| |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Qvar, Beconase AQ, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a681047 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | inhalation, nasal, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Converted to beclometasone-17-monopropionate (17-BMP) during absorption |
| Protein binding | 87% of 17-BMP to albumin and transcortin |
| Metabolism | By esterase enzymes found in most tissues |
| Elimination half-life | 2.8 hours |
| Excretion | Biliary (60%), renal (12%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.442 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
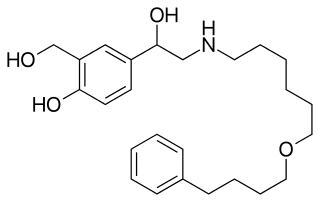
| Formula | C28H37ClO7 |
| Molar mass | 521.042 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
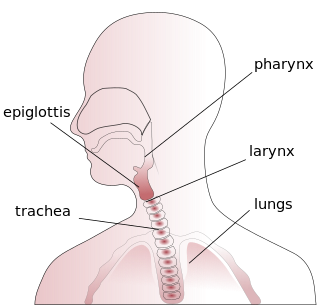
Beclometasone dipropionate, also spelled beclomethasone dipropionate and sold under the brand name Qvar among others, is a steroid medication. [1] It is available as an inhaler, cream, pills, and nasal spray. [2] The inhaled form is used in the long-term management of asthma. [1] The cream may be used for dermatitis and psoriasis. [3] The pills have been used to treat ulcerative colitis. [4] The nasal spray is used to treat allergic rhinitis and nasal polyps. [5]

Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior.

An inhaler is a medical device used for delivering medication into the body via the lungs. It is mainly used in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zanamivir, used to treat influenza, must be administered via inhaler.

Nasal sprays, are used to deliver medications locally in the nasal cavities or systemically. They are used locally for conditions such as nasal congestion and allergic rhinitis. In some situations, the nasal delivery route is preferred for systemic therapy because it provides an agreeable alternative to injection or pills. Substances can be assimilated extremely quickly and directly through the nose. Many pharmaceutical drugs exist as nasal sprays for systemic administration. Other applications include hormone replacement therapy, treatment of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Nasal sprays are seen as a more efficient way of transporting drugs with potential use in crossing the blood–brain barrier.
Contents
Common side effects with the inhaled form include respiratory infections, headaches, and throat inflammation. [1] Serious side effects include an increased risk of infection, cataracts, Cushing’s syndrome, and severe allergic reactions. [1] Long-term use of the pill form may cause adrenal insufficiency. [4] The pills may also cause mood or personality changes. [4] The inhaled form is generally regarded as safe in pregnancy. [6] Beclometasone is mainly a glucocorticoid. [1]

Respiratory tract infection (RTI) refers to any of a number of infectious diseases involving the respiratory tract. An infection of this type is normally further classified as an upper respiratory tract infection or a lower respiratory tract infection. Lower respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, tend to be far more serious conditions than upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold.
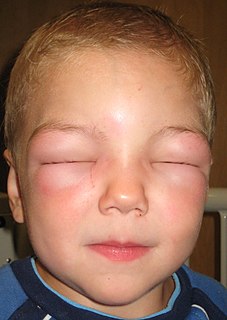
Anaphylaxis is a serious allergic reaction that is rapid in onset and may cause death. It typically causes more than one of the following: an itchy rash, throat or tongue swelling, shortness of breath, vomiting, lightheadedness, and low blood pressure. These symptoms typically come on over minutes to hours.
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones, primarily cortisol; but may also include impaired production of aldosterone, which regulates sodium conservation, potassium secretion, and water retention. Craving for salt or salty foods due to the urinary losses of sodium is common.
Beclometasone dipropionate was first patented in 1962 and used medically in 1972. [7] It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1976. [1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. [8] The wholesale price in the developing world for an inhaler containing 200 doses of medication is about US$3.20 as of 2014. [9] In the United States it costs between 50 and US$100 for a typical month supply of the inhaled form. [10]
A health system, also sometimes referred to as health care system or as healthcare system, is the organization of people, institutions, and resources that deliver health care services to meet the health needs of target populations.