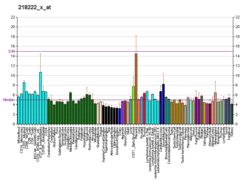
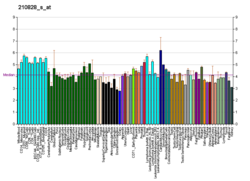
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AHR gene. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression. It was originally thought to function primarily as a sensor of xenobiotic chemicals and also as the regulator of enzymes such as cytochrome P450s that metabolize these chemicals. The most notable of these xenobiotic chemicals are aromatic (aryl) hydrocarbons from which the receptor derives its name.
The aryl-hydrocarbon receptor repressor also known as AHRR is a human gene.
The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCOA1), also called steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1), is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor–interacting domains and possesses intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. It is encoded by the gene NCOA1.
The nuclear receptor coactivator 2 also known as NCoA-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA2 gene. NCoA-2 is also frequently called glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 (GRIP1), steroid receptor coactivator-2 (SRC-2), or transcriptional mediators/intermediary factor 2 (TIF2).

The small heterodimer partner (SHP) also known as NR0B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR0B2 gene. SHP is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. SHP is unusual for a nuclear receptor in that it lacks a DNA binding domain. Therefore, it is technically neither a transcription factor nor nuclear receptor but nevertheless it is still classified as such due to relatively high sequence homology with other nuclear receptor family members.

Retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR-alpha), also known as NR2B1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRA gene.

POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU2F1 gene.

Nuclear receptor-interacting protein 1 (NRIP1) also known as receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NRIP1 gene.

Prostaglandin E synthase 3 (cytosolic) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES3 gene.

Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 7 also known as TAFII55 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAF7 gene.
Endothelial PAS domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that is encoded by the EPAS1 gene in mammals. It is a type of hypoxia-inducible factor, a group of transcription factors involved in the physiological response to oxygen concentration. The gene is active under hypoxic conditions. It is also important in the development of the heart, and for maintaining the catecholamine balance required for protection of the heart. Mutation often leads to neuroendocrine tumors.

COUP-TF1 also known as NR2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F1 gene. This protein is a member of nuclear hormone receptor family of steroid hormone receptors.

Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2A gene. MEF2A is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. In humans it is located on chromosome 15q26. Certain mutations in MEF2A cause an autosomal dominant form of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.

AH receptor-interacting protein (AIP) also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor-interacting protein, immunophilin homolog ARA9, or HBV X-associated protein 2 (XAP-2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AIP gene. The protein is a member of the FKBP family.

Tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) also known as transcriptional intermediary factor 1α (TIF1α) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TRIM24 gene.

Single-minded homolog 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIM2 gene. It plays a major role in the development of the central nervous system midline as well as the construction of the face and head.

Single-minded homolog 1, also known as class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 14 (bHLHe14), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIM1 gene.

Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARNT2 gene.
General transcription factor IIF subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2F2 gene.

Basic helix-loop-helix ARNT-like protein 1 or aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (ARNTL), or brain and muscle ARNT-like 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMAL1 gene on chromosome 11, region p15.3. It's also known as MOP3, and, less commonly, bHLHe5, BMAL, BMAL1C, JAP3, PASD3, and TIC.