
Hyder Ali was the Sultan and de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers. Rising to the post of Dalavayi (commander-in-chief) to Krishnaraja Wodeyar II, he came to dominate the titular monarch and the Mysore government. He became the de facto ruler, King of Mysore as Sarvadhikari by 1761. During intermittent conflicts against the East India Company during the First and Second Anglo–Mysore Wars, Hyder Ali was the military leader.

Kodagu district is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.

Madikeri is city and headquarters of Kodagu district in the Karnataka state of India. It is recognised as one of the world's eight "hottest hotspots" of biological diversity and also one of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The city is ranked 1st in India for having cleanest air and best AQI in 2024.
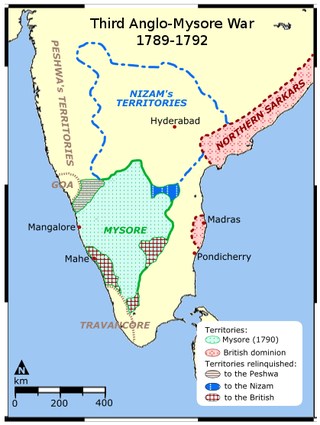
The Third Anglo-Mysore War (1790–1792) was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, the Kingdom of Travancore, the Maratha Confederacy, and the Nizam of Hyderabad. It was the third of four Anglo-Mysore Wars.

The Kodavas also called Coorgs are an endogamous Dravidian ethnolinguistic group from the region of Kodagu in the southern Indian state of Karnataka, who natively speak the Kodava language. Kodavas worship ancestors, nature, and weapons such as swords, bows, arrows, and later guns.

The district of Kodagu in present-day Karnataka comprises the area of the former princely state of the same name.

Rama Varma I often referred to as Dharma Raja, was the Maharajah of Travancore from 1758 until his death in 1798. He succeeded his uncle Marthanda Varma, who is credited with the title of "maker of modern Travancore". During his reign Dharma Raja not only retained all the territories his predecessor had gained but administered the kingdom with success. He was addressed as Dharma Raja on account of his strict adherence to Dharma Sastra, the Hindu principles of justice by providing asylum to thousands of Hindus and Christians fleeing Malabar during the Mysorean conquest of Malabar.

Velayudhan Chempakaraman Thampi ofThalakulam (1765–1809) was the Dalawa or Prime Minister of the Indian kingdom of Travancore between 1802 and 1809 during the reign of Bala Rama Varma Kulasekhara Perumal. He is best known for being one of the earliest individuals to rebel against the British East India Company's authority in India.
The captivity of Kodavas (Coorgis) at Seringapatam was the period of capture, deportation, and imprisonment of Kodava Takk speaking kodavas who rebelled against Tippu Sultan, the de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore, they (60,000-70,000) were caught during a number of attempts to suppress their rebellion in the 1780s.

The siege of Trichinopoly (1751–1752) was conducted by Chanda Sahib, who had been recognized as the Nawab of the Carnatic by representatives of the French East India Company, against the fortress town of Tiruchirappalli, held by Muhammed Ali Khan Wallajah.
Dewan Bahadur Ketolira Chengappa, C.I.E. (1878–1963) was an Indian civil servant and administrator who served as the Chief Commissioner of Coorg Province from 1943 to 1949.

Coorg State was a Part-C state in India which existed from 1950 to 1956. When the Constitution of India came into force on 26 January 1950, most of the existing provinces were reconstituted into states. Thus, Coorg Province became Coorg State. Coorg State was ruled by a Chief Commissioner with Mercara as its capital. The head of the government was the Chief Minister. Coorg State was abolished on 1 November 1956 as per the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 and its territory was merged with Mysore State. Currently, Coorg forms a district of Karnataka state.

Coorg Province was a province of British India from 1834 to 1947 and the Dominion of India from 1947 to 1950. Mercara was the capital of the province. It was administered by a Commissioner and later, Chief Commissioner appointed by the Government of India. The Chief Commissioner, was usually based in Bangalore. From 1834 to 1881, the Chief Commissioner, was also the Commissioner of Mysore. From 1881 to 1940, the Chief Commissioner was usually the British Resident to the princely state of Mysore.

Victoria Gouramma was an Indian princess.

The Kingdom of Coorg was an independent kingdom that existed in India from the 16th century until 1834. It was ruled by a branch of the Ikkeri Nayaka. From 1780 to 1788, the kingdom was occupied by neighbouring Mysore but the Rajah of Coorg was restored by the British and became a protectorate of the British East India Company on 26 October 1790. In 1834, the then Raja of Coorg rebelled against British authority, sparking the Coorg War. The brief conflict led to the British to annex the kingdom in the same year, who transformed the region into a province of British India.

The St. Mark's Church, is located within the Mercara Fort, Coorg, India and was raised in 1859, by the officers and men of the East India Company. The church building was funded by the Government of Madras, and placed under the Church of England in India, Diocese of Madras. The Church was closed after Indian independence, and taken over by the Government of Karnataka in 1971. The building now houses the Madikeri Fort Museum, managed by the Karnataka State Archaeological Department.

The Amara Sullia Rebellion was an armed uprising against the British government organized by the people of Arebhashe, and Tulunadu that took place in 1837, twenty years before the Sepoy Mutiny of 1857.
Kalyatanda Ponnappa was a 17th-century warrior of Kodagu (Coorg). Since he was deified after his death, the people of Kodagu consider him to be a god. He is also known as Kaliat-Achchappa or Kaliat Ajjappa.

Mathanda Appachu was an Indian warrior and freedom fighter. He was an officer in Chikka Vira Rajendra's army. He was from Bollumad village in Beppunad in Kodagu. He was also known as Madanta Appachu. He defeated the British in battle in 1834.
Kannanda Doddayya was a Kodava commander who defeated Hyder Ali's forces thrice. He was also known as Kannana Doddayya and Doddanna.


















