
The 1987 Whittier Narrows earthquake occurred in the southern San Gabriel Valley and surrounding communities of Southern California, United States, at on October 1. The moderate magnitude 5.9 blind thrust earthquake was centered several miles north of Whittier in the town of Rosemead, had a relatively shallow depth, and was felt throughout southern California and southern Nevada. Many homes and businesses were affected, along with roadway disruptions, mainly in Los Angeles and Orange counties. Damage estimates ranged from $213–358 million, with 200 injuries, three directly-related deaths, and five additional fatalities that were associated with the event.
Seismic magnitude scales are used to describe the overall strength or "size" of an earthquake. These are distinguished from seismic intensity scales that categorize the intensity or severity of ground shaking (quaking) caused by an earthquake at a given location. Magnitudes are usually determined from measurements of an earthquake's seismic waves as recorded on a seismogram. Magnitude scales vary on what aspect of the seismic waves are measured and how they are measured. Different magnitude scales are necessary because of differences in earthquakes, the information available, and the purposes for which the magnitudes are used.
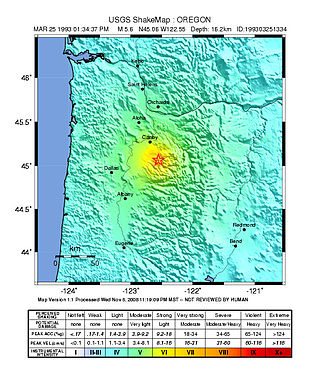
The 1993 Scotts Mills earthquake, also known as the "Spring break quake", occurred in the U.S. state of Oregon on March 25 at 5:34 AM Pacific Standard Time. With a moment magnitude of 5.6 and a maximum perceived intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale, it was the largest earthquake in the Pacific Northwest since the Elk Lake and Goat Rocks earthquakes of 1981. Ground motion was widely felt in Oregon's Willamette Valley, the Portland metropolitan area, and as far north as the Puget Sound area near Seattle, Washington.

The 1935 Temiskamingue earthquake occurred on November 1 with a moment magnitude of 6.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The event took place in the Western Quebec Seismic Zone in the Abitibi-Témiscamingue region of Quebec.
The 2008 Illinois earthquake was one of the largest earthquakes ever recorded in the Midwest state of Illinois. This moderate strike-slip shock measured 5.2 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII (Very strong). It occurred at on April 18 near Bellmont and Mount Carmel, Illinois, within the Wabash Valley Seismic Zone. Earthquakes in this part of the country are often felt at great distances.
Body-waves consist of P-waves that are the first to arrive, or S-waves, or reflections of either. Body-waves travel through rock directly.
The 1663 Charlevoix earthquake occurred on February 5 in New France, and was assessed to have a moment magnitude of between 7.3 and 7.9. The earthquake occurred at 5:30 p.m. local time and was estimated to have a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The main shock epicentre is suggested to have occurred along the Saint Lawrence River, between the mouth of the Malbaie River on the north and the mouth of the Ouelle River on the south. A large portion of eastern North America felt the effects. Landslides and underwater sediment slumps were a primary characteristic of the event with much of the destruction occurring near the epicentral region of the St. Lawrence estuary and also in the area of the Saguenay Graben.
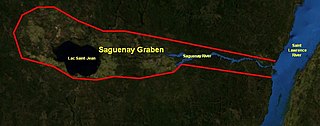
The Saguenay Graben is a rift valley or graben in the geological Grenville Province of southern Quebec, Canada. It is an elongated flat-bottomed basin 250 km (155 mi) long and 50 km (31 mi) wide, bounded by normal faults running parallel to its length.
The 1918 Vancouver Island earthquake occurred in British Columbia, Canada at 12:41 a.m. Pacific Standard Time on December 6. The earthquake was most likely of the strike-slip type, and was estimated to have a maximum perceived intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale. The epicenter was located east of the Stewardson inlet on the west coast of Vancouver Island, with damage occurring at the Estevan Point lighthouse on the Hesquiat Peninsula. The event registered 7.2 on the moment magnitude scale and was felt as far as northern Washington state and the interior of British Columbia.

This list of 20th-century earthquakes is a global list of notable earthquakes that occurred in the 20th century. After 1900 most earthquakes have some degree of instrumental records and this means that the locations and magnitudes are more reliable than for earlier events. To prevent this list becoming unmanageable, only those of magnitude 6 and above are included unless they are notable for some other reason.

The Ramapo Fault zone is a system of faults between the northern Appalachian Mountains and Piedmont areas to the east. Spanning more than 185 miles (298 km) in New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, it is perhaps the best known fault zone in the Mid-Atlantic region, and some small earthquakes have been known to occur in its vicinity. Recently, public knowledge about the fault has increased, especially after the 1970s, when the fault's proximity to the Indian Point nuclear plant in New York was noted.

