Sodium cyanide is a poisonous compound with the formula NaCN. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its high reactivity toward metals. It is a moderately strong base.
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane), is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.

Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula NO2. One of several nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas. It is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. Industrially, NO2 is an intermediate in the synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year, primarily for the production of fertilizers.
Nitromethane, sometimes shortened to simply "nitro", is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH
3NO
2. It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel additive in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft.
Decane is an alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H22. Although 75 structural isomers are possible for decane, the term usually refers to the normal-decane ("n-decane"), with the formula CH3(CH2)8CH3. All isomers, however, exhibit similar properties and little attention is paid to the composition. These isomers are flammable liquids. Decane is present in small quantities (less than 1%) in gasoline (petrol) and kerosene. Like other alkanes, it is a nonpolar solvent, and does not dissolve in water, and is readily combustible. Although it is a component of fuels, it is of little importance as a chemical feedstock, unlike a handful of other alkanes.
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula (CN)2. The simplest stable carbon nitride, it is a colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as Cl2, but far less oxidizing. The two cyano groups are bonded together at their carbon atoms: N≡C‒C≡N, although other isomers have been detected. The name is also used for the CN radical, and hence is used for compounds such as cyanogen bromide (NCBr) (but see also Cyano radical.). When burned at increased pressure with oxygen, it is possible to get a blue tinted flame, the temperature of which is approximately 4 800 °C (A higher temperature is possible with ozone.). It is as such regarded as the gas with the second highest temperature of burning (after Dicyanoacetylene)

Pentane is an organic compound with the formula C5H12—that is, an alkane with five carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of three structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, pentane means exclusively the n-pentane isomer, in which case pentanes refers to a mixture of them; the other two are called isopentane (methylbutane) and neopentane (dimethylpropane). Cyclopentane is not an isomer of pentane because it has only 10 hydrogen atoms where pentane has 12.

Nonane is a linear alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20. It is a colorless, flammable liquid, occurring primarily in the component of the petroleum distillate fraction commonly called kerosene, which is used as a heating, tractor, and jet fuel. Nonane is also used as a solvent, distillation chaser, fuel additive, and a component in biodegradable detergents.
Dodecane (also known as dihexyl, bihexyl, adakane 12, or duodecane) is an oily liquid n-alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C12H26 (which has 355 isomers).

Copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuO. A black solid, it is one of the two stable oxides of copper, the other being Cu2O or copper(I) oxide (cuprous oxide). As a mineral, it is known as tenorite. It is a product of copper mining and the precursor to many other copper-containing products and chemical compounds.
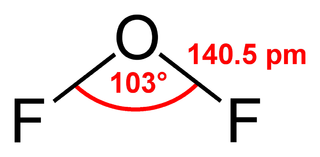
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula OF2. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a bent molecular geometry. It is a strong oxidizer and has attracted attention in rocketry for this reason. With a boiling point of −144.75 °C, OF2 is the most volatile (isolable) triatomic compound. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.
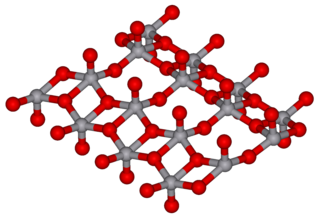
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.
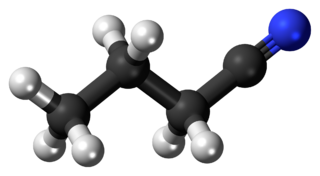
Butyronitrile or butanenitrile or propyl cyanide, is a nitrile with the formula C3H7CN. This colorless liquid is miscible with most polar organic solvents.

Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorinating agent.

Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid.
Higher alkanes are alkanes having nine or more carbon atoms. Nonane is the lightest alkane to have a flash point above 25 °C, and is not classified as dangerously flammable.
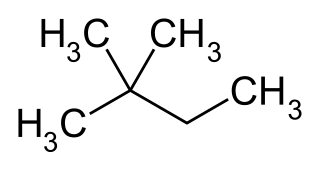
2,2-Dimethylbutane, trivially known as neohexane, is an organic compound with formula C6H14 or (H3C-)3-C-CH2-CH3. It is therefore an alkane, indeed the most compact and branched of the hexane isomers — the only one with a quaternary carbon and a butane (C4) backbone.
3-Methylpentane is a branched alkane with the molecular formula C6H14. It is a structural isomer of hexane composed of a methyl group bonded to the third carbon atom in a pentane chain. It is of similar structure to the isomeric 2-methylpentane, which has the methyl group located on the second carbon of the pentane chain.

Butane or n-butane is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature and pressure. The name butane comes from the root but- (from butyric acid, named after the Greek word for butter) and the suffix -ane. It was discovered in crude petroleum in 1864 by Edmund Ronalds, who was the first to describe its properties, and commercialized by Walter O. Snelling in the early 1910s.
Propionitrile, also known as ethyl cyanide and propanenitrile, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CN. It is a simple aliphatic nitrile. The compound is a colourless, water-soluble liquid. It is used as a solvent and a precursor to other organic compounds.