
Kannada, previously also known as Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a second or third language for around 15 million non-native speakers in Karnataka.

Kannada literature is the corpus of written forms of the Kannada language, spoken mainly in the Indian state of Karnataka and written in the Kannada script.
Kāvya refers to the Sanskrit literary style used by Indian court poets flourishing between c.200 BCE and 1200 CE.

Cāmuṇḍarāya or Chavundaraya was an Indian Jain ruler. He served in the court of the Western Ganga dynasty of Talakad. A person of many talents, in 981 he commissioned the construction of the monolithic statue of Bahubali, the Gomateshwara, at Shravanabelagola, an important place of pilgrimage for Jainism. He was a devotee of the Jain Acharya Nemichandra and Ajitasena Bhattaraka and was an influential person during the reigns of Marasimha II Satyavakya, (963–975). Rachamalla IV Satyavakya, (975–986) and Rachamalla V (Rakkasaganga), (986–999).
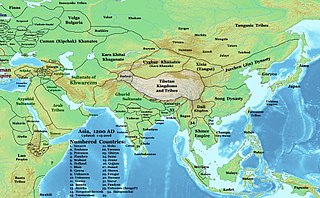
Hoysala literature is the large body of literature in the Kannada and Sanskrit languages produced by the Hoysala Empire (1025–1343) in what is now southern India. The empire was established by Nripa Kama II, came into political prominence during the rule of King Vishnuvardhana (1108–1152), and declined gradually after its defeat by the Khalji dynasty invaders in 1311.
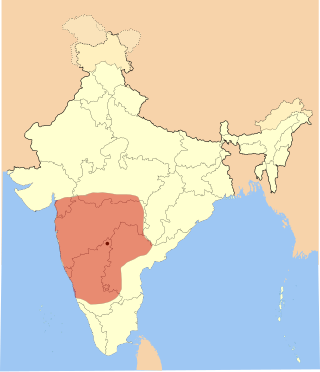
A large body of Western Chalukya literature in the Kannada language was produced during the reign of the Western Chalukya Empire in what is now southern India. This dynasty, which ruled most of the western Deccan in South India, is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya dynasty after its royal capital at Kalyani, and sometimes called the Later Chalukya dynasty for its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. For a brief period (1162–1183), the Kalachuris of Kalyani, a dynasty of kings who had earlier migrated to the Karnataka region from central India and served as vassals for several generations, exploited the growing weakness of their overlords and annexed the Kalyani. Around 1183, the last Chalukya scion, Someshvara IV, overthrew the Kalachuris to regain control of the royal city. But his efforts were in vain, as other prominent Chalukya vassals in the Deccan, the Hoysalas, the Kakatiyas and the Seunas destroyed the remnants of the Chalukya power.
Nāgavarma I (c. 990) was a noted Jain writer and poet in the Kannada language in the late 10th century. His two important works, both of which are extant, are Karnātaka Kādambari, a champu based romance novel and an adaptation of Bana's Sanskrit Kādambari, and Chandōmbudhi, the earliest available work on Kannada prosody which Nāgavarma I claims would command the respect even of poet Kalidasa. According to the scholars K.A. Nilakanta Shastri and R. Narasimhacharya, Nāgavarma I belonged to a migrant Brahmin family originally from Vengi. According to the modern Kannada poet and scholar Govinda Pai, Nāgavarma I lived from 950 CE to 1015 CE. So popular was Nāgavarma I's poetic skills that King Bhoja of Malwa presented him with horses, in appreciation of his poetic skills.
Nagavarma II was a Kannada language scholar and grammarian in the court of the Western Chalukya Empire that ruled from Basavakalyan, in modern Karnataka state, India. He was the earliest among the three most notable and authoritative grammarians of Old-Kannada language. Nagavarma II's reputation stems from his notable contributions to various genres of Kannada literature including prosody, rhetoric, poetics, grammar and vocabulary. According to the scholar R. Narasimhacharya, Nagavarma II is unique in all of ancient Kannada literature, in this aspect. His writings are available and are considered standard authorities for the study of Kannada language and its growth.

