Related Research Articles

Causantín mac Áeda was an early King of Scotland, known then by the Gaelic name Alba. The Kingdom of Alba, a name which first appears in Constantine's lifetime, was situated in what is now Northern Scotland.

Edmund I or Eadmund I was King of the English from 27 October 939 until his death in 946. He was the elder son of King Edward the Elder and his third wife, Queen Eadgifu, and a grandson of King Alfred the Great. After Edward died in 924, he was succeeded by his eldest son, Edmund's half-brother Æthelstan. Edmund was crowned after Æthelstan died childless in 939. He had two sons, Eadwig and Edgar, by his first wife Ælfgifu, and none by his second wife Æthelflæd. His sons were young children when he was killed in a brawl with an outlaw at Pucklechurch in Gloucestershire, and he was succeeded by his younger brother Eadred, who died in 955 and was followed by Edmund's sons in succession.

Mercia was one of the three main Anglic kingdoms founded after Sub-Roman Britain was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England.

Eadwig was King of England from 23 November 955 until his death in 959. He was the elder son of Edmund I and his first wife Ælfgifu, who died in 944. Eadwig and his brother Edgar were young children when their father was killed trying to rescue his seneschal from attack by an outlawed thief on 26 May 946. As Edmund's sons were too young to rule he was succeeded by his brother Eadred, who suffered from ill health and died unmarried in his early 30s.

Edward the Martyr was King of the English from 8 July 975 until he was killed in 978. He was the eldest son of King Edgar. On Edgar's death, the succession to the throne was contested between Edward's supporters and those of his younger half-brother, the future King Æthelred the Unready. As they were both children, it is unlikely that they played an active role in the dispute, which was probably between rival family alliances. Edward's principal supporters were Dunstan, Archbishop of Canterbury, and Æthelwine, Ealdorman of East Anglia, while Æthelred was backed by his mother, Queen Ælfthryth and her friend Æthelwold, Bishop of Winchester. The dispute was quickly settled. Edward was chosen as king and Æthelred received the lands traditionally allocated to the king's eldest son in compensation.

Æthelflæd ruled as Lady of the Mercians in the English Midlands from 911 until her death in 918. She was the eldest child of Alfred the Great, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex, and his wife Ealhswith.

Edgar was King of the English from 959 until his death in 975. He became king of all England on his brother's death. He was the younger son of King Edmund I and his first wife Ælfgifu. A detailed account of Edgar's reign is not possible, because only a few events were recorded by chroniclers and monastic writers were more interested in recording the activities of the leaders of the church.

Æthelstan or Athelstan was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 924 to 927 and King of the English from 927 to his death in 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder and his first wife, Ecgwynn. Modern historians regard him as the first King of England and one of the "greatest Anglo-Saxon kings". He never married and had no children; he was succeeded by his half-brother, Edmund I.

Æthelred became Lord of the Mercians in England shortly after the death or disappearance of Mercia's last king, Ceolwulf II, in 879. He is also sometimes called the Ealdorman of Mercia. Æthelred's rule was confined to the western half, as eastern Mercia was then part of the Viking-ruled Danelaw. His ancestry is unknown. He was probably the leader of an unsuccessful Mercian invasion of Wales in 881, and soon afterwards he acknowledged the lordship of King Alfred the Great of Wessex. This alliance was cemented by the marriage of Æthelred to Alfred's daughter Æthelflæd.

Æthelwold or Æthelwald was the younger of two known sons of Æthelred I, King of Wessex from 865 to 871. Æthelwold and his brother Æthelhelm were still infants when their father the king died while fighting a Danish Viking invasion. The throne passed to the king's younger brother Alfred the Great, who carried on the war against the Vikings and won a crucial victory at the Battle of Edington in 878.
Ælfgifu was Queen of the English as wife of King Eadwig of England for a brief period of time until 957 or 958. What little is known of her comes primarily by way of Anglo-Saxon charters, possibly including a will, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle and hostile anecdotes in works of hagiography. Her union with the king, annulled within a few years of Eadwig's reign, seems to have been a target for factional rivalries which surrounded the throne in the late 950s. By c. 1000, when the careers of the Benedictine reformers Dunstan and Oswald became the subject of hagiography, its memory had suffered heavy degradation. In the mid-960s, however, she appears to have become a well-to-do landowner on good terms with King Edgar and, through her will, a generous benefactress of ecclesiastical houses associated with the royal family, notably the Old Minster and New Minster at Winchester.
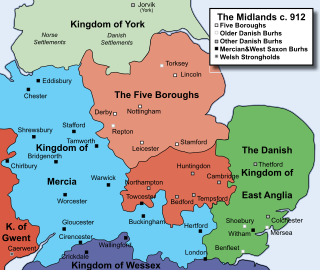
The Five Boroughs or The Five Boroughs of the Danelaw were the five main towns of Danish Mercia under the Danelaw. These were Derby, Leicester, Lincoln, Nottingham and Stamford. The first four later became county towns.

