
The GE 44-ton switcher is a four-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Electric between 1940 and 1956. It was designed for industrial and light switching duties, often replacing steam locomotives that had previously been assigned these chores.

The Delta Valley and Southern Railway is a short-line railroad headquartered in Wilson, Arkansas.

The Sierra Railroad Corporation is a privately owned common carrier. Its Sierra Northern Railway freight division handles all freight operations for all branches owned by the Sierra Railroad. The company's Mendocino Railway group operates the diesel- and steam-powered Sacramento RiverTrain (Woodland-Sacramento) and the Skunk Train. The company's Sierra Energy division is for energy projects.

The Northwestern Pacific Railroad is a 271-mile (436 km) mainline railroad from the former ferry connections in Sausalito, California north to Eureka, with a connection to the national railroad system at Schellville. The railroad has gone through a complex history of different ownership and operators but has maintained a generic name of reference as the Northwestern Pacific Railroad, despite no longer being officially named that.

The Pacific Harbor Line was formed in 1998 to take over the Harbor Belt Line (HBL). In 1998, the Alameda Corridor was nearing completion, allowing for a massive amount of railroad traffic from the largest harbors in the Western hemisphere: Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach.

The McCloud Railway was a class III railroad operated around Mount Shasta, California. It began operations on July 1, 1992, when it took over operations from the McCloud River Railroad. The MCR was incorporated on April 21, 1992.

The Modesto and Empire Traction Company is a Class III short-line railroad operating in California's San Joaquin Valley. It is owned by the Beard Land & Investment Company; the Beard family has always owned the railroad. The Beards also created the Beard Industrial Park where the MET's customers are located. The railroad was unique in that it had operated for nearly 50 years exclusively with GE 70-ton switchers built between 1947 and 1955; however, a former Southern Pacific EMD SW1500 switcher was added to the roster as of late. The MET operates on 5 miles (8 km) of mainline track, as well as an additional 48.7 miles (78.4 km) of yard and industry track, providing switching services in the Beard Industrial Park. The MET interchanges with the Union Pacific at Modesto and with the BNSF Railway Stockton Subdivision at Empire.
The Oakland Terminal Railway was a terminal railroad in West Oakland, California. The OTR was jointly acquired in 1943 by the Western Pacific Railroad and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway to take over the Key System's freight railroad known as the Oakland Terminal Railroad. Today, the OTR is now the West Oakland Pacific Railroad that operates on 10 miles (16 km) of track. OTR was jointly owned by the Union Pacific Railroad and BNSF Railway. The railroad operated in the industrial area around the Oakland Army Base.

The Quincy Railroad is a 3.27-mile terminal railroad located at Quincy, California. The QRR interchanges with the Union Pacific at Quincy Junction in Plumas County, California, United States.

The Trona Railway is a 30.5 mi (49.1 km) short-line railroad owned by Searles Valley Minerals. The TRC interchanges with the Lone Pine Subdivision of the Union Pacific Railroad at Searles, California.

The Arcata and Mad River Railroad, founded in 1854, was the oldest working railroad in California. It operated on a unique narrow gauge until the 1940s when standard gauge rails were laid. Service ceased in 1983 due to landslides. It is California Historical Landmark #842.
The Santa Maria Valley Railroad is a 14.8 miles (23.8 km) shortline railroad that interchanges with the Union Pacific Railroad's Coast Line at Guadalupe, California. As of 2006, the Railroad is owned by the Coast Belle Rail Corporation.

The Oregon, Pacific and Eastern Railway is an Oregon-based short line railroad that began near Eugene as the Oregon and Southeastern Railroad (O&SE) in 1904. O&SE's line ran 18 miles (29 km) along the Row River between the towns of Cottage Grove and Disston. The Oregon, Pacific & Eastern Railway Company incorporated in 1912, purchased the physical assets of the O&SE two years later, and shortened their total trackage to operate 16.6 miles (26.7 km) from an interchange yard with the Southern Pacific Railroad at Cottage Grove, east to a 528' x 156' turnaround loop at Culp Creek. The last of this track was closed and scrapped in 1994, and ownership of its abandoned right of way property was later reverted to the state of Oregon to become one of the first-ever Government/Private Sector cooperative partnership Rails to Trails programs in the US, forming the Row River National Recreation Trail. A successor corporation now operates a communications company and a narrow-gauge line at Wildlife Safari.

The Crab Orchard and Egyptian Railway is a Class III common carrier shortline railroad that operates in the cities of Marion and Herrin in the Southern Illinois region. It is most historically recognized by the FRA for being the last U.S. railroad of any kind to use steam locomotives exclusively in regular revenue freight service up until March 1986.
The Manufacturers' Junction Railway is a shortline railroad in Cicero, Illinois. Originally a subsidiary of Western Electric used to switch their Hawthorne Works, after the plants were phased out it was sold to OmniTRAX, a company offering railroad management and other services.
Southern Pacific Transportation Company formed the Oregon and Eureka Railroad Company in 1903 in an agreement to use logging railroads as part of a line connecting Humboldt County (California) sawmills with the national rail network. Northwestern Pacific Railroad offered service over the route from 1911 through 1933. The northern 6-mile (9.7 km) of the line remained in use as a Hammond Lumber Company logging branch until 1948.
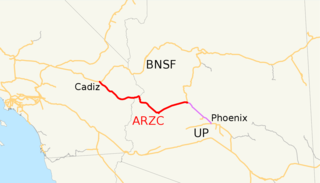
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.
The Yancey Railroad was an American Class III shortline railroad that operated for freight service from a connection with the Clinchfield Railroad at Kona, North Carolina, through Micaville, to Burnsville, 10.6 miles (17.1 km). A short branch ran from Micaville to Bowditch, North Carolina, 2.11 miles (3.40 km). Total mileage was 12.83 miles (20.65 km). Rail was 60–65 pounds and the maximum load limit was 75 tons. Traffic was feldspar, mica, fertilizer, building materials, livestock feed and steel spring wire.
Barstow Yard is a classification yard operated by Burlington Northern Santa Fe Railway (BNSF) in Barstow, California. With 48 directional tracks and a total area of approximately 600 acres (240 ha), it is the second largest classification yard west of the Rocky Mountains after the J.R. Davis Yard. Today, almost all freight traffic to and from Southern California runs through the junction.