Rashtrakuta literature is the body of work created during the rule of the Rastrakutas of Manyakheta, a dynasty that ruled the southern and central parts of the Deccan, India between the 8th and 10th centuries. The period of their rule was an important time in the history of South Indian literature in general and Kannada literature in particular. This era was practically the end of classical Prakrit and Sanskrit writings when a whole wealth of topics were available to be written in Kannada. Some of Kannada's most famous poets graced the courts of the Rashtrakuta kings. Court poets and royalty created eminent works in Kannada and Sanskrit, that spanned such literary forms as prose, poetry, rhetoric, epics and grammar. Famous scholars even wrote on secular subjects such as mathematics. Rashtrakuta inscriptions were also written in expressive and poetic Kannada and Sanskrit, rather than plain documentary prose.
This is a chronology of the literature of Karnataka, India.

Western Ganga literature refers to a body of writings created during the rule of the Western Ganga Dynasty, a dynasty that ruled the region historically known as Gangavadi between the 4th and 11th centuries. The period of their rule was an important time in the history of South Indian literature in general and Kannada literature in particular, though many of the writings are deemed extinct. Some of the most famous poets of Kannada language graced the courts of the Ganga kings. Court poets and royalty created eminent works in Kannada language and Sanskrit language that spanned such literary forms as prose, poetry, Hindu epics, Jain Tirthankaras (saints) and elephant management.
Sri Narayana Panditacharya, is an Indian scholar and philosopher in the Dvaita Vedānta tradition. He was the youngest son of Trivikrama Panditacharya, one of the direct disciples of Sri Madhva He is the author of Sri Madhva Vijaya, a metrical biography of the rejuvenator of the Dvaita school of philosophy, Sri Madhvacharya. Indologist B. N. K. Sharma writes, "Narayana has earned a lasting fame for himself by his great metrical biography of Madhva".
Medieval Kannada literature covered a wide range of subjects and genres which can broadly be classified under the Jain, Virashaiva, Vaishnava and secular traditions. These include writings from the 7th century rise of the Badami Chalukya empire to the 16th century, coinciding with the decline of Vijayanagara Empire. The earliest known literary works until about the 12th century CE were mostly authored by the Jainas along with a few works by Virashaivas and Brahmins and hence this period is called the age of Jain literature,. The 13th century CE, to the 15th century CE, saw the emergence of numerous Virashaiva and Brahminical writers with a proportional decline in Jain literary works. Thereafter, Virashaiva and Brahmin writers have dominated the Kannada literary tradition. Some of the earliest metres used by Jain writers prior to 9th century include the chattana, bedande and the melvadu metres, writings in which have not been discovered but are known from references made to them in later centuries. Popular metres from the 9th century onwards when Kannada literature is available are the champu-kavyas or just champu, vachanasangatya, shatpadi, ragale, tripadi, and kavya.

Mysore literature in Kannada is a body of literature composed in the Kannada language in the historical Kingdom of Mysore in Southern India and written in the Kannada script. The writings date from the Kingdom of Mysore, which existed from around 1600 CE until the establishment of modern India in 1947. Many of the works of this literature written on religious themes are labeled Veerashaiva or Vaishnava in acknowledgment of the two faiths that gave form to the literature and fostered it until the advent of the modern era. Despite a gradual decline in the popularity of Jainism, authors devoted to the faith produced some works of merit. Secular themes dealing with a wide range of subjects were also written on. Kannada literature flourished for a short while in the court of the neighbouring kingdom of the Nayakas of Keladi whose territory was annexed by Mysore in 1763.

Vijayanagara literature in Kannada is the body of literature composed in the Kannada language of South India during the ascendancy of the Vijayanagara Empire which lasted from the 14th through the 16th century. The Vijayanagara empire was established in 1336 by Harihara I and his brother Bukka Raya I. Although it lasted until 1664, its power declined after a major military defeat by the Shahi Sultanates in the battle of Talikota in 1565. The empire is named after its capital city Vijayanagara, whose ruins surround modern Hampi, now a World Heritage Site in Karnataka.
Champu or Chapu-Kavya is a genre of literary composition in Indian literature. The word 'Champu' means a combination of poetry and prose. A champu-kavya consists of a mixture of prose (Gadya-Kavya) and poetry passages (Padya-Kavya), with verses interspersed among prose sections.

Annadanaiah (Annadanayya) Puranik, Indian writer, cultural activist, freedom fighter, modern vachanakara and an advocate. After Indian independence, he has served as an Advocate in state high court of Karnataka for five decades. He was also conferred the title Sahityaratna, for his contribution to Kannada literature and enormous contribution during a secretarial term with Kannada Sahitya Parishat.









