by the village name Dubu, is a Western Pauwasi language of West New Guinea. It is spoken in Affi, Dubu, and Jembatan Web villages of Keerom Regency. It is mostly used by older adults.
Mato is a minor Austronesian language of northern Papua New Guinea just inside Morobe Province. Mato is also referred to by the names Nenaya, Nengaya, and Nineia. Mato language has two minor variations, Tabares and Remuk, and the two variations are each spoken in three separate villages. While Mato is surrounded by several other languages, this has no effect on the grammar changes within Mato boundaries. The linguistic situation is very stable, due in part to the geographical isolation of the Mato people.

Pahanan Agta, also called Paranan Agta or Palanan Agta, is an Aeta language of Palanan, Isabela northern Philippines. Lexically but not grammatically it is extremely close to Paranan, a non-Negrito language with a very similar name. Speaker groups of both languages were together isolated from other communities and remained in constant interaction.
Iduna is an Austronesian language spoken on Goodenough Island of Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea.
Luang, also known as Literi Lagona, is an Austronesian language spoken in the Leti Islands and the Babar Islands in Maluku, Indonesia. It is closely related to the neighboring Leti language, with 89% shared basic vocabulary.
References
Johnson, Eric. 2005. Étude sociolinguistique de la langue Zirenkel du Tchad. SIL Electronic Survey Reports 2005–023. Dallas: SIL International. Online. URL: https://sil.org/silesr/abstract.asp?ref=2005-023.