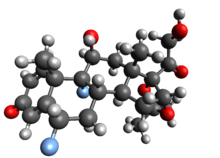
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior.

Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cava syndrome, and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis. In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone. In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby. It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye. The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days.

Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and adrenal insufficiency along with other steroids. It is taken by mouth.

Macular edema occurs when fluid and protein deposits collect on or under the macula of the eye and causes it to thicken and swell (edema). The swelling may distort a person's central vision, because the macula holds tightly packed cones that provide sharp, clear, central vision to enable a person to see detail, form, and color that is directly in the centre of the field of view.
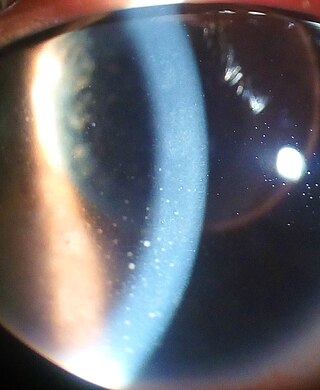
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis (iridocyclitis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms may be overcome resulting in inflammation and tissue destruction associated with T-cell activation.

Betamethasone dipropionate is a glucocorticoid steroid with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive abilities. It is applied as a topical cream, ointment, lotion or gel (Diprolene) to treat itching and other skin conditions such as eczema. Minor side effects include dry skin and mild, temporary stinging when applied. Betamethasone dipropionate is a "super high potency" corticosteroid used to treat inflammatory skin conditions such as dermatitis, eczema and psoriasis. It is a synthetic analog of the adrenal corticosteroids. Although its exact mechanism of action is not known, it is effective when applied topically to cortico-responsive inflammatory dermatoses. It is available as a generic medication.

Triamcinolone acetonide, sold under the brand name Kenalog among others, is a synthetic corticosteroid medication used topically to treat various skin conditions, to relieve the discomfort of mouth sores, and by injection into joints to treat various joint conditions. It is also injected into lesions to treat inflammation in some parts of the body, particularly the skin. In nasal spray form, it is used to treat allergic rhinitis. It is used for the treatment of macular edema associated with uveitis. It is a more potent derivative of triamcinolone, and is about eight times as potent as prednisone.

Ganciclovir, sold under the brand name Cytovene among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections.
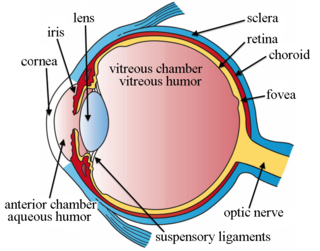
Intravitreal is a route of administration of a drug, or other substance, in which the substance is delivered into the vitreous humor of the eye. "Intravitreal" literally means "inside an eye". Intravitreal injections were first introduced in 1911 when Ohm gave an injection of air into the vitreous humor to repair a detached retina. In the mid-1940s, intravitreal injections became a standard way to administer drugs to treat endophthalmitis and cytomegalovirus retinitis.
Acne medicamentosa is acne that is caused or aggravated by medication. Because acne is generally a disorder of the pilosebaceous units caused by hormones, the medications that trigger acne medicamentosa most frequently are hormone analogs. It is also often caused by corticosteroids; in this case, it is referred to as steroid acne.
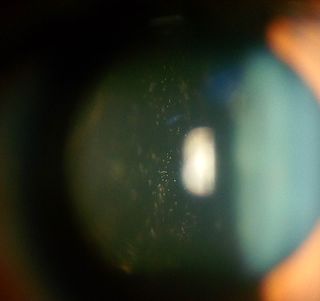
Intermediate uveitis is a form of uveitis localized to the vitreous and peripheral retina. Primary sites of inflammation include the vitreous of which other such entities as pars planitis, posterior cyclitis, and hyalitis are encompassed. Intermediate uveitis may either be an isolated eye disease or associated with the development of a systemic disease such as multiple sclerosis or sarcoidosis. As such, intermediate uveitis may be the first expression of a systemic condition. Infectious causes of intermediate uveitis include Epstein–Barr virus infection, Lyme disease, HTLV-1 virus infection, cat scratch disease, and hepatitis C.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent cells found in multiple human adult tissues, including bone marrow, synovial tissues, and adipose tissues. Since they are derived from the mesoderm, they have been shown to differentiate into bone, cartilage, muscle, and adipose tissue. MSCs from embryonic sources have shown promise scientifically while creating significant controversy. As a result, many researchers have focused on adult stem cells, or stem cells isolated from adult humans that can be transplanted into damaged tissue.
Topical steroids are the topical forms of corticosteroids. Topical steroids are the most commonly prescribed topical medications for the treatment of rash and eczema. Topical steroids have anti-inflammatory properties and are classified based on their skin vasoconstrictive abilities. There are numerous topical steroid products. All the preparations in each class have the same anti-inflammatory properties but essentially differ in base and price.

Alimera Sciences, Inc. is a biopharmaceutical sales company based in Alpharetta, Georgia that specializes in the commercialization and sales of prescription ophthalmic pharmaceuticals. The company's main selling focus is on diseases affecting the back of the eye, or retina. The company is the licensee for Iluvien, a fluocinolone acetonide intravitreal implant.

Intravitreal injection is the method of administration of drugs into the eye by injection with a fine needle. The medication will be directly applied into the vitreous humor. It is used to treat various eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, and infections inside the eye such as endophthalmitis. As compared to topical administration, this method is beneficial for a more localized delivery of medications to the targeted site, as the needle can directly pass through the anatomical eye barrier and dynamic barrier. It could also minimize adverse drug effects on other body tissues via the systemic circulation, which could be a possible risk for intravenous injection of medications. Although there are risks of infections or other complications, with suitable precautions throughout the injection process, chances for these complications could be lowered.

Topical glucocorticoids are the topical forms of glucocorticoids. Topical glucocorticoids are used in the treatment of many skin conditions. They provide anti-inflammatory, antimitotic, and immune-system suppressing actions through various mechanisms.

Secondary glaucoma is a collection of progressive optic nerve disorders associated with a rise in intraocular pressure (IOP) which results in the loss of vision. In clinical settings, it is defined as the occurrence of IOP above 21 mmHg requiring the prescription of IOP-managing drugs. It can be broadly divided into two subtypes: secondary open-angle glaucoma and secondary angle-closure glaucoma, depending on the closure of the angle between the cornea and the iris. Principal causes of secondary glaucoma include optic nerve trauma or damage, eye disease, surgery, neovascularization, tumours and use of steroid and sulfa drugs. Risk factors for secondary glaucoma include uveitis, cataract surgery and also intraocular tumours. Common treatments are designed according to the type and the underlying causative condition, in addition to the consequent rise in IOP. These include drug therapy, the use of miotics, surgery or laser therapy.

Uveitic glaucoma is most commonly a progression stage of noninfectious anterior uveitis or iritis.

Intravitreal implants are micro device-like inserts injected into the posterior segment of the eye to treat retinal diseases releasing therapeutic drugs at a set rate over a desired period of time. The posterior segment of the eye consists of the sclera, choroid, fovea, vitreous humor, optic nerve, and retina.