Sitric Cáech or Sihtric Cáech or Sigtrygg Gále, was a Hiberno-Scandinavian Viking leader who ruled Dublin and then Viking Northumbria in the early 10th century. He was a grandson of Ímar and a member of the Uí Ímair. Sitric was most probably among those Vikings expelled from Dublin in 902, whereafter he may have ruled territory in the eastern Danelaw in England. In 917, he and his kinsman Ragnall ua Ímair sailed separate fleets to Ireland where they won several battles against local kings. Sitric successfully recaptured Dublin and established himself as king, while Ragnall returned to England to become King of Northumbria. In 919, Sitric won a victory at the Battle of Islandbridge over a coalition of local Irish kings who aimed to expel the Uí Ímair from Ireland. Six Irish kings were killed in the battle, including Niall Glúndub, overking of the Northern Uí Néill and High King of Ireland.
Ælfric Cild was a wealthy Anglo-Saxon nobleman from the east Midlands, Ealdorman of Mercia between 983 and 985, and possibly brother-in-law to his predecessor Ælfhere. He was also associated with the monastic reformer Æthelwold, bishop of Winchester, he is also notable for being involved in a number of land transactions for the refounding and endowment of Peterborough Abbey, as well as with Thorney Abbey during the 970s and early 980s.

Edward the Elder was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 899 until his death in 924. He was the elder son of Alfred the Great and his wife Ealhswith. When Edward succeeded to the throne, he had to defeat a challenge from his cousin Æthelwold, who had a strong claim to the throne as the son of Alfred's elder brother and predecessor, Æthelred I.
Ælfhere was Ealdorman of Mercia. His family, along with those of Æthelstan Half-King and Æthelstan Rota, rose to greatness in the middle third of the 10th century. In the reign of Edward the Martyr, Ælfhere was a leader of the anti-monastic reaction and an ally of Edward's stepmother Queen Dowager Ælfthryth. After the killing of Edward by Ælfthryth's servants in 978, Ælfhere supported the new king, Ælfthryth's son Æthelred the Unready, and was the leading nobleman in the Kingdom of England until his death in 983.
Edwin was the younger son of King Edward the Elder and Ælfflæd, his second wife. He drowned at sea in circumstances which are unclear. Edward the Elder died in 924, leaving five sons by three marriages. Of these, Edmund and Eadred were infants and thus excluded from the succession. Edward's careful work of expansion was undone when the Mercians chose Edward's oldest son Æthelstan – probably raised in Mercia at the court of Edward's sister Æthelflæd – to be their king while the West Saxons picked Ælfweard, elder son of Edward's second wife Ælfflæd, who was perhaps Edward's own choice as successor. Ælfweard's "sudden and convenient" death followed 16 days after that of his father, but Æthelstan appears not to have been recognised as king by the West Saxons until a year after his father's death, suggesting that there was considerable resistance to him and perhaps also support for Edwin.
Events from the 10th century in the Kingdom of England.

St Oswald's Priory was founded by Æthelflæd, daughter of Alfred the Great, and her husband Æthelred, ealdorman of Mercia, in the late 880s or the 890s. It appears to have been an exact copy of the Old Minster, Winchester It is a Grade I listed building.

Ælfwynn or Ælfwyn was a member of a wealthy Anglo-Saxon family in Huntingdonshire who married Æthelstan Half-King, the powerful ealdorman of East Anglia, in about 932. She is chiefly known for having been foster-mother to the future King Edgar the Peaceful following his mother's death in 944, when he was an infant. She had four sons, and the youngest, Æthelwine, became the chief secular magnate and leading supporter of the monastic reform movement. Ælfwynn donated her estates for his foundation of Ramsey Abbey in 966 and was probably buried there.
References
- ↑ Clarkson 2018, p. 152.
- ↑ Swanton 2000, p. 105.
- ↑ Bailey 2001, pp. 115–17; Molyneaux 2015, p. 28.
- ↑ Swanton 2000, pp. xxiv, 103.
- ↑ "Anglo-Saxons.net: S 1280" . Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ↑ "Anglo-Saxons.net: S 225" . Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ↑ "Anglo-Saxons.net: S 367" . Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ↑ "Anglo-Saxons.net: S 535" . Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ↑ Bailey 2001, pp. 122–125.
- ↑ Jayakumar 2008, p. 94.
- ↑ Livingston 2011 , p. 6, n. 11, citing Laura Hibbard Loomis, Medieval Romance in England, p. 110
