
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.

A mouth ulcer (aphtha) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause. Rarely, a mouth ulcer that does not heal may be a sign of oral cancer. These ulcers may form individually or multiple ulcers may appear at once. Once formed, an ulcer may be maintained by inflammation and/or secondary infection.

In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.

The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.

Cat anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic cat, which are similar to those of other members of the genus Felis.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved.

Equine anatomy encompasses the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses, ponies and other equids, including donkeys, mules and zebras. While all anatomical features of equids are described in the same terms as for other animals by the International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature in the book Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria, there are many horse-specific colloquial terms used by equestrians.
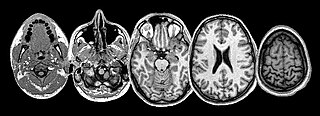
This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.
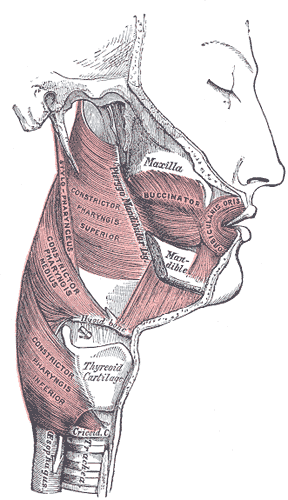
The buccal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe.

The mouth is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity, is also the first part of the alimentary canal, which leads to the pharynx and the gullet. In tetrapod vertebrates, the mouth is bounded on the outside by the lips and cheeks — thus the oral cavity is also known as the buccal cavity — and contains the tongue on the inside. Except for some groups like birds and lissamphibians, vertebrates usually have teeth in their mouths, although some fish species have pharyngeal teeth instead of oral teeth.
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body.
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth, jaws and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin. The mouth is an important organ with many different functions. It is also prone to a variety of medical and dental disorders.
Morsicatio buccarum is a condition characterized by chronic irritation or injury to the buccal mucosa, caused by repetitive chewing, biting, or nibbling.
The cheek constitutes the facial periphery and plays a key role in the maintenance of oral competence and mastication. It is also involved in the facial manifestation of human emotion and supports neighboring primary structures.

In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.

Cheek pouches are pockets on both sides of the head of some mammals between the jaw and the cheek. They can be found on mammals including the platypus, some rodents, and most monkeys, as well as the marsupial koala. The cheek pouches of chipmunks can reach the size of their body when full.

Lingual papillae are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circumvallate, fungiform, filiform, and foliate. All except the filiform papillae are associated with taste buds.
Buccal administration is a topical route of administration by which drugs held or applied in the buccal area diffuse through the oral mucosa and enter directly into the bloodstream. Buccal administration may provide better bioavailability of some drugs and a more rapid onset of action compared to oral administration because the medication does not pass through the digestive system and thereby avoids first pass metabolism. Drug forms for buccal administration include tablets and thin films.
Fascial spaces are potential spaces that exist between the fasciae and underlying organs and other tissues. In health, these spaces do not exist; they are only created by pathology, e.g. the spread of pus or cellulitis in an infection. The fascial spaces can also be opened during the dissection of a cadaver. The fascial spaces are different from the fasciae themselves, which are bands of connective tissue that surround structures, e.g. muscles. The opening of fascial spaces may be facilitated by pathogenic bacterial release of enzymes which cause tissue lysis. The spaces filled with loose areolar connective tissue may also be termed clefts. Other contents such as salivary glands, blood vessels, nerves and lymph nodes are dependent upon the location of the space. Those containing neurovascular tissue may also be termed compartments.

The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion. Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase.















