
Aortic stenosis is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart, such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without causing obstruction is known as aortic sclerosis.

Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of agonizing chest or back pain, often described as "tearing" in character. Vomiting, sweating, and lightheadedness may also occur. Damage to other organs may result from the decreased blood supply, such as stroke, lower extremity ischemia, or mesenteric ischemia. Aortic dissection can quickly lead to death from insufficient blood flow to the heart or complete rupture of the aorta.

Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echocardiogram, a cardiac echo, or simply an echo.
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.

A transesophageal echocardiogram is an alternative way to perform an echocardiogram. A specialized probe containing an ultrasound transducer at its tip is passed into the patient's esophagus. This allows image and Doppler evaluation which can be recorded. It is commonly used during cardiac surgery and is an excellent modality for assessing the aorta, although there are some limitations.
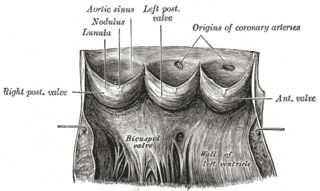
Aneurysm of the aortic sinus, also known as the sinus of Valsalva, is a rare abnormality of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The aorta normally has three small pouches that sit directly above the aortic valve, and an aneurysm of one of these sinuses is a thin-walled swelling. Aneurysms may affect the right (65–85%), non-coronary (10–30%), or rarely the left coronary sinus. These aneurysms may not cause any symptoms but if large can cause shortness of breath, palpitations or blackouts. Aortic sinus aneurysms can burst or rupture into adjacent cardiac chambers, which can lead to heart failure if untreated.

Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms. It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portuguese neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon, who also helped develop thorotrast for use in the procedure.

Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass.

Cardiac catheterization is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.

The ascending aorta (AAo) is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of the third costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum.
Coronary artery anomalies are variations of the coronary circulation, affecting <1% of the general population. Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath and syncope, although cardiac arrest may be the first clinical presentation. Several varieties are identified, with a different potential to cause sudden cardiac death.

Computed tomography angiography is a computed tomography technique used for angiography—the visualization of arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, images are created to look for blockages, aneurysms, dissections, and stenosis. CTA can be used to visualize the vessels of the heart, the aorta and other large blood vessels, the lungs, the kidneys, the head and neck, and the arms and legs. CTA can also be used to localise arterial or venous bleed of the gastrointestinal system.

Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a type of minimally-invasive endovascular surgery used to treat pathology of the aorta, most commonly an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). When used to treat thoracic aortic disease, the procedure is then specifically termed TEVAR for "thoracic endovascular aortic/aneurysm repair." EVAR involves the placement of an expandable stent graft within the aorta to treat aortic disease without operating directly on the aorta. In 2003, EVAR surpassed open aortic surgery as the most common technique for repair of AAA, and in 2010, EVAR accounted for 78% of all intact AAA repair in the United States.

Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, also known as cardiovascular MRI, is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology used for non-invasive assessment of the function and structure of the cardiovascular system. Conditions in which it is performed include congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathies and valvular heart disease, diseases of the aorta such as dissection, aneurysm and coarctation, coronary heart disease. It can also be used to look at pulmonary veins.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cardiology, the branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the human heart. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiology are called cardiologists.

Injury of the thoracic aorta refers to any injury which affects the portion of the aorta which lies within the chest cavity. Injuries of the thoracic aorta are usually the result of physical trauma; however, they can also be the result of a pathological process. The main causes of this injury are deceleration and crush injuries. There are different grades to injuries to the aorta depending on the extent of injury, and the treatment whether surgical or medical depends on that grade. It is difficult to determine if a patient has a thoracic injury just by their symptoms, but through imaging and a physical exam the extent of injury can be determined. All patients with a thoracic aortic injury need to be treated either surgically with endovascular repair or open surgical repair or with medicine to keep their blood pressure and heart rate in the appropriate range. However, most patients that have a thoracic aortic injury do not live for 24 hours.

Familial aortic dissection or FAD refers to the splitting of the wall of the aorta in either the arch, ascending or descending portions. FAD is thought to be passed down as an autosomal dominant disease and once inherited will result in dissection of the aorta, and dissecting aneurysm of the aorta, or rarely aortic or arterial dilation at a young age. Dissection refers to the actual tearing open of the aorta. However, the exact gene(s) involved has not yet been identified. It can occur in the absence of clinical features of Marfan syndrome and of systemic hypertension. Over time this weakness, along with systolic pressure, results in a tear in the aortic intima layer thus allowing blood to enter between the layers of tissue and cause further tearing. Eventually complete rupture of the aorta occurs and the pleural cavity fills with blood. Warning signs include chest pain, ischemia, and hemorrhaging in the chest cavity. This condition, unless found and treated early, usually results in death. Immediate surgery is the best treatment in most cases. FAD is not to be confused with PAU and IMH, both of which present in ways similar to that of familial aortic dissection.
Double aortic arch is a relatively rare congenital cardiovascular malformation. DAA is an anomaly of the aortic arch in which two aortic arches form a complete vascular ring that can compress the trachea and/or esophagus. Most commonly there is a larger (dominant) right arch behind and a smaller (hypoplastic) left aortic arch in front of the trachea/esophagus. The two arches join to form the descending aorta which is usually on the left side. In some cases the end of the smaller left aortic arch closes and the vascular tissue becomes a fibrous cord. Although in these cases a complete ring of two patent aortic arches is not present, the term ‘vascular ring’ is the accepted generic term even in these anomalies.
Cardiac imaging refers to minimally invasive imaging of the heart using ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), or nuclear medicine (NM) imaging with PET or SPECT. These cardiac techniques are otherwise referred to as echocardiography, Cardiac MRI, Cardiac CT, Cardiac PET and Cardiac SPECT including myocardial perfusion imaging.

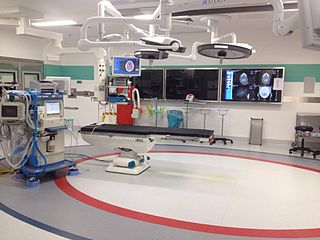
A hybrid cardiac surgical procedure in a narrow sense is defined as a procedure that combines a conventional, more invasive surgical part with an interventional part, using some sort of catheter-based procedure guided by fluoroscopy imaging in a hybrid operating room (OR) without interruption. The hybrid technique has a reduced risk of surgical complications and has shown decreased recovery time. It can be used to treat numerous heart diseases and conditions and with the increasing complexity of each case, the hybrid surgical technique is becoming more common.















