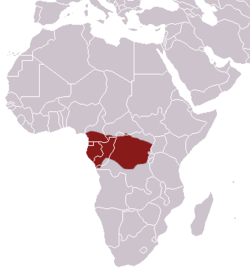
Taxonomy
The Central African oyan or "Richardson's genette" was first described in 1842 as Genetta richardsonii, in honour of John Richardson, by T. R. H. Thomson, based on a zoological specimen collected in Fernando Po. [7] In an 1864 paper, published the following year, John Edward Gray transferred the species from Genetta to his newly erected genus Poiana . [8] : 520 [9] In 1907, Oldfield Thomas and Robert Charles Wroughton described a new subspecies, Poiana Richardsoni ochracea, in the original orthography, from the area of the Aruwimi River near Yambuya, in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. [10] : 372 In a paper read at the 26 November 1907 meeting of the Zoological Society of London and published the following year, Reginald Innes Pocock described a further subspecies based on a specimen collected in Liberia, Poiana richardsoni leightoni, but in 1974 Donovan Reginald Rosevear elevated "Leighton's linsang" or the West African oyan from subspecies to independent species rank. [11] [12]
Two subspecies are recognized: [2] [13]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.