
An axon, or nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons, such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types – group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. These groups include both sensory fibers and motor fibers. Another classification groups only the sensory fibers as Type I, Type II, Type III, and Type IV.

Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses pass along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin ensheaths the axon segmentally: in general, each axon is encased in multiple long sheaths with short gaps between, called nodes of Ranvier. At the nodes of Ranvier, which are approximately one thousandth of a mm in length, the axon's membrane is bare of myelin.
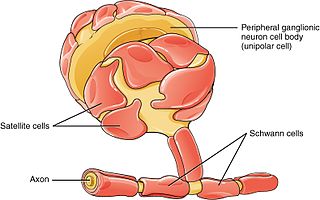
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory ensheathing cells, enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings, such as the Pacinian corpuscle. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating. Myelinating Schwann cells wrap around axons of motor and sensory neurons to form the myelin sheath. The Schwann cell promoter is present in the downstream region of the human dystrophin gene that gives shortened transcript that are again synthesized in a tissue-specific manner.
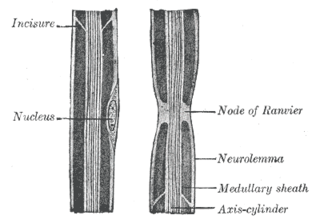
In neuroscience and anatomy, nodes of Ranvier, also known as myelin-sheath gaps, occur along a myelinated axon where the axolemma is exposed to the extracellular space. Nodes of Ranvier are uninsulated and highly enriched in ion channels, allowing them to participate in the exchange of ions required to regenerate the action potential. Nerve conduction in myelinated axons is referred to as saltatory conduction due to the manner in which the action potential seems to "jump" from one node to the next along the axon. This results in faster conduction of the action potential.

Wallerian degeneration is an active process of degeneration that results when a nerve fiber is cut or crushed and the part of the axon distal to the injury degenerates. A related process of dying back or retrograde degeneration known as 'Wallerian-like degeneration' occurs in many neurodegenerative diseases, especially those where axonal transport is impaired such as ALS and Alzheimer's disease. Primary culture studies suggest that a failure to deliver sufficient quantities of the essential axonal protein NMNAT2 is a key initiating event.
A neurite or neuronal process refers to any projection from the cell body of a neuron. This projection can be either an axon or a dendrite. The term is frequently used when speaking of immature or developing neurons, especially of cells in culture, because it can be difficult to tell axons from dendrites before differentiation is complete.

The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) was first identified in 1973 as the low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (LNGFR) before discovery that p75NTR bound other neurotrophins equally well as nerve growth factor. p75NTR is a neurotrophic factor receptor. Neurotrophic factor receptors bind Neurotrophins including Nerve growth factor, Neurotrophin-3, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and Neurotrophin-4. All neurotrophins bind to p75NTR. This also includes the immature pro-neurotrophin forms. Neurotrophic factor receptors, including p75NTR, are responsible for ensuring a proper density to target ratio of developing neurons, refining broader maps in development into precise connections. p75NTR is involved in pathways that promote neuronal survival and neuronal death.

Nerve injury is an injury to nervous tissue. There is no single classification system that can describe all the many variations of nerve injuries. In 1941, Seddon introduced a classification of nerve injuries based on three main types of nerve fiber injury and whether there is continuity of the nerve. Usually, however, peripheral nerve injuries are classified in five stages, based on the extent of damage to both the nerve and the surrounding connective tissue, since supporting glial cells may be involved.
Neuroregeneration involves the regrowth or repair of nervous tissues, cells or cell products. Neuroregenerative mechanisms may include generation of new neurons, glia, axons, myelin, or synapses. Neuroregeneration differs between the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and the central nervous system (CNS) by the functional mechanisms involved, especially in the extent and speed of repair. When an axon is damaged, the distal segment undergoes Wallerian degeneration, losing its myelin sheath. The proximal segment can either die by apoptosis or undergo the chromatolytic reaction, which is an attempt at repair. In the CNS, synaptic stripping occurs as glial foot processes invade the dead synapse.

The subcommissural organ (SCO) is one of the circumventricular organs of the brain. It is a small glandular structure that is located in the posterior region of the third ventricle, near the entrance of the cerebral aqueduct.
Reticulon 4, also known as Neurite outgrowth inhibitor or Nogo, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RTN4 gene that has been identified as an inhibitor of neurite outgrowth specific to the central nervous system. During neural development Nogo is expressed mainly by neurons and provides an inhibitory signal for the migration and sprouting of CNS endothelial (tip) cells, thereby restricting blood vessel density.

