A borate is any of a range of boron oxyanions, anions containing boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate BO3−3, metaborate BO−2, or tetraborate B4O2−7; or any salt of such anions, such as sodium metaborate, Na+[BO2]− and borax (Na+)2[B4O7]2−. The name also refers to esters of such anions, such as trimethyl borate B(OCH3)3 but they are alkoxides.

Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the formula Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fractures and deep, underground spaces, where the water table and hydrothermal fluids provide the means for chemical precipitation. Individual crystals are rare, but occur as slender to acicular prisms. Pseudomorphs after more tabular or blocky azurite crystals also occur.

Azurite is a soft, deep-blue copper mineral produced by weathering of copper ore deposits. During the early 19th century, it was also known as chessylite, after the type locality at Chessy-les-Mines near Lyon, France. The mineral, a basic carbonate with the chemical formula Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2, has been known since ancient times, and was mentioned in Pliny the Elder's Natural History under the Greek name kuanos (κυανός: "deep blue," root of English cyan) and the Latin name caeruleum. Copper (Cu2+) gives it its blue color.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.
Cuprates are a class of compounds that contain copper (Cu) atom(s) in an anion. They can be broadly categorized into two main types:
Sodium borate is a generic name for any salt of sodium with an anion consisting of boron and oxygen, and possibly hydrogen, or any hydrate thereof. It can be seen as a hydrated sodium salt of the appropriate boroxy acid, although the latter may not be a stable compound.

The Borate Minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures which include hydroxide or halogen anions. The [B(O,OH)4]− anion exists as well.
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written NaH2BO4, Na2H4B2O8, or, more properly, [Na+]2[B2O4(OH)4]2−. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS.

Copper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is 7778-41-8 or 10103-61-4.

Copper(II) phosphate are inorganic compounds with the formula Cu3(PO4)2. They can be regarded as the cupric salts of phosphoric acid. Anhydrous copper(II) phosphate and a trihydrate are blue solids.

Chevreul's salt (copper(I,II) sulfite dihydrate, Cu2SO3•CuSO3•2H2O or Cu3(SO3)2•2H2O), is a copper salt which was prepared for the first time by a French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul in 1812. Its unusual property is that it contains copper in both of its common oxidation states, making it a mixed-valence complex. It is insoluble in water and stable in air. What was known as Rogojski's salt is a mixture of Chevreul's salt and metallic copper.
The borate fluorides or fluoroborates are compounds containing borate or complex borate ions along with fluoride ions that form salts with cations such as metals. They are in the broader category of mixed anion compounds. They are not to be confused with tetrafluoroborates (BF4) or the fluorooxoborates which have fluorine bonded to boron.
The borate carbonates are mixed anion compounds containing both borate and carbonate ions. Compared to mixed anion compounds containing halides, these are quite rare. They are hard to make, requiring higher temperatures, which are likely to decompose carbonate to carbon dioxide. The reason for the difficulty of formation is that when entering a crystal lattice, the anions have to be correctly located, and correctly oriented. They are also known as carbonatoborates or borocarbonates. Although these compounds have been termed carboborate, that word also refers to the C=B=C5− anion, or CB11H12− anion. This last anion should be called 1-carba-closo-dodecaborate or monocarba-closo-dodecaborate.
The borosulfates are heteropoly anion compounds which have sulfate groups attached to boron atoms. Other possible terms are sulfatoborates or boron-sulfur oxides. The ratio of sulfate to borate reflects the degree of condensation. With [B(SO4)4]5- there is no condensation, each ion stands alone. In [B(SO4)3]3- the anions are linked into a chain, a chain of loops, or as [B2(SO4)6]6− in a cycle. Finally in [B(SO4)2]− the sulfate and borate tetrahedra are all linked into a two or three-dimensional network. These arrangements of oxygen around boron and sulfur can have forms resembling silicates. The first borosulfate to be discovered was K5[B(SO4)4] in 2012 by the research group of Henning Höppe, although the compound class as such had been postulated already in 1962 by G. Schott and H. U. Kibbel. Over 80 unique compounds are known as of 2024.
The borotellurates are heteropoly anion compounds which have tellurate groups attached to boron atoms. The ratio of tellurate to borate reflects the degree of condensation. In [TeO4(BO3)2]8- the anions are linked into a chain. In [TeO2(BO3)4]10− the structure is zero dimensional with isolated anions. These arrangements of oxygen around boron and tellurium can have forms resembling silicates. The first borotellurates to be discovered were the mixed sodium rare earth compounds in 2015.
Borate sulfates are mixed anion compounds containing separate borate and sulfate anions. They are distinct from the borosulfates where the borate is linked to a sulfate via a common oxygen atom.
Borate phosphates are mixed anion compounds containing separate borate and phosphate anions. They are distinct from the borophosphates where the borate is linked to a phosphate via a common oxygen atom. The borate phosphates have a higher ratio of cations to number of borates and phosphates, as compared to the borophosphates.
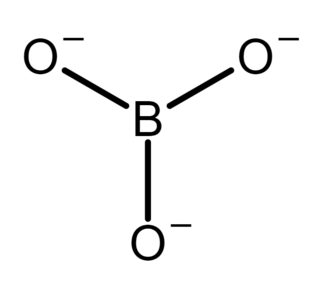
In inorganic chemistry, an orthoborate is a polyatomic anion with formula [BO3]3− or a salt containing the anion; such as trisodium orthoborate (Na+)3[BO3]3−. It is one of several boron oxyanions, or borates.
Trisodium borate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen, with formula Na3BO3, or (Na+)3[BO3]3−. It is a sodium salt of the orthoboric acid B(OH)3.

Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). Terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state in these compounds, such as in TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6. Terbium can also form compounds in the 0, +1 and +2 oxidation states.