The 1968 Illinois earthquake was the largest recorded earthquake in the U.S. Midwestern state of Illinois. Striking at 11:02 am on November 9, it measured 5.4 on the Richter scale. Although no fatalities occurred, the event caused considerable structural damage to buildings, including the toppling of chimneys and shaking in Chicago, the region's largest city. The earthquake was one of the most widely felt in U.S. history, largely affecting 23 states over an area of 580,000 sq mi (1,500,000 km2). In studying its cause, scientists discovered the Cottage Grove Fault in the Southern Illinois Basin.

The 1940 New Hampshire earthquakes struck on December 20 and again on December 24. Both shocks had an estimated magnitude of 5.6, and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. These doublet earthquakes were the largest to hit the state in several hundred years. Damage included minor fractures or knocked over chimneys in a zone extending through New Hampshire and four other states: Maine, New York, Vermont and Massachusetts.
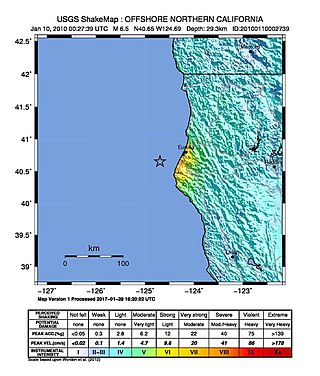
The 2010 Eureka earthquake occurred on January 9 at 4:27:38 pm PST offshore of Humboldt County, California, United States. The magnitude was measured 6.5 on the scale, and its epicenter was located offshore in the Pacific Ocean 33 miles (53 km) west of the nearest major city, Eureka. Additionally, there was a separate earthquake further offshore of Eureka on February 4 with a slightly lower magnitude of 5.9. It was also the most significant earthquake in the Eureka area in terms of magnitude since the 1992 Cape Mendocino earthquakes. It was felt from Santa Cruz County, California in the south, to Eugene, Oregon in the north and to the east as far as Reno, Nevada.
The 1986 Chalfant Valley earthquake struck southern Mono County near Bishop and Chalfant, California at Pacific Daylight Time on July 21. With a moment magnitude of 6.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong), the shock injured two people and caused property damage estimated at $2.7 million in the affected areas. There was a significant foreshock and aftershock sequence that included a few moderate events, and was the last in a series of three earthquakes that affected southern California and the northern Owens Valley in July 1986.
The 1872 North Cascades earthquake occurred at in central Washington Territory. A maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe) was assessed for several locations, though less intense shaking was observed at many other locations in Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia. Some of these intermediate outlying areas reported V (Moderate) to VII shaking, but intensities as high as IV (Light) were reported as far distant as Idaho and Montana. Due to the remote location of the mainshock and a series of strong aftershocks, damage to structures was limited to a few cabins close to the areas of the highest intensity.
The 1989 Ungava earthquake occurred at 09:24 local time on 25 December to the north of Lac Bécard in a remote part of the Ungava Peninsula in northern Quebec. It had a magnitude of 6.3 on the surface wave magnitude scale and 6.2–6.5 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum felt intensity of only IV (Light) on the Mercalli intensity scale, due to its remoteness from any inhabited areas. The mainshock was preceded by a magnitude 5.1 foreshock ten hours earlier. It was the first earthquake in eastern North America known to be associated with ground rupture.
The 2012 Haida Gwaii earthquake occurred just after . The shock had a moment magnitude of 7.8 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of V (Moderate). The earthquake's epicentre was on Moresby Island of the Haida Gwaii archipelago. This was the second largest Canadian earthquake ever recorded by a seismometer, after the 1949 Queen Charlotte Islands earthquake, about 135 kilometres (84 mi) away. One person died due to a car crash related to the tsunami in Oahu, Hawaii.
The 1987 Superstition Hills and Elmore Ranch earthquakes were a pair of earthquakes measuring Mw 6.0 and 6.5 that rattled the Imperial Valley of California. The earthquakes caused damage in Southern California and Mexico, but was limited due to their location in a sparsely populated area. It was felt as far as Las Vegas and Phoenix. More than 90 were injured, and two people were killed in Mexico.
The 1870 Charlevoix earthquake occurred on 20 October in the Canadian province of Quebec. It had a moment magnitude of 6.6 Mw and a Modified Mercalli intensity rating of X (Extreme). The town of Baie-Saint-Paul was seriously damaged by the event, with the loss of six lives. Effects from the earthquake were felt as far as Virginia and along the New England coast of the United States.