Reticulon 4 receptor (RTN4R) also known as Nogo-66 Receptor (NgR) or Nogo receptor 1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the RTN4R gene. This gene encodes the receptor for reticulon 4, oligodendrocytemyelin glycoprotein and myelin-associated glycoprotein. This receptor mediates axonal growth inhibition and may play a role in regulating axonal regeneration and plasticity in the adult central nervous system.

Semaphorin-3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEMA3A gene.

Leucine rich repeat and Immunoglobin-like domain-containing protein 1 also known as LINGO-1 is a protein which is encoded by the LINGO1 gene in humans. It belongs to the family of leucine-rich repeat proteins which are known for playing key roles in the biology of the central nervous system. LINGO-1 is a functional component of the Nogo receptor also known as the reticulon 4 receptor.
Reticulons are a group of evolutionary conservative proteins residing predominantly in endoplasmic reticulum, primarily playing a role in promoting membrane curvature. In addition, reticulons may play a role in nuclear pore complex formation, vesicle formation, and other processes yet to be defined. They have also been linked to oligodendrocyte roles in inhibition of neurite outgrowth. Some studies link RTNs with Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
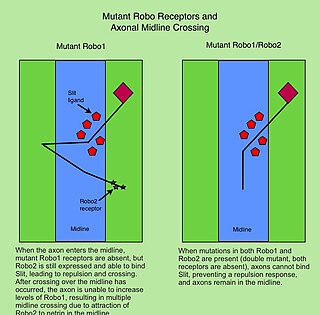
The Roundabout (Robo) family of proteins are single-pass transmembrane receptors that are highly conserved across many branches of the animal kingdom, from C. elegans to humans. They were first discovered in Drosophila, through a mutant screen for genes involved in axon guidance. The Drosophila roundabout mutant was named after its phenotype, which resembled the circular traffic junctions. The Robo receptors are most well known for their role in the development of the nervous system, where they have been shown to respond to secreted Slit ligands. One well-studied example is the requirement for Slit-Robo signaling in regulation of axonal midline crossing. Slit-Robo signaling is also critical for many neurodevelopmental processes including formation of the olfactory tract, the optic nerve, and motor axon fasciculation. In addition, Slit-Robo signaling contributes to cell migration and the development of other tissues such as the lung, kidney, liver, muscle and breast. Mutations in Robo genes have been linked to multiple neurodevelopmental disorders in humans.
Collapsin response mediator protein family or CRMP family consists of five intracellular phosphoproteins of similar molecular size and high (50–70%) amino acid sequence identity. CRMPs are predominantly expressed in the nervous system during development and play important roles in axon formation from neurites and in growth cone guidance and collapse through their interactions with microtubules. Cleaved forms of CRMPs have also been linked to neuron degeneration after trauma induced injury.

Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) are proteoglycans consisting of a protein core and a chondroitin sulfate side chain. They are known to be structural components of a variety of human tissues, including cartilage, and also play key roles in neural development and glial scar formation. They are known to be involved in certain cell processes, such as cell adhesion, cell growth, receptor binding, cell migration, and interaction with other extracellular matrix constituents. They are also known to interact with laminin, fibronectin, tenascin, and collagen. CSPGs are generally secreted from cells.

Olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs), also known as olfactory ensheathing glia or olfactory ensheathing glial cells, are a type of macroglia found in the nervous system. They are also known as olfactory Schwann cells, because they ensheath the non-myelinated axons of olfactory neurons in a similar way to which Schwann cells ensheath non-myelinated peripheral neurons. They also share the property of assisting axonal regeneration.
Anti-MAG peripheral neuropathy is a specific type of peripheral neuropathy in which the person's own immune system attacks cells that are specific in maintaining a healthy nervous system. As these cells are destroyed by antibodies, the nerve cells in the surrounding region begin to lose function and create many problems in both sensory and motor function. Specifically, antibodies against myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) damage Schwann cells. While the disorder occurs in only 10% of those afflicted with peripheral neuropathy, people afflicted have symptoms such as muscle weakness, sensory problems, and other motor deficits usually starting in the form of a tremor of the hands or trouble walking. There are, however, multiple treatments that range from simple exercises in order to build strength to targeted drug treatments that have been shown to improve function in people with this type of peripheral neuropathy.


















