
Upminster Windmill is a Grade II* listed smock mill located in Upminster in the London Borough of Havering, England. It was formerly known as Abraham's Mill and was in Essex when built. It has been restored and is a museum open to the public at selected times.

Denver Windmill is a Grade II* listed tower mill at Denver, Norfolk, England. In March 2010, there were about 374,000 list entries of which 5.5% were Grade II* and even fewer were superior.

Great Bircham Windmill is a Grade II listed tower mill in Great Bircham, Norfolk, England.

Caston Tower Windmill is a grade II* listed tower mill at Caston, Norfolk, England which is under restoration. The mill is also a scheduled monument.
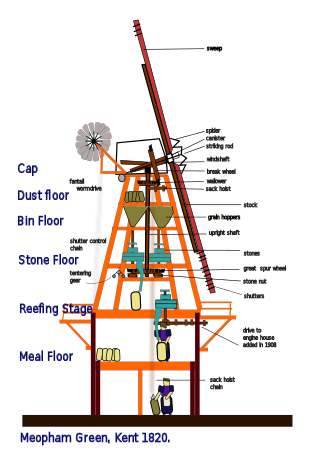
This glossary of mill machinery covers the major pieces of machinery to be found in windmills, watermills and horse mills. It does not cover machinery found in modern factories.

Cley Windmill is a Grade II* listed tower mill at Cley next the Sea, Norfolk, England which has been converted to residential accommodation.

Union Mill is a Grade I listed smock mill in Cranbrook, Kent, England, which has been restored to working order. It is the tallest smock mill in the United Kingdom.

Charing Windmill is a Grade II listed smock windmill, now converted to a house, on Charing Hill in Kent in southeast England. It is sometimes known as Field Mill, but that name was also used by a watermill in Charing.

Swingate Mill is a Grade II listed tower mill in Guston, Kent, England that was built in 1849.

New Mill is a Grade II listed smock mill in Northbourne, Kent, England that was built in 1848 and which has been converted to residential accommodation.
Stanford Windmill is a Grade II* listed tower mill in Stanford, Kent, England that was built in 1857. It stands on Kennett Lane in Stanford.

Thelnetham Windmill, also known as Button's Mill is a Grade II* listed tower mill constructed of brick. The windmill is located at Thelnetham, Suffolk, England. It was built in the early nineteenth century to grind wheat into flour. Thelnetham windmill worked by wind power until 1924, latterly on two sails, after which it became derelict.

Cawston Road Mill is a tower mill at Aylsham, Norfolk, England which has been truncated and converted for use as a holiday home.

Union Mills or Roy's Mills are a Grade II listed combined tower mill and watermill at Burnham Overy, Norfolk, England which has been converted to residential accommodation.
Mill Lane Mill is a Grade II listed tower mill at Carbrooke, Norfolk, England which has been conserved with some machinery remaining.

Jay's Mill, Button's Mill or Victoria Road Mill is a tower mill at Diss, Norfolk, England which has been truncated and converted to residential accommodation.
Kenninghall Road Mill is a Grade II listed tower mill at East Harling, Norfolk, England which has been converted to residential accommodation.

Frettenham Mill is a Grade II listed tower mill at Frettenham, Norfolk, England which has been converted to residential accommodation.

Garboldisham Mill is a Grade II* listed post mill at Garboldisham, Norfolk, that has been restored.

For the Gayton Windmill now in Merseyside see Gayton Windmill, Cheshire


















