
Ahab was the son and successor of King Omri and the husband of Jezebel of Sidon, according to the Hebrew Bible. He was widely criticized for causing "moral decline" in Israel, according to the Yahwists. But modern scholars argue that Ahab was a Yahwist and introduced his god to the Kingdom of Judah via imperialism. This mostly occurred in the latter half of his reign.
The Book of Amos is the third of the Twelve Minor Prophets in the Old Testament (Tanakh) and the second in the Greek Septuagint tradition. According to the Bible, Amos was an older contemporary of Hosea and Isaiah, and was active c. 750 BC during the reign of Jeroboam II of Samaria, while Uzziah was King of Judah. Amos is said to have lived in the kingdom of Judah but preached in the northern Kingdom of Israel with themes of social justice, God's omnipotence, and divine judgment became staples of prophecy. In recent years, scholars have grown more skeptical of The Book of Amos’ presentation of Amos’ biography and background. It is known for its distinct “sinister tone and violent portrayal of God.”
The Book of Jeremiah is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, and the second of the Prophets in the Christian Old Testament. The superscription at chapter Jeremiah 1:1–3 identifies the book as "the words of Jeremiah son of Hilkiah". Of all the prophets, Jeremiah comes through most clearly as a person, ruminating to his scribe Baruch about his role as a servant of God with little good news for his audience.
The Book of Micah is the sixth of the twelve minor prophets in the Hebrew Bible. Ostensibly, it records the sayings of Micah, whose name is Mikayahu, meaning "Who is like Yahweh?", an 8th-century BCE prophet from the village of Moresheth in Judah.
The Book of Malachi is the last book of the Neviim contained in the Tanakh, canonically the last of the Twelve Minor Prophets. In most Christian orderings, the grouping of the prophetic books is the last section of the Old Testament, making Malachi the last book before the New Testament.

Deuteronomy is the fifth book of the Torah, where it is called Devarim and the fifth book of the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament.

In the Hebrew Bible, Hosea, also known as Osee, son of Beeri, was an 8th-century BCE prophet in Israel and the nominal primary author of the Book of Hosea. He is the first of the Twelve Minor Prophets, whose collective writings were aggregated and organized into a single book in the Jewish Tanakh by the Second Temple period but which are distinguished as individual books in Christianity. Hosea is often seen as a "prophet of doom", but underneath his message of destruction is a promise of restoration. The Talmud claims that he was the greatest prophet of his generation. The period of Hosea's ministry extended to some sixty years, and he was the only prophet of Israel of his time who left any written prophecy. Though its date is contested among scholars, the majority agree that the bulk of the book was probably composed around the times of Jeroboam II of Israel.

Yahweh was an ancient Levantine deity, and national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Though no consensus exists regarding the deity's origins, scholars generally contend that Yahweh is associated with Seir, Edom, Paran and Teman, and later with Canaan. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age, if not somewhat earlier.
The Nevi'im is the second major division of the Hebrew Bible, lying between the Torah ("instruction") and Ketuvim ("writings"). The Nevi'im are divided into two groups. The Former Prophets consists of the narrative books of Joshua, Judges, Samuel and Kings; while the Latter Prophets include the books of Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel, and the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Baal, or Baʻal, was a title and honorific meaning 'owner' or 'lord' in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied to gods. Scholars previously associated the theonym with solar cults and with a variety of unrelated patron deities, but inscriptions have shown that the name Ba'al was particularly associated with the storm and fertility god Hadad and his local manifestations.

Jeremiah, also called Jeremias or the "weeping prophet", was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition, Jeremiah authored the book that bears his name, the Books of Kings and the Book of Lamentations, with the assistance and under the editorship of Baruch ben Neriah, his scribe and disciple.
The Deuteronomist, abbreviated as either Dtr or simply D, may refer either to the source document underlying the core chapters (12–26) of the Book of Deuteronomy, or to the broader "school" that produced all of Deuteronomy as well as the Deuteronomistic history of Joshua, Judges, Samuel, Kings, and also the Book of Jeremiah. The adjectives "Deuteronomic" and "Deuteronomistic" are sometimes used interchangeably; if they are distinguished, then the first refers to the core of Deuteronomy and the second to all of Deuteronomy and the history.

According to the Bible and the Quran, the golden calf was a cult image made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as "the sin of the calf". It is first mentioned in the Book of Exodus.

Jezebel was the daughter of Ithobaal I of Tyre and the wife of Ahab, King of Israel, according to the Book of Kings of the Hebrew Bible.

The Exodus is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four of the five books of the Pentateuch.

The origins of Judaism lie in Bronze Age polytheistic Canaanite religion. Judaism also syncretized elements of other Semitic religions such as Babylonian religion, which is reflected in the early prophetic books of the Hebrew Bible.

Hosea 1 is the first chapter of the Book of Hosea in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet Hosea, son of Beeri, and this chapter especially sets forth the spiritual whoredom of Israel by symbolical acts. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Hosea 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Hosea in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet Hosea, son of Beeri, and this chapter contains the application of the symbols in the first chapter. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Jeremiah 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Jeremiah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains prophecies attributed to the prophet Jeremiah, and is one of the Books of the Prophets. Chapters 2 to 6 contain the earliest preaching of Jeremiah on the apostasy of Israel. Verses 2:1 to 3:5 dramatize the ending of "marriage" between Yahweh and Israel.
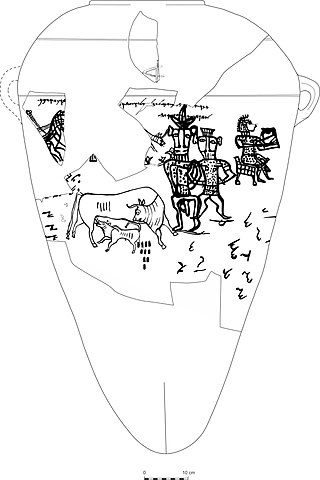
Yahwism, as it is called by modern scholars, was the religion of ancient Israel and Judah. An ancient Semitic religion of the Iron Age, Yahwism was essentially polytheistic and had a pantheon, with various gods and goddesses being worshipped by the Israelites. At the head of this pantheon was Yahweh—held in an especially high regard as the two Israelite kingdoms' national god—and his consort Asherah. Following this duo were second-tier gods and goddesses, such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, each of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees.















