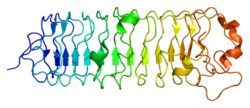Decorin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCN gene.
Contents
- Naming
- Function
- Clinical significance
- Animal studies
- Interactions
- References
- Further reading
- External links
Decorin is a proteoglycan that is on average 90 - 140 kilodaltons (kDa) in molecular weight. It belongs to the small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) family and consists of a protein core containing leucine repeats with a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain consisting of either chondroitin sulfate (CS) or dermatan sulfate (DS).
Decorin is a small cellular or pericellular matrix proteoglycan and is closely related in structure to biglycan protein. Decorin and biglycan are thought to be the result of a gene duplication. This protein is a component of connective tissue, binds to type I collagen fibrils, and plays a role in matrix assembly. [5]