The 1946 United States Senate elections were held November 5, 1946, in the middle of Democratic President Harry S. Truman's first term after Roosevelt's passing. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and four special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans took control of the Senate by picking up twelve seats, mostly from the Democrats. This was the first time since 1932 that the Republicans had held the Senate, recovering from a low of 16 seats following the 1936 Senate elections.

The 1932 United States Senate elections coincided with Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt's landslide victory over incumbent Herbert Hoover in the presidential election. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1930 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Republican President Herbert Hoover's term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. With the Great Depression beginning to take hold, Republican incumbents became unpopular, and Democrats picked up a net of eight seats, erasing the Republican gains from the previous election cycle. Republicans retained control of the U.S. Senate since Vice President Charles Curtis cast the tie-breaking vote. This was the first of four consecutive Senate elections during the Depression in which Democrats made enormous gains, achieving a cumulative pick-up of 34 seats.

The 1932 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 73rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 8, 1932, while Maine held theirs on September 12. They coincided with the landslide election of President Franklin D. Roosevelt.
The 1898 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1898, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They were held during the middle of President William McKinley's first term. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 56th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1896 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 3, 1896, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election of President William McKinley. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 55th United States Congress. The size of the House increased by one seat after Utah gained statehood on January 4, 1896. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
The 1894 United States House of Representatives elections were held from June 4, 1894 to November 6, 1894, with special elections throughout the year. Elections were held to elect representatives from all 356 congressional districts across each of the 44 U.S. states at the time, as well as non-voting delegates from the inhabited U.S. territories. The winners of this election served in the 54th Congress, with seats apportioned among the states based on the 1890 United States census.
The 1892 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1892, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election of Grover Cleveland as president for the second, non-continuous, time, defeating incumbent Benjamin Harrison. Elections were held for 356 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 44 states, to serve in the 53rd United States Congress. They were the first elections after reapportionment following the 1890 United States Census, increasing the size of the House. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1890 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1890, with five states holding theirs early in between June and October. They occurred in the middle of President Benjamin Harrison's term. Elections were held for 332 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 44 states, to serve in the 52nd United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1888 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1888, with three states holding theirs early between June and September. They occurred at the same time as the election of President Benjamin Harrison. Elections were initially held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 51st United States Congress. Six new states would later join the union and increase the House to 332 seats. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
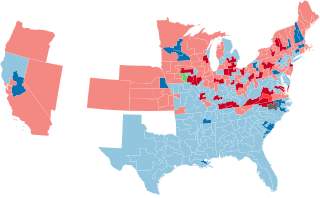
The 1886 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 2, 1886, with three states holding theirs early between June and September. They occurred in the middle of President Grover Cleveland's first term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 50th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1884 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1884, with four states holding theirs early between June and October. They coincided with the election of President Grover Cleveland. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 49th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1882 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 7, 1882, with five states holding theirs early between June and October. They occurred during President Chester A. Arthur's term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 48th United States Congress. They were the first elections after reapportionment following the 1880 United States Census, increasing the size of the House. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
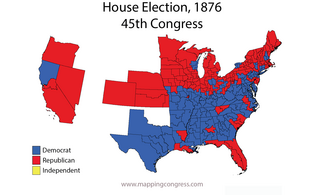
The 1876–77 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1876 and March 13, 1877. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 45th United States Congress convened on October 15, 1877. The size of the House increased to 293 seats with the addition of the new state of Colorado.
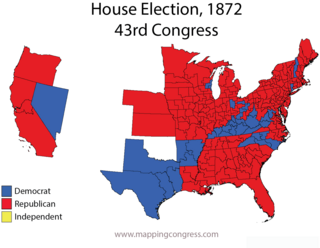
The 1872–73 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 4, 1872 and April 7, 1873. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 43rd United States Congress convened on December 1, 1873. They coincided with the re-election of United States President Ulysses S. Grant. The congressional reapportionment based on the 1870 United States Census increased the number of House seats to 292.

The 1868–69 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 1, 1868 and August 2, 1869. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 41st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1869. They coincided with the 1868 United States presidential election, which was won by Ulysses S. Grant. Elections were held for all 243 seats, representing 37 states. All of the former Confederate states were represented in Congress for the first time since they seceded from the Union.
The 1864–65 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1864 and November 7, 1865, in the midst of the American Civil War and President Abraham Lincoln's reelection. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. Members were elected before the first session of the 39th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1865, including the at-large seat from the new state of Nevada, and the 8 from Tennessee, the first secessionist state to be readmitted. The other 10 secessionist states had not yet been readmitted, and therefore were not seated.

The 1860–61 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 6, 1860 and October 24, 1861, before or after the first session of the 37th United States Congress convened on July 4, 1861. The number of House seats initially increased to 239 when California was apportioned an extra one, but these elections were affected by the outbreak of the American Civil War and resulted in over 56 vacancies.
The 1858–59 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 7, 1858 and December 1, 1859. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 238 representatives were elected in the new state of Oregon, the pending new state of Kansas, and the other 32 states before the first session of the 36th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1859. They were held during President James Buchanan's term.
The 1848–49 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 1848 and November 1849. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 31st United States Congress convened on December 3, 1849. The new state of Wisconsin elected its first representatives, and California also held its first congressional elections before officially achieving statehood in 1850, increasing the size of the House to 233 seats.