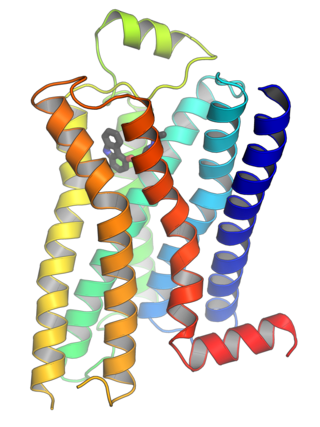
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops or to the binding site within transmembrane helices. They are all activated by agonists, although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor has also been observed.

The beta-1 adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRB1, can refer to either the protein-encoding gene or one of the four adrenergic receptors. It is a G-protein coupled receptor associated with the Gs heterotrimeric G-protein that is expressed predominantly in cardiac tissue. In addition to cardiac tissue, beta-1 adrenergic receptors are also expressed in the cerebral cortex.
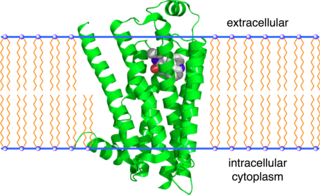
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increases cAMP, and, via downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation.

Arrestins are a small family of proteins important for regulating signal transduction at G protein-coupled receptors. Arrestins were first discovered as a part of a conserved two-step mechanism for regulating the activity of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in the visual rhodopsin system by Hermann Kühn, Scott Hall, and Ursula Wilden and in the β-adrenergic system by Martin J. Lohse and co-workers.

G protein-coupled receptor kinases are a family of protein kinases within the AGC group of kinases. Like all AGC kinases, GRKs use ATP to add phosphate to Serine and Threonine residues in specific locations of target proteins. In particular, GRKs phosphorylate intracellular domains of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GRKs function in tandem with arrestin proteins to regulate the sensitivity of GPCRs for stimulating downstream heterotrimeric G protein and G protein-independent signaling pathways.

G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADRBK1 gene. GRK2 was initially called Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase, and is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinases that is most highly similar to GRK3(βARK2).
Rhodopsin kinase is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase involved in phototransduction. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:

The alpha-2A adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRA2A, is an α2 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

The alpha-1B adrenergic receptor (α1B-adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRA1B, is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it. The crystal structure of the α1B-adrenergic receptor has been determined in complex with the inverse agonist (+)-cyclazosin.

Arrestin, beta 1, also known as ARRB1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ARRB1 gene.

This gene encodes a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and is most highly similar to GRK4 and GRK5. The protein phosphorylates the activated forms of G protein-coupled receptors to regulate their signaling.

Cytohesin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYTH2 gene.

G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinases, and is most highly similar to GRK4 and GRK6. The protein phosphorylates the activated forms of G protein-coupled receptors to regulate their signaling.

S-arrestin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SAG gene.

G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 (GRK4) is an enzyme that is encoded by the GRK4 gene in humans.

Homologous desensitization occurs when a receptor decreases its response to an agonist at high concentration. It is a process through which, after prolonged agonist exposure, the receptor is uncoupled from its signaling cascade and thus the cellular effect of receptor activation is attenuated.

The G beta-gamma complex (Gβγ) is a tightly bound dimeric protein complex, composed of one Gβ and one Gγ subunit, and is a component of heterotrimeric G proteins. Heterotrimeric G proteins, also called guanosine nucleotide-binding proteins, consist of three subunits, called alpha, beta, and gamma subunits, or Gα, Gβ, and Gγ. When a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) is activated, Gα dissociates from Gβγ, allowing both subunits to perform their respective downstream signaling effects. One of the major functions of Gβγ is the inhibition of the Gα subunit.
G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 7 is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase involved in phototransduction. This enzyme catalyses the phosphorylation of cone (color) photopsins in retinal cones during high acuity color vision primarily in the fovea.

G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 3 (GRK3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADRBK2 gene. GRK3 was initially called Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 (βARK-2), and is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinases that is most highly similar to GRK2.
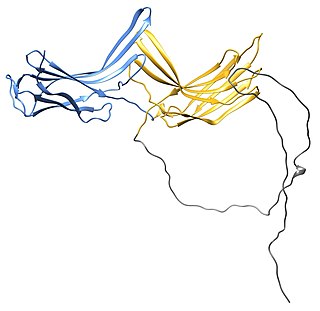
The arrestin family of proteins is subdivided into α-arrestins (also referred to as arrestin-related trafficking adaptors or arrestin-like yeast proteins in yeast or ARRDCs in mammals, β-arrestins and Vps26-like arrestins proteins. The α-Arrestins are an ancestral branch of the larger arrestin family of proteins and they are conserved across eukaryotes but are best characterized in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae; to-date there are 6 α-arrestins identified in mammalian cells and 14 α-arrestins identified in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The yeast α-arrestin family comprises Ldb19/Art1, Ecm21/Art2, Aly1/Art6, Aly2/Art3, Rod1/Art4, Rog3/Art7, Art5, Csr2/Art8, Rim8/Art9, Art10, Bul1, Bul2, Bul3 and Spo23. The best characterized α-arrestin function to date is their endocytic regulation of plasma membrane proteins, including G-protein coupled receptors and nutrient transporters. α-Arrestins control endocytosis of these membrane proteins in response to cellular stressors, including nutrient or metal ion excess.




















