
Bone morphogenetic protein 8A (BMP8A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMP8A gene.
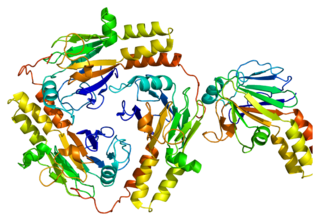
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 also known as SMAD family member 1 or SMAD1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD1 gene.
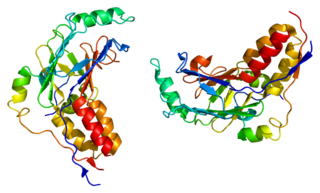
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 also known as SMAD family member 2 or SMAD2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD2 gene. MAD homolog 2 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways.
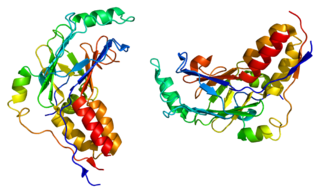
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.

SMAD4, also called SMAD family member 4, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4, or DPC4 is a highly conserved protein present in all metazoans. It belongs to the SMAD family of transcription factor proteins, which act as mediators of TGF-β signal transduction. The TGFβ family of cytokines regulates critical processes during the lifecycle of metazoans, with important roles during embryo development, tissue homeostasis, regeneration, and immune regulation.

SMAD family member 6, also known as SMAD6, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD6 gene.

Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 5 also known as SMAD5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD5 gene.

Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 or SMAD7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD7 gene.
The transforming growth factor beta (TGFB) signaling pathway is involved in many cellular processes in both the adult organism and the developing embryo including cell growth, cell differentiation, cell migration, apoptosis, cellular homeostasis and other cellular functions. The TGFB signaling pathways are conserved. In spite of the wide range of cellular processes that the TGFβ signaling pathway regulates, the process is relatively simple. TGFβ superfamily ligands bind to a type II receptor, which recruits and phosphorylates a type I receptor. The type I receptor then phosphorylates receptor-regulated SMADs (R-SMADs) which can now bind the coSMAD SMAD4. R-SMAD/coSMAD complexes accumulate in the nucleus where they act as transcription factors and participate in the regulation of target gene expression.

Zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 9 or SARA is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZFYVE9 gene. SARA contains a double zinc finger.

Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II or BMPR2 is a serine/threonine receptor kinase. It binds Bone morphogenetic proteins, members of the TGF beta superfamily of ligands, which are involved in paracrine signalling. BMPs are involved in a host of cellular functions including osteogenesis, cell growth and cell differentiation. Signaling in the BMP pathway begins with the binding of a BMP to the type II receptor. This causes the recruitment of a BMP type I receptor, which it phosphorylates. The Type I receptor phosphorylates an R-SMAD a transcriptional regulator.

The bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IA also known as BMPR1A is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BMPR1A gene. BMPR1A has also been designated as CD292.

Activin receptor type-1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR1B gene.

Activin A receptor, type I (ACVR1) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ACVR1 gene; also known as ALK-2. ACVR1 has been linked to the 2q23-24 region of the genome. This protein is important in the bone morphogenic protein (BMP) pathway which is responsible for the development and repair of the skeletal system. While knock-out models with this gene are in progress, the ACVR1 gene has been connected to fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, a disease characterized by the formation of heterotopic bone throughout the body. It is a bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type 1.

Transforming growth factor beta receptor I is a membrane-bound TGF beta receptor protein of the TGF-beta receptor family for the TGF beta superfamily of signaling ligands. TGFBR1 is its human gene.

Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-1B also known as CDw293 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMPR1B gene.

The SKI protein is a nuclear proto-oncogene that is associated with tumors at high cellular concentrations. SKI has been shown to interfere with normal cellular functioning by both directly impeding expression of certain genes inside the nucleus of the cell as well as disrupting signaling proteins that activate genes.

E3 SUMO-protein ligase PIAS4 is one of several protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) proteins. It is also known as protein inhibitor of activated STAT protein gamma, and is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIAS4 gene.

Homeobox protein Hox-C8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXC8 gene.

Protein pellino homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PELI1 gene.




















