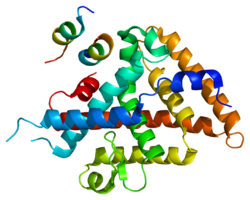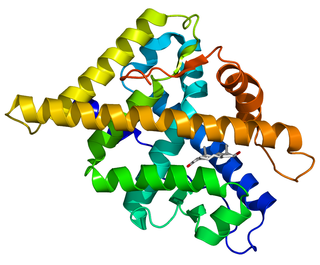
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.

Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1, is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ESR1.

The bile acid receptor (BAR), also known as farnesoid X receptor (FXR) or NR1H4, is a nuclear receptor that is encoded by the NR1H4 gene in humans.

In the field of molecular biology, the pregnane X receptor (PXR), also known as the steroid and xenobiotic sensing nuclear receptor (SXR) or nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (NR1I2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I2 gene.
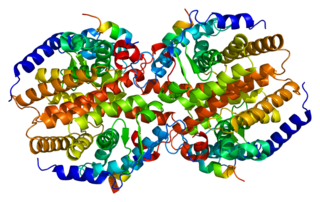
The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I3 gene. CAR is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and along with pregnane X receptor (PXR) functions as a sensor of endobiotic and xenobiotic substances. In response, expression of proteins responsible for the metabolism and excretion of these substances is upregulated. Hence, CAR and PXR play a major role in the detoxification of foreign substances such as drugs.

The nuclear receptor 4A1 also known as Nur77, TR3, and NGFI-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A1 gene.

The small heterodimer partner (SHP) also known as NR0B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR0B2 gene. SHP is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. SHP is unusual for a nuclear receptor in that it lacks a DNA binding domain. Therefore, it is technically neither a transcription factor nor nuclear receptor but nevertheless it is still classified as such due to relatively high sequence homology with other nuclear receptor family members.

Peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor gamma, also known as the glitazone reverse insulin resistance receptor, or NR1C3 is a type II nuclear receptor functioning as a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the PPARG gene.

Rev-Erb alpha (Rev-Erbɑ), also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 1 (NR1D1), is one of two Rev-Erb proteins in the nuclear receptor (NR) family of intracellular transcription factors. In humans, REV-ERBɑ is encoded by the NR1D1 gene, which is highly conserved across animal species.

RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORα), also known as NR1F1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RORA gene. RORα participates in the transcriptional regulation of some genes involved in circadian rhythm. In mice, RORα is essential for development of cerebellum through direct regulation of genes expressed in Purkinje cells. It also plays an essential role in the development of type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) and mutant animals are ILC2 deficient. In addition, although present in normal numbers, the ILC3 and Th17 cells from RORα deficient mice are defective for cytokine production.

Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1(Notch 1) is a protein encoded in humans by the NOTCH1 gene. Notch 1 is a single-pass transmembrane receptor.

Retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR-alpha), also known as NR2B1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRA gene.
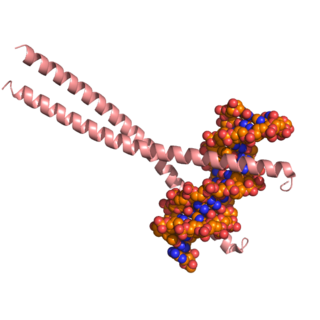
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPB gene.
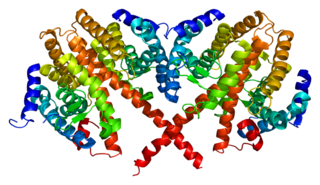
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4A) also known as NR2A1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the HNF4A gene.

Liver X receptor alpha (LXR-alpha) is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1H3 gene.

Nuclear receptor-interacting protein 1 (NRIP1) also known as receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NRIP1 gene.

COUP-TF1 also known as NR2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F1 gene. This protein is a member of nuclear hormone receptor family of steroid hormone receptors.

The testicular receptor 2 (TR2) also known as NR2C1 is protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2C1 gene. TR2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors.

Testicular receptor 4 also known as NR2C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2C2 gene.
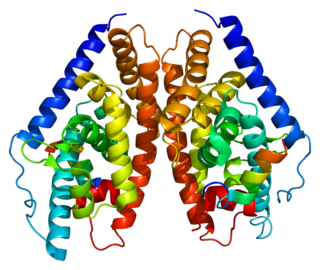
Liver X receptor beta (LXR-β) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. LXR-β is encoded by the NR1H2 gene